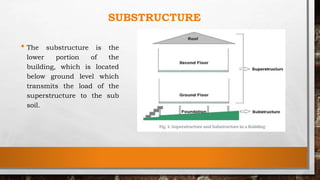
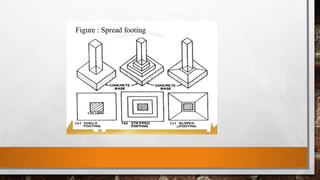
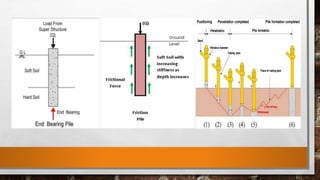
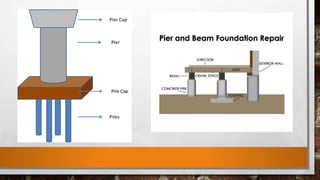
This document discusses the basic components of buildings and different types of foundations. It explains that the substructure is the lower portion of a building located below ground level, and includes the foundation. Shallow foundations include spread footings, combined footings, strap footings, and mat/raft foundations. Deep foundations include pile foundations, piers, and wells/caissons. Pile foundations are used when firm bearing strata are not available and loads are uneven, and can be end bearing, friction, or compaction piles. Pier foundations consist of large diameter cylindrical columns to support large loads.