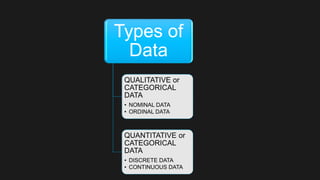
This document discusses the different types of data used in statistics. There are two main types: qualitative or categorical data, and quantitative or numerical data. Qualitative data includes nominal data, which classifies variables into mutually exclusive categories, and ordinal data, which groups variables into descriptive ordered categories. Quantitative data contains discrete data, which can only take certain numerical values, and continuous data, which can take any numerical value. In summary, the document outlines the key differences between qualitative and quantitative data, and identifies the sub-types of each.