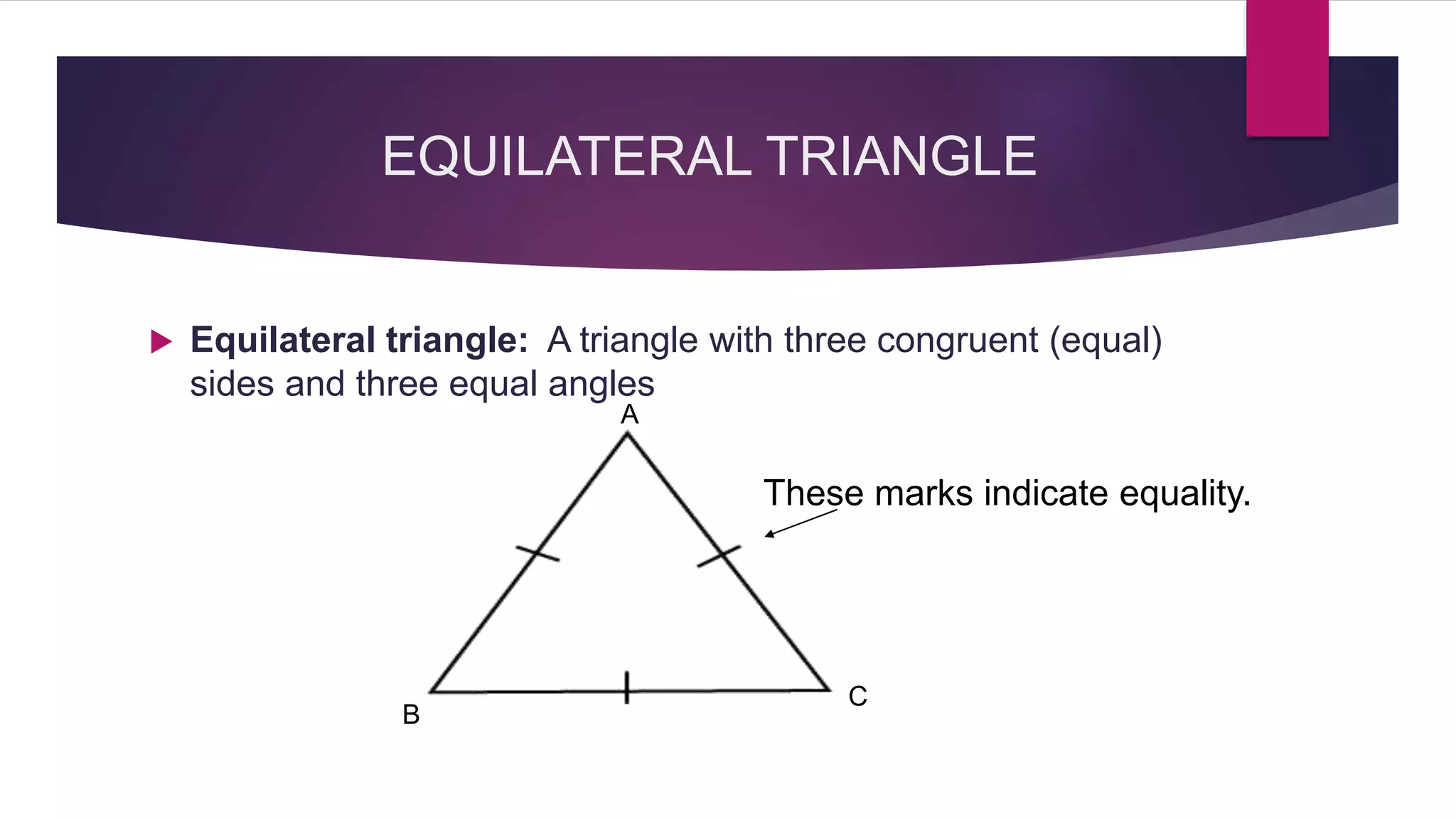
