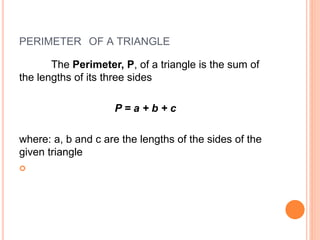
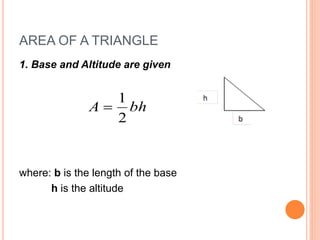
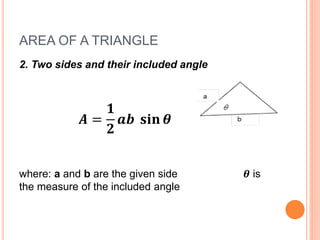
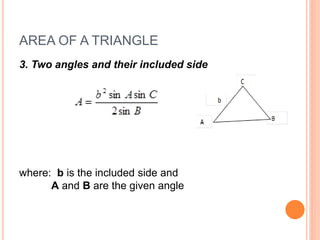
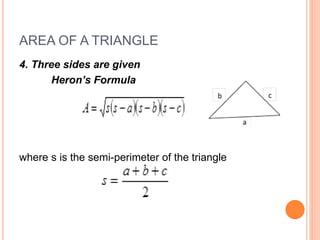
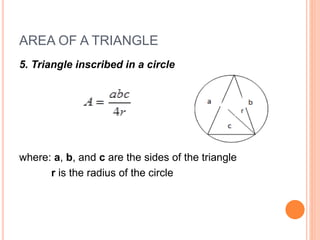
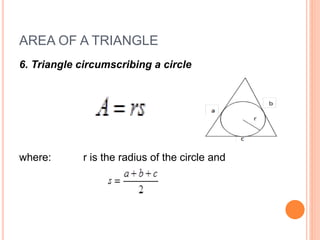
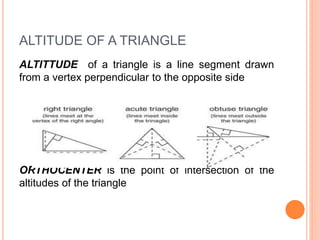
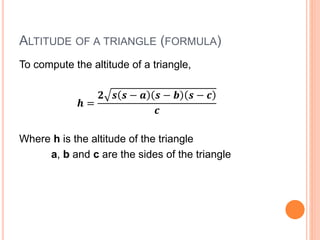
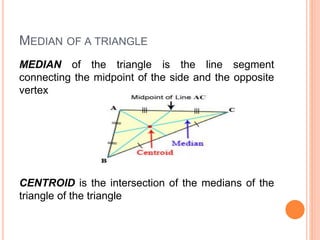
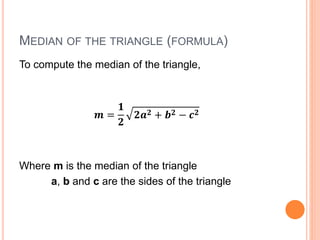
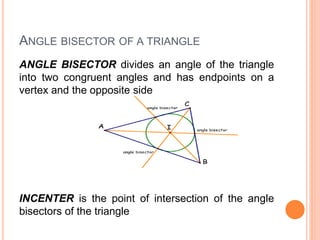
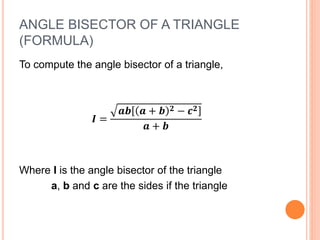
This document defines and explains different types of triangles based on their sides and angles. It discusses equilateral, isosceles, scalene, right, obtuse, and acute triangles. It also covers calculating the perimeter, area, altitude, median, angle bisector, and inscribed/circumscribed triangles. Formulas are provided for calculating the altitude, median, angle bisector, and area using different known properties of triangles. Sample problems are included at the end to test understanding.