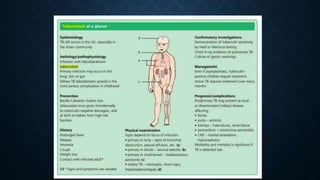
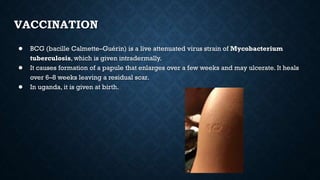
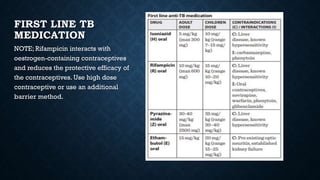
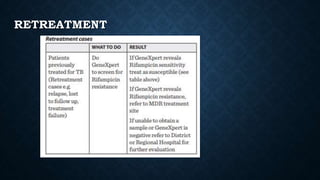
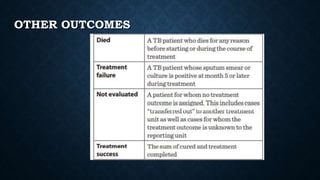
Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic infection caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex, primarily affecting the lungs, but can involve other organs. In 2019, an estimated 10 million people were diagnosed with TB globally, with significant incidence in children, and it remains the second leading infectious cause of death worldwide. Effective treatment involves a structured regimen of antibiotics under direct observation, with a goal of ending the TB epidemic by 2030 as part of the UN's Sustainable Development Goals.