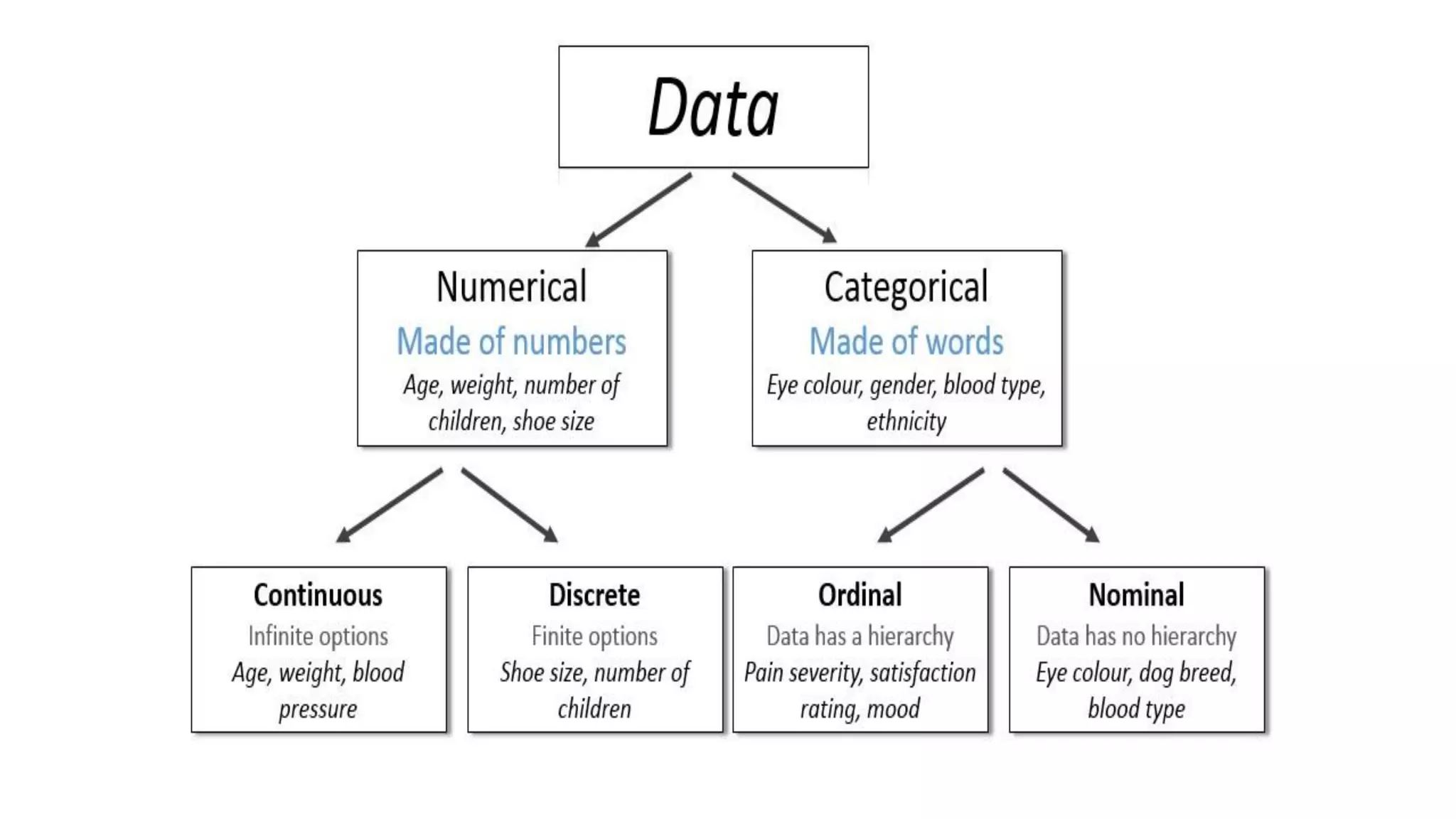
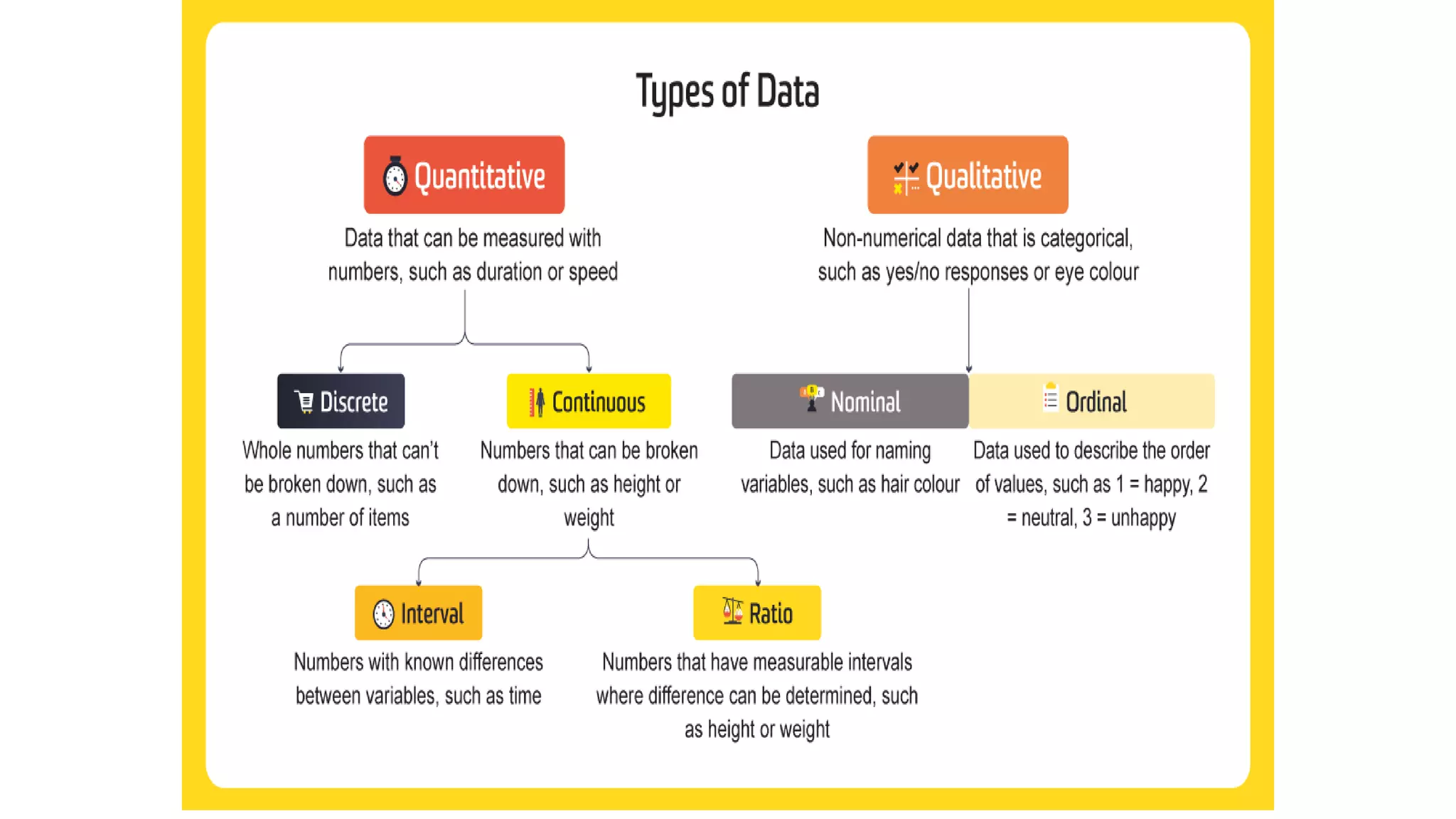
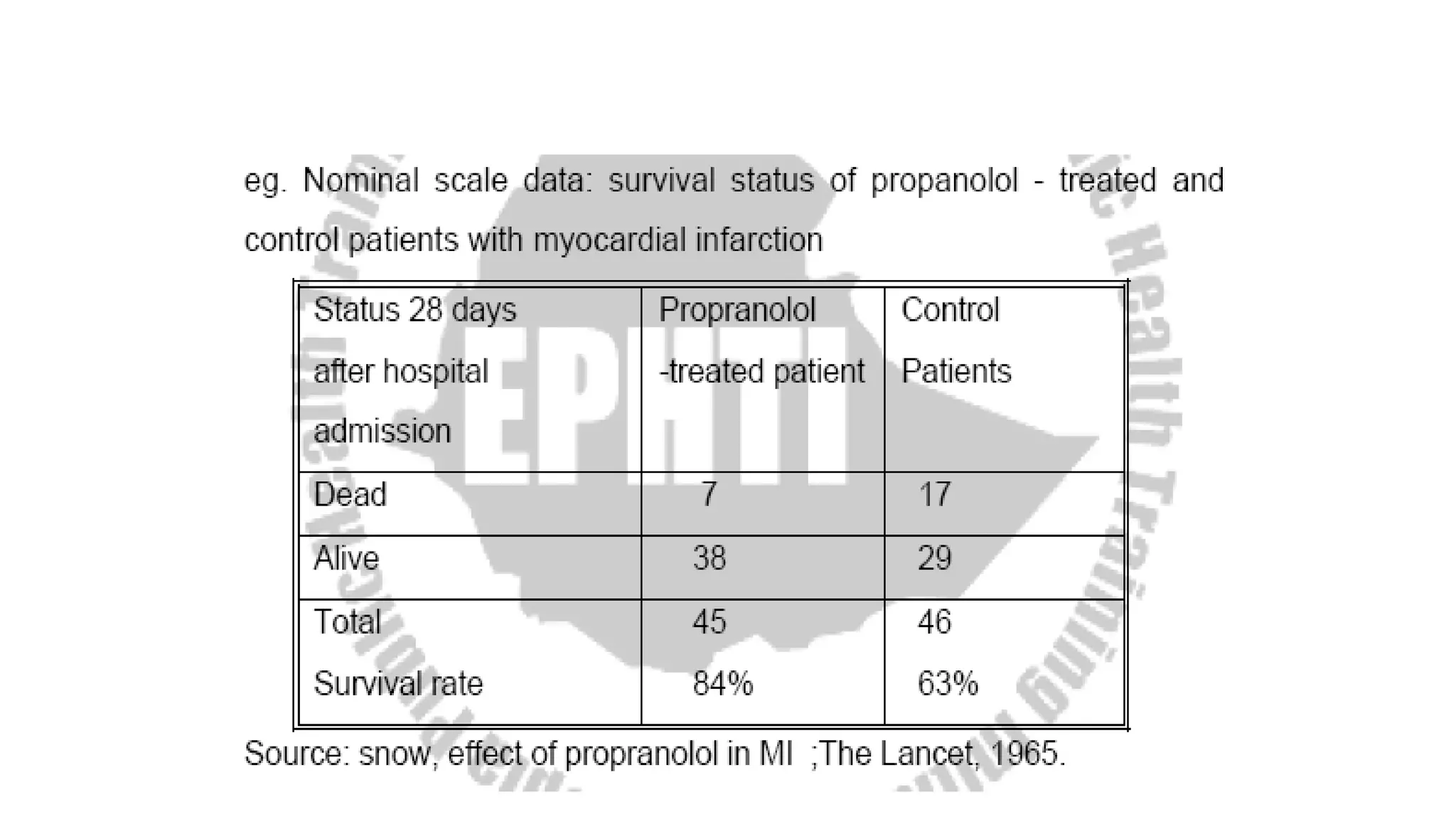
