Types of system
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
15 likes•18,810 views
types of systems
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
DSP_2018_FOEHU - Lec 03 - Discrete-Time Signals and Systems

DSP_2018_FOEHU - Lec 03 - Discrete-Time Signals and Systems
DSP_2018_FOEHU - Lec 1 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing

DSP_2018_FOEHU - Lec 1 - Introduction to Digital Signal Processing
Similar to Types of system
Similar to Types of system (20)
Chapter-I Classification of Signals and Systems.pptx

Chapter-I Classification of Signals and Systems.pptx
More from mihir jain
More from mihir jain (14)
Recently uploaded
Scaling in conventional MOSFETScaling in conventional MOSFET for constant electric field and constant voltage

Scaling in conventional MOSFET for constant electric field and constant voltageRCC Institute of Information Technology
Recently uploaded (20)
Cloud-Computing_CSE311_Computer-Networking CSE GUB BD - Shahidul.pptx

Cloud-Computing_CSE311_Computer-Networking CSE GUB BD - Shahidul.pptx
A CASE STUDY ON ONLINE TICKET BOOKING SYSTEM PROJECT.pdf

A CASE STUDY ON ONLINE TICKET BOOKING SYSTEM PROJECT.pdf
The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair.pdf

The Benefits and Techniques of Trenchless Pipe Repair.pdf
Scaling in conventional MOSFET for constant electric field and constant voltage

Scaling in conventional MOSFET for constant electric field and constant voltage
NO1 Pandit Black Magic Removal in Uk kala jadu Specialist kala jadu for Love ...

NO1 Pandit Black Magic Removal in Uk kala jadu Specialist kala jadu for Love ...
Online resume builder management system project report.pdf

Online resume builder management system project report.pdf
shape functions of 1D and 2 D rectangular elements.pptx

shape functions of 1D and 2 D rectangular elements.pptx
Introduction to Machine Learning Unit-4 Notes for II-II Mechanical Engineering

Introduction to Machine Learning Unit-4 Notes for II-II Mechanical Engineering
KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-5.pdf Frame Works and Visualization

KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-5.pdf Frame Works and Visualization
KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-3.pdf Mining Data Stream

KIT-601 Lecture Notes-UNIT-3.pdf Mining Data Stream
Construction method of steel structure space frame .pptx

Construction method of steel structure space frame .pptx
Introduction to Machine Learning Unit-5 Notes for II-II Mechanical Engineering

Introduction to Machine Learning Unit-5 Notes for II-II Mechanical Engineering
Types of system
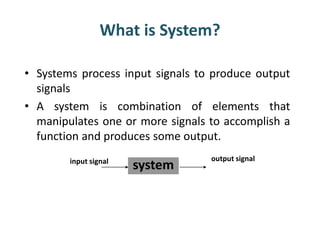
- 1. What is System? • Systems process input signals to produce output signals • A system is combination of elements that manipulates one or more signals to accomplish a function and produces some output. system output signalinput signal
- 2. Types of Systems • Causal & Anticausal • Linear & Non Linear • Time Variant &Time-invariant • Stable & Unstable • Static & Dynamic • Invertible & Inverse Systems
- 3. Causal & Anticausal Systems • Causal system : A system is said to be causal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the present and/or past values of the input signal. • Example: y[n]=x[n]+1/2x[n-1]
- 4. Causal & Anticausal Systems Contd. • Anticausal system : A system is said to be anticausal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the future values of the input signal. • Example: y[n]=x[n+1]+1/2x[n-1]
- 5. Linear & Non Linear Systems • A system is said to be linear if it satisfies the principle of superposition • For checking the linearity of the given system, firstly we check the response due to linear combination of inputs • Then we combine the two outputs linearly in the same manner as the inputs are combined and again total response is checked • If response in step 2 and 3 are the same,the system is linear othewise it is non linear.
- 6. Time Invariant and Time Variant Systems • A system is said to be time invariant if a time delay or time advance of the input signal leads to a identical time shift in the output signal.
- 7. Stable & Unstable Systems • A system is said to be bounded-input bounded- output stable (BIBO stable) if every bounded input results in a bounded output.
- 8. Stable & Unstable Systems Contd. Example - y[n]=1/3(x[n]+x[n-1]+x[n-2]) 1 [ ] [ ] [ 1] [ 2] 3 1 (| [ ]| | [ 1]| | [ 2]|) 3 1 ( ) 3 x x x x y n x n x n x n x n x n x n M M M M
- 9. Stable & Unstable Systems Contd. Example: The system represented by y(t) = A x(t) is unstable ; A˃1 Reason: let us assume x(t) = u(t), then at every instant u(t) will keep on multiplying with A and hence it will not be bonded.
- 10. Static & Dynamic Systems • A static system is memoryless system • It has no storage devices • its output signal depends on present values of the input signal • For example
- 11. Static & Dynamic Systems Contd. • A dynamic system possesses memory • It has the storage devices • A system is said to possess memory if its output signal depends on past values and future values of the input signal
- 12. Example: Static or Dynamic?
- 13. Example: Static or Dynamic? Answer: • The system shown above is RC circuit • R is memoryless • C is memory device as it stores charge because of which voltage across it can’t change immediately • Hence given system is dynamic or memory system
- 14. Invertible & Inverse Systems • If a system is invertible it has an Inverse System • Example: y(t)=2x(t) – System is invertible must have inverse, that is: – For any x(t) we get a distinct output y(t) – Thus, the system must have an Inverse • x(t)=1/2 y(t)=z(t) y(t) System Inverse System x(t) x(t) y(t)=2x(t)System (multiplier) Inverse System (divider) x(t) x(t)