The document discusses neonatal hypoglycemia, including its definition, symptoms, risk factors, treatment, and monitoring. Some key points:
- Neonatal hypoglycemia is defined as a blood glucose level below certain thresholds in the first 24 hours and thereafter. It is a common problem in newborns.
- Babies at higher risk include preterms, those of diabetic mothers, or experiencing other stresses. Symptoms can be nonspecific.
- Treatment involves glucose administration via IV bolus or infusion to raise blood glucose to the normal range. Frequent monitoring is needed until levels stabilize.
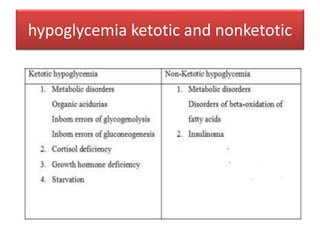
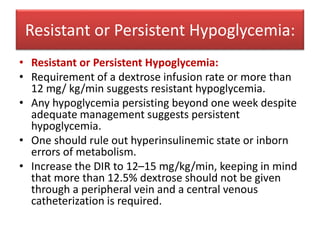
- Persistent or resistant hypoglycemia may require additional drugs or referral to a specialist to investigate underlying