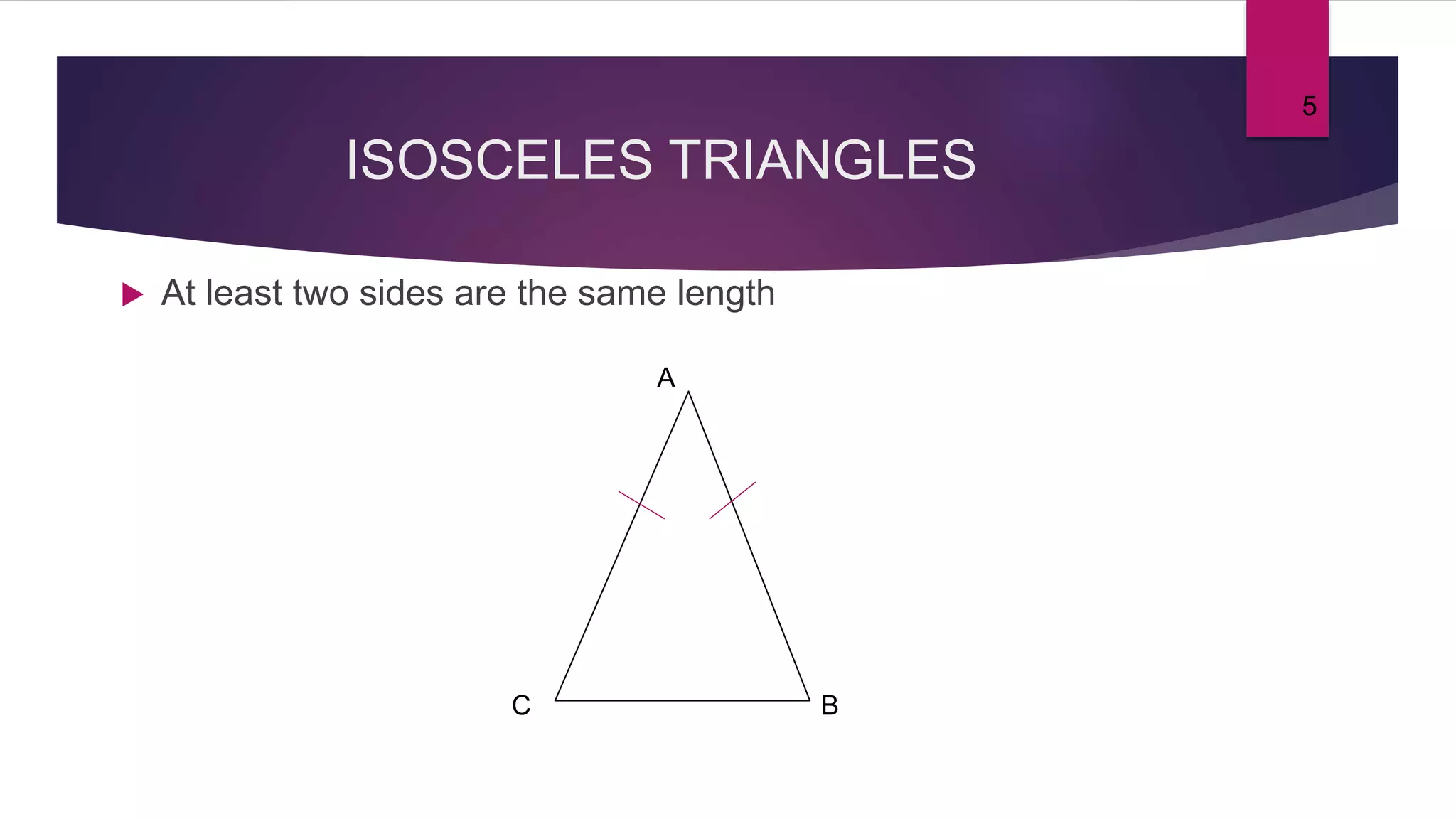
