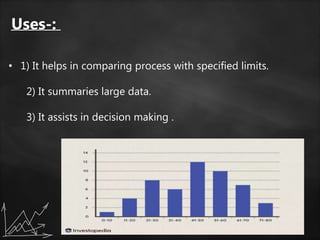
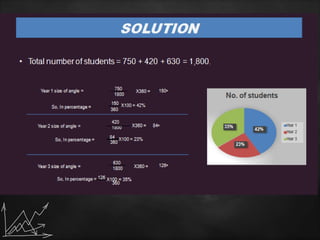
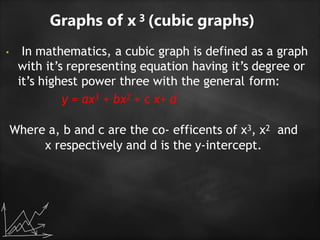
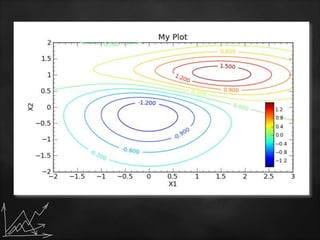
The document discusses various statistical graphs and methodologies, including histograms, pie charts, cubic graphs, and response surface methodology (RSM). Histograms are used for organizing and displaying continuous sample data, while pie charts visualize the distribution of data in sectors. RSM aids in optimizing processes influenced by multiple variables and finds applications across several scientific and industrial fields.