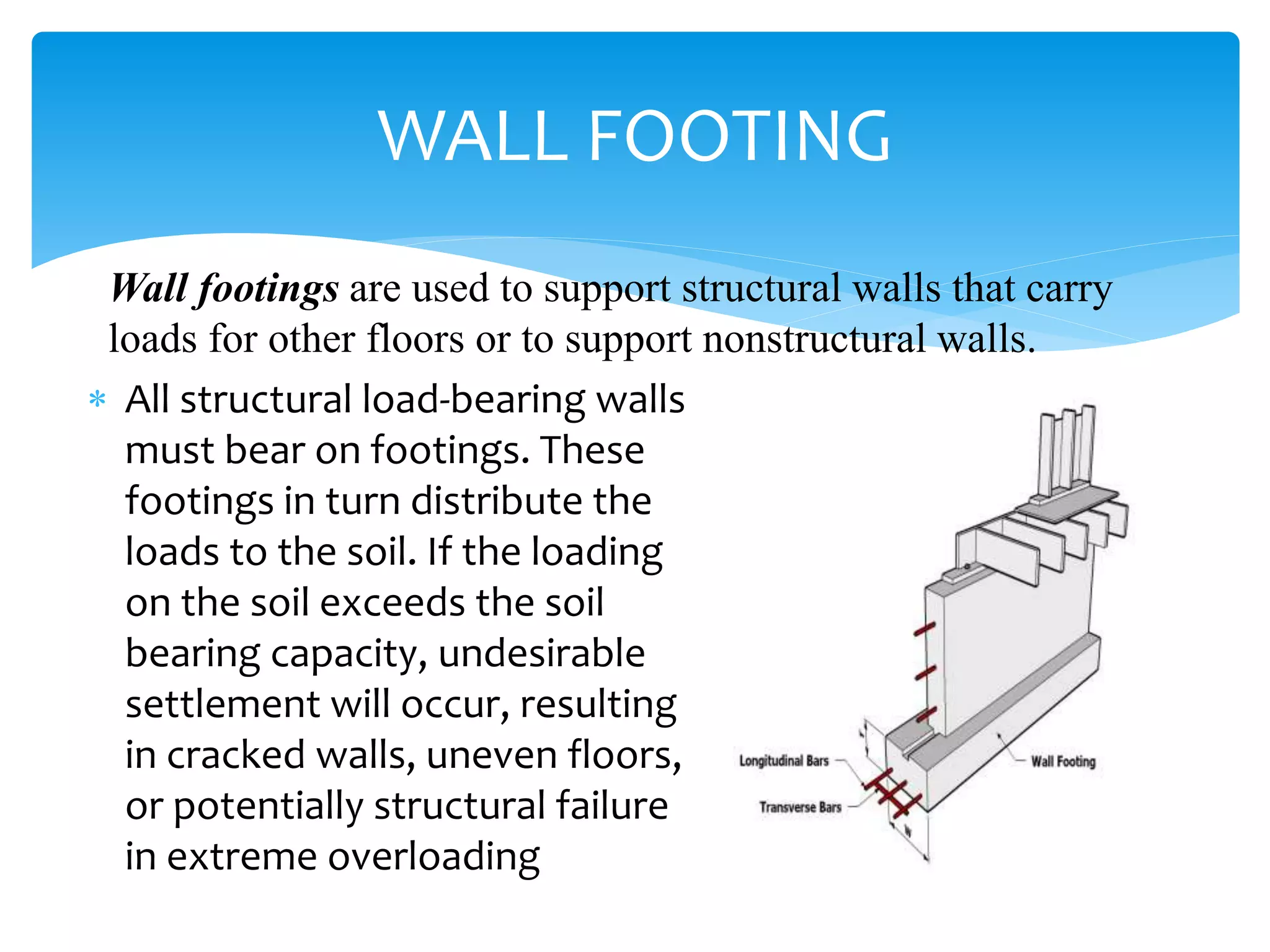
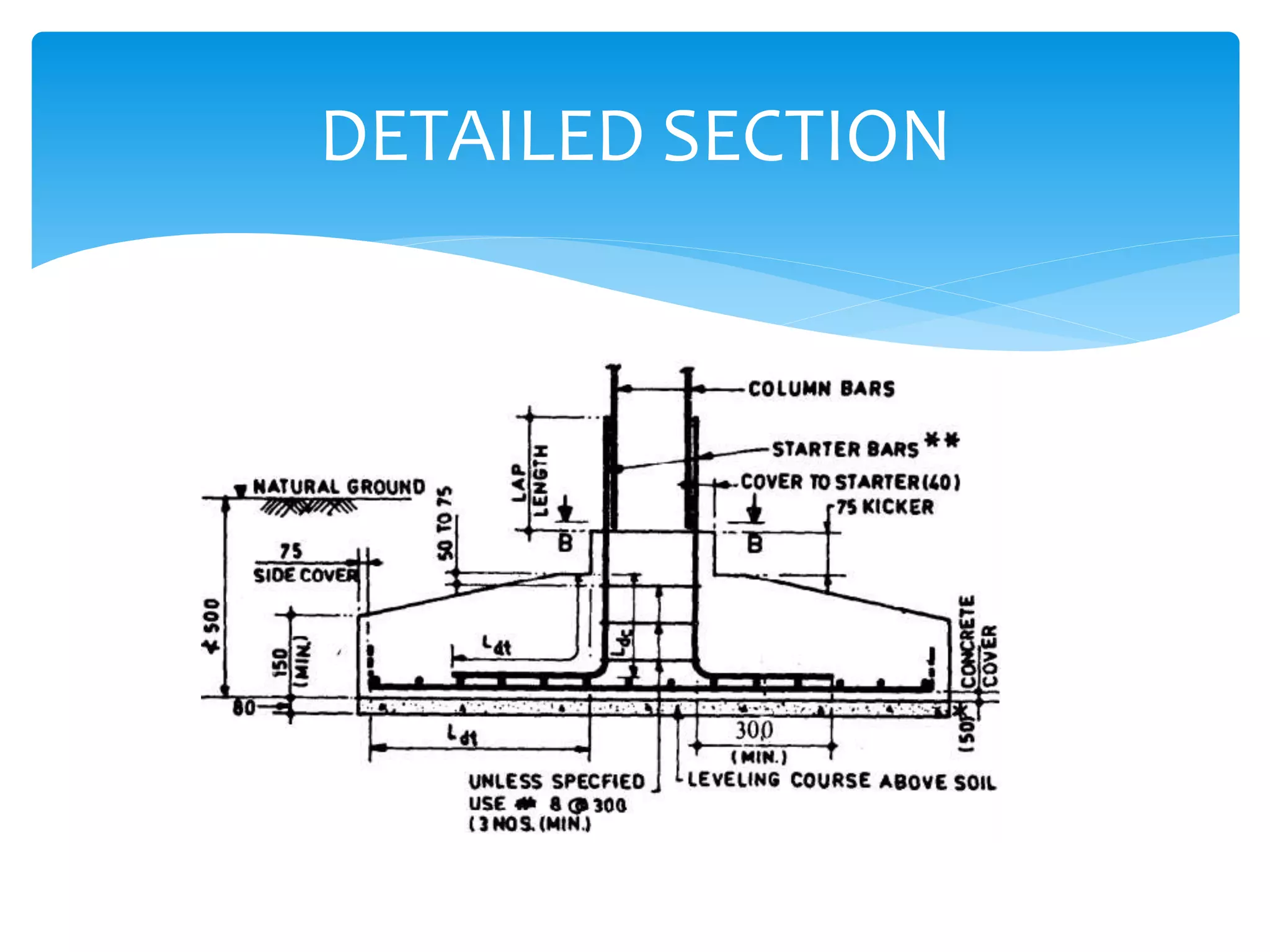
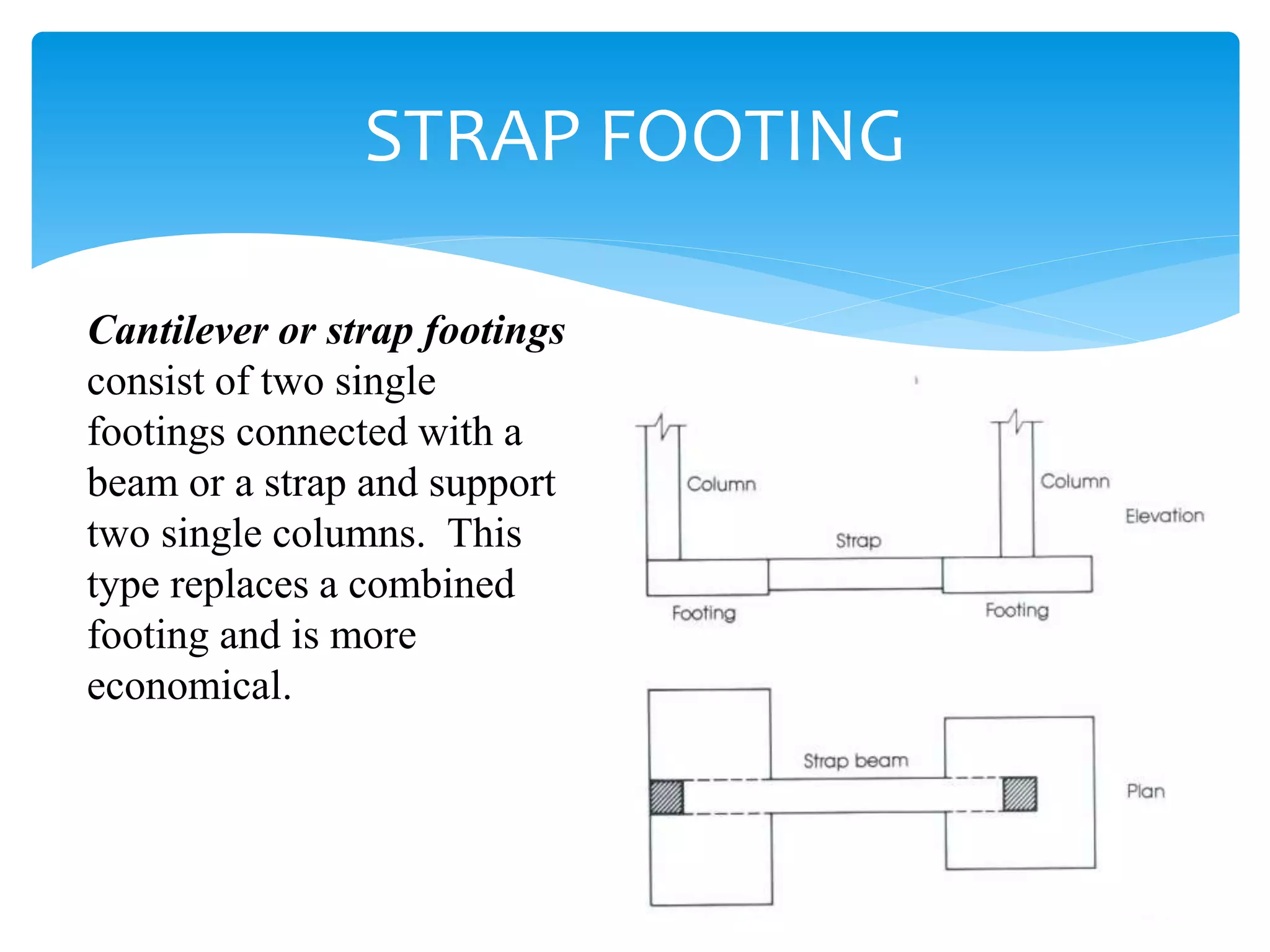
This document discusses different types of foundations including wall footings, isolated footings, combined footings, cantilever footings, continuous footings, mat footings, and machine foundations. Wall footings support structural walls, isolated footings support single columns, combined footings support two or three close columns, cantilever footings connect two isolated footings, continuous footings support rows of three or more columns, and mat footings extend under an entire building or portion. Machine foundations can be block or frame types and their analysis involves dynamic and static stages.