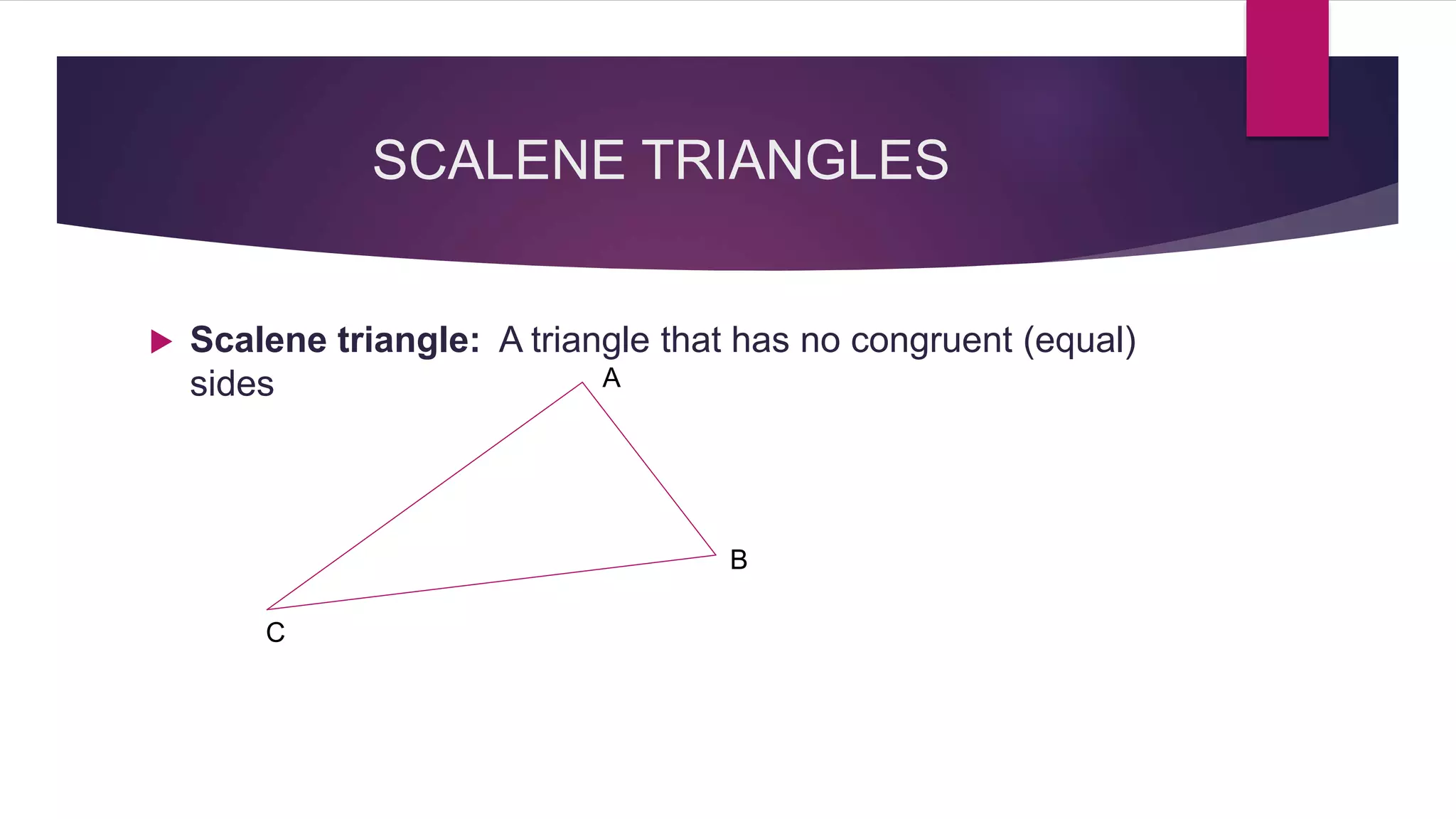
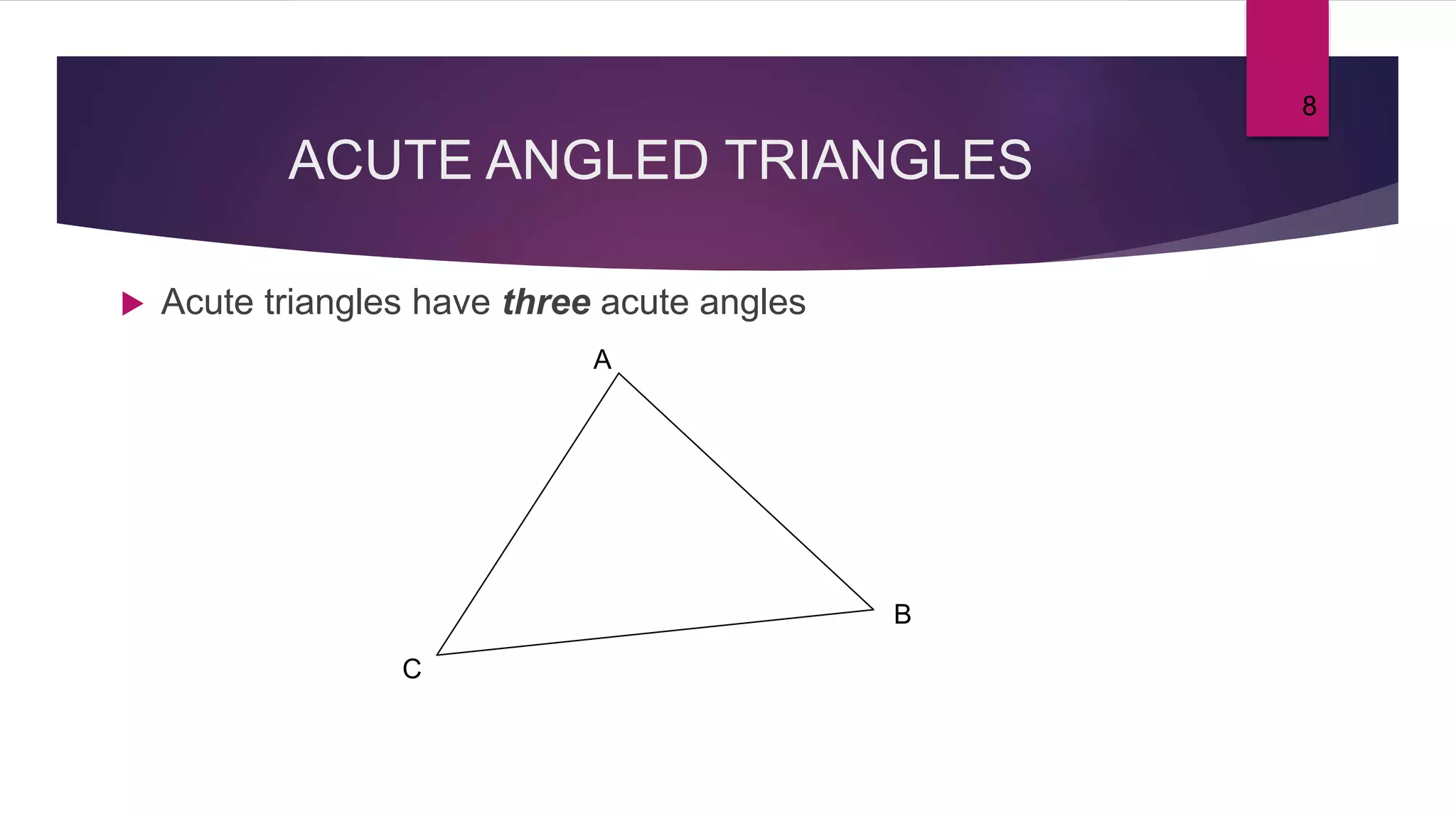
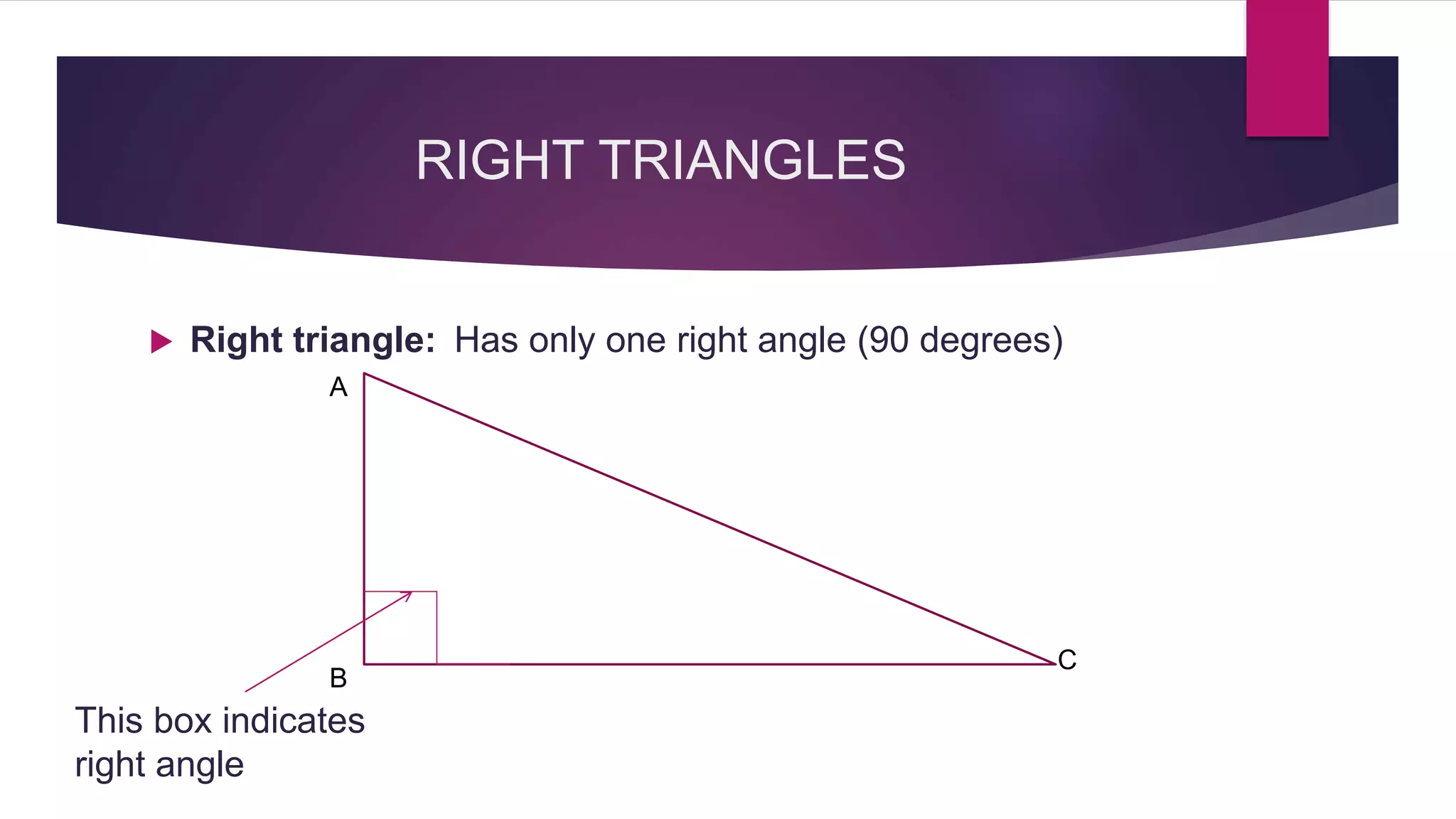
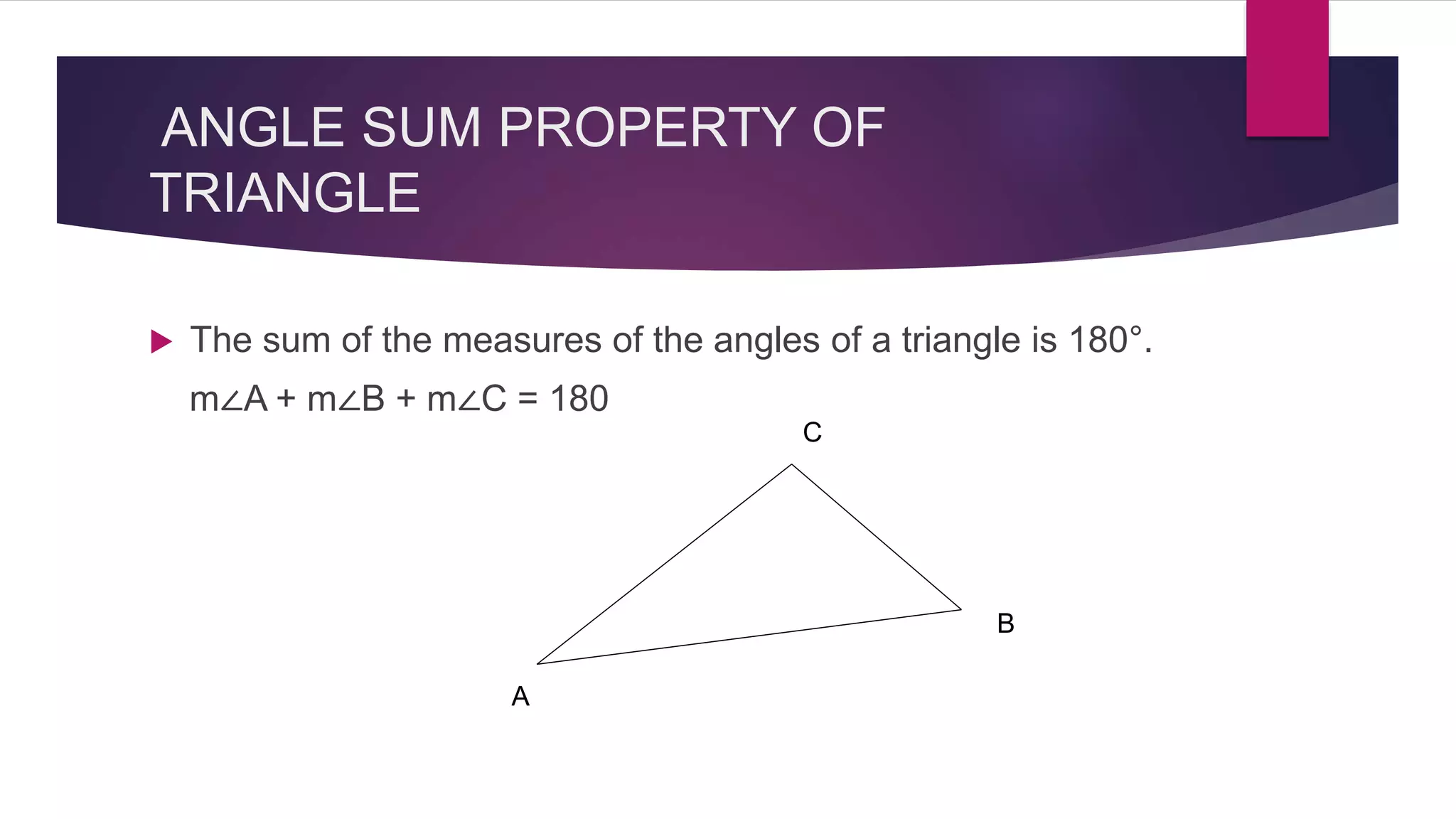
