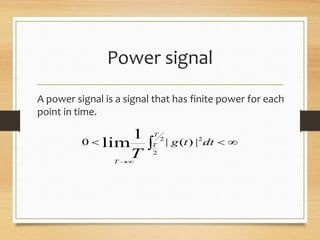
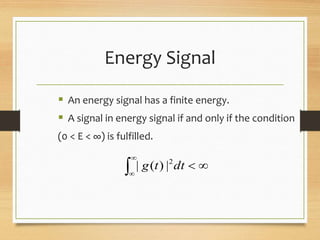
This document discusses different types of signals and their representations. It describes:
- Analog and digital signals as the two main types.
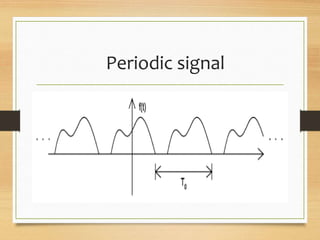
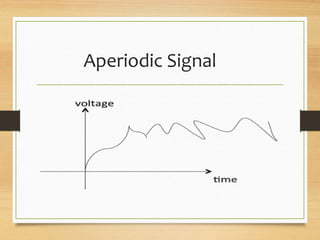
- Periodic signals that repeat over a measurable time frame called a period. Aperiodic signals do not repeat.
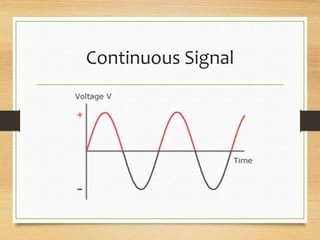
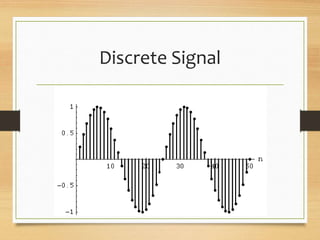
- Continuous signals having time as a continuum, while discrete signals are obtained by sampling continuous signals at discrete time intervals.
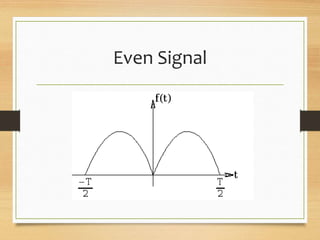
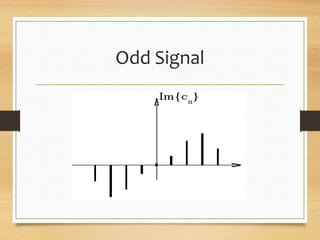
- Even signals being identical to their time-reversed counterparts, odd signals changing sign when reversed, and orthogonal signals having no relationship between components.