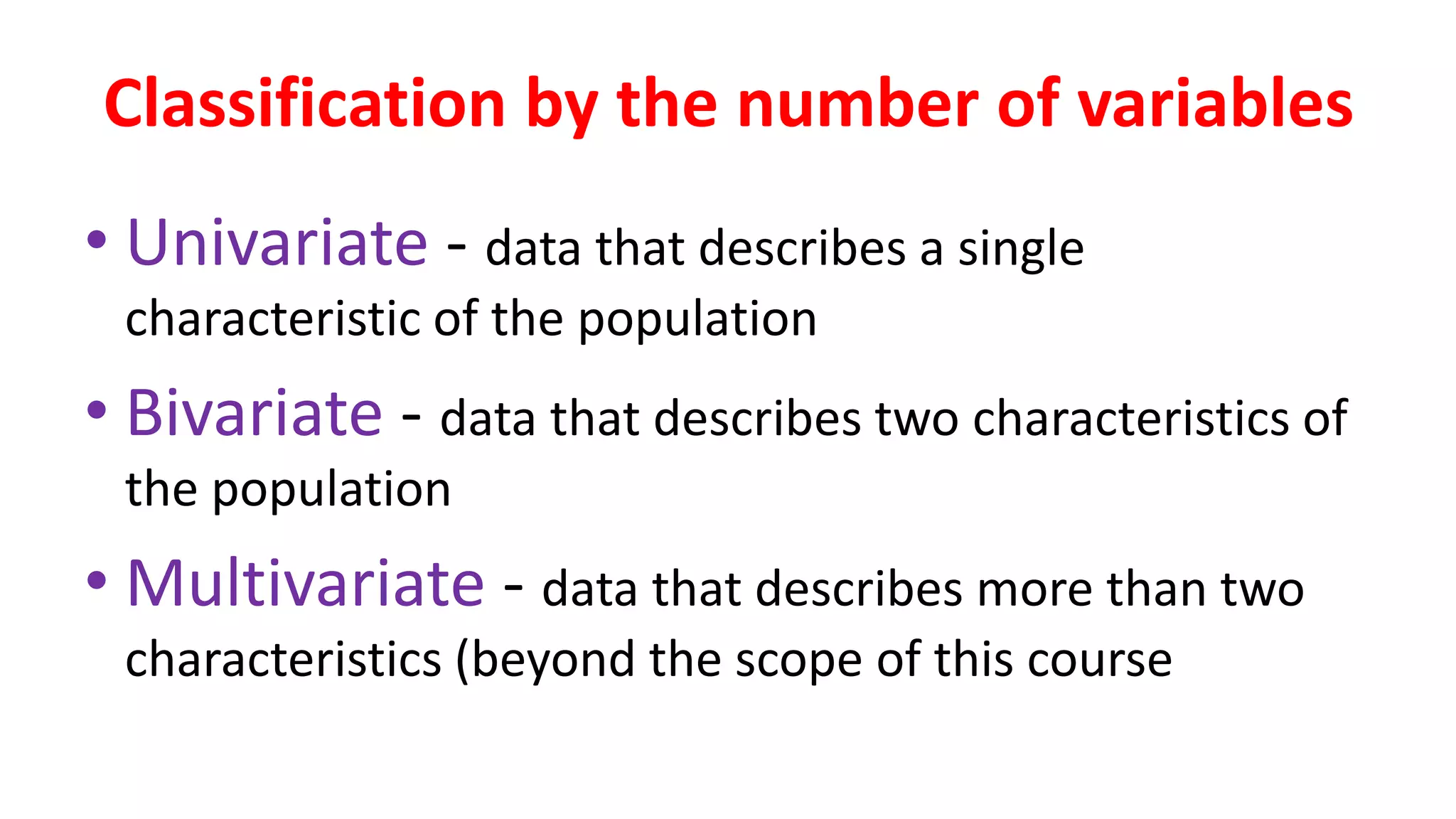
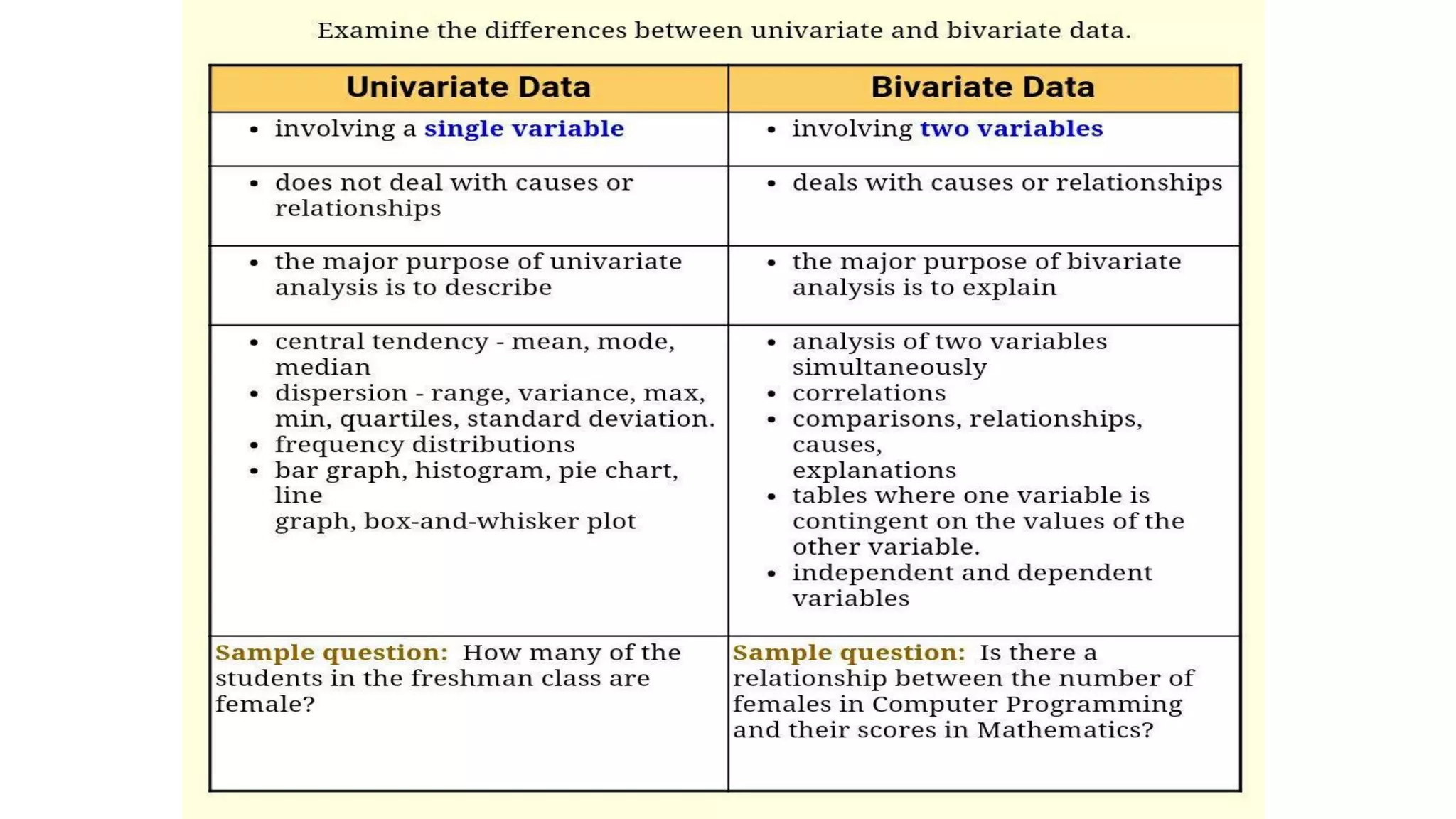
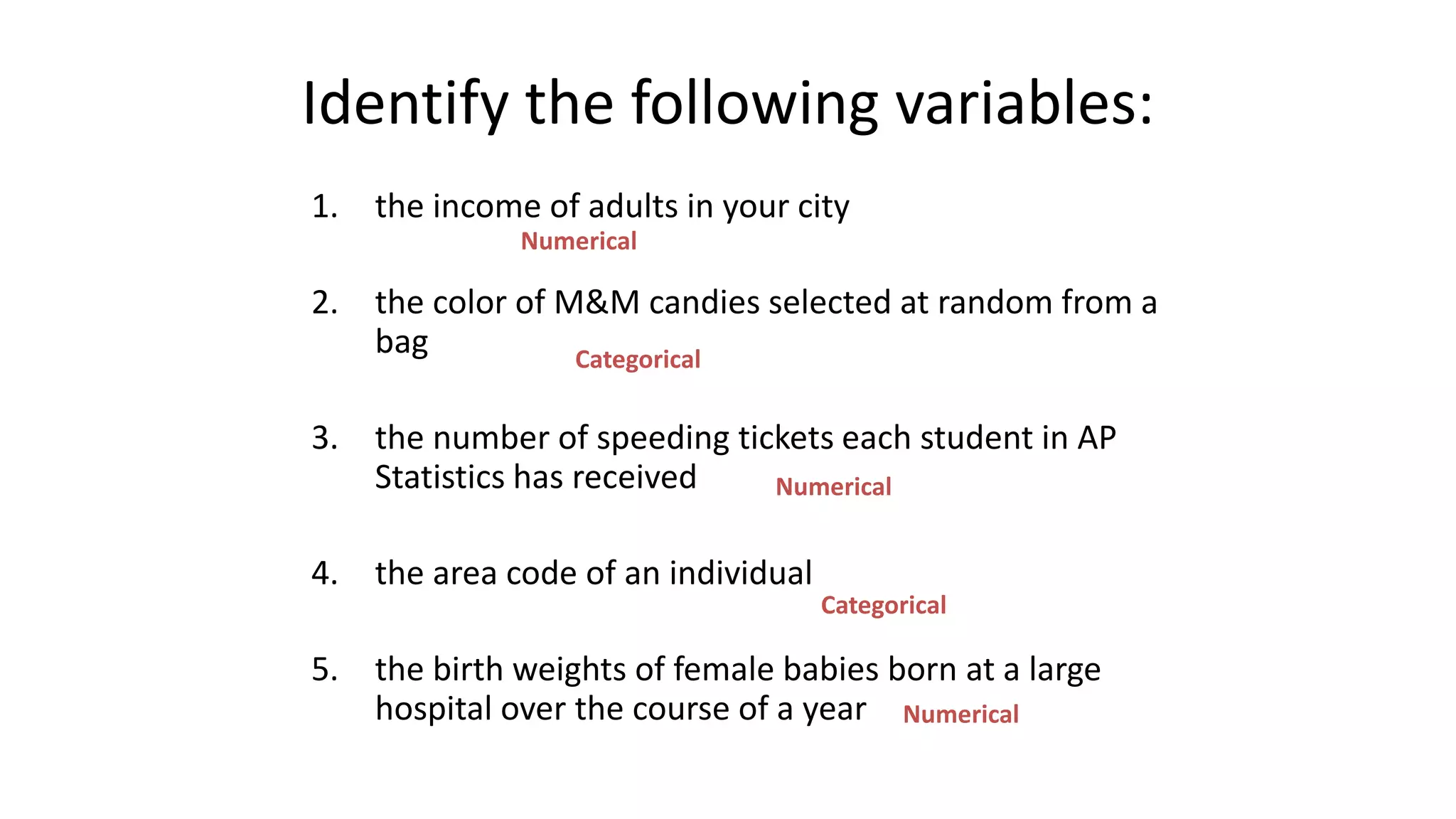
This document discusses different types of data that can be collected from variables in a population or sample. It defines qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data come from categorical variables and can be nominal or ordinal. Quantitative data are numerical and can be discrete or continuous. Examples of each type of variable and data are provided. The key types discussed are nominal, ordinal, interval, ratio, discrete, and continuous variables. The document also discusses how to classify data by the number of variables as univariate, bivariate, or multivariate.