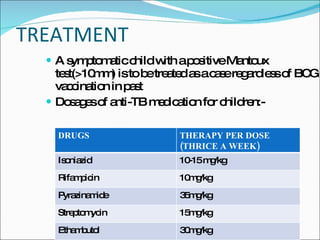
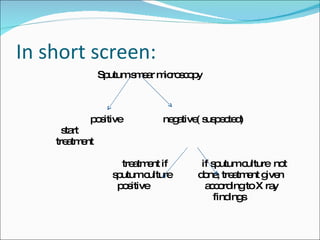
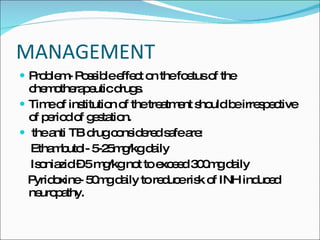
This document discusses tuberculosis (TB) in children, the relationship between TB and HIV, and TB during pregnancy. It notes that 10-20% of TB cases are in children under 5 years old. Children are usually sputum-negative and not infectious. The main sources of infection are adults with sputum-positive TB. Treatment involves several anti-TB drugs given in specific doses over several months. Chemoprophylaxis is recommended for children exposed to sputum-positive individuals. Co-infection with HIV greatly increases the risk of active TB. Diagnosis is more difficult and extra-pulmonary TB is more common. Standard TB treatment is still used but drug interactions with HIV medications must be considered. TB in pregnancy does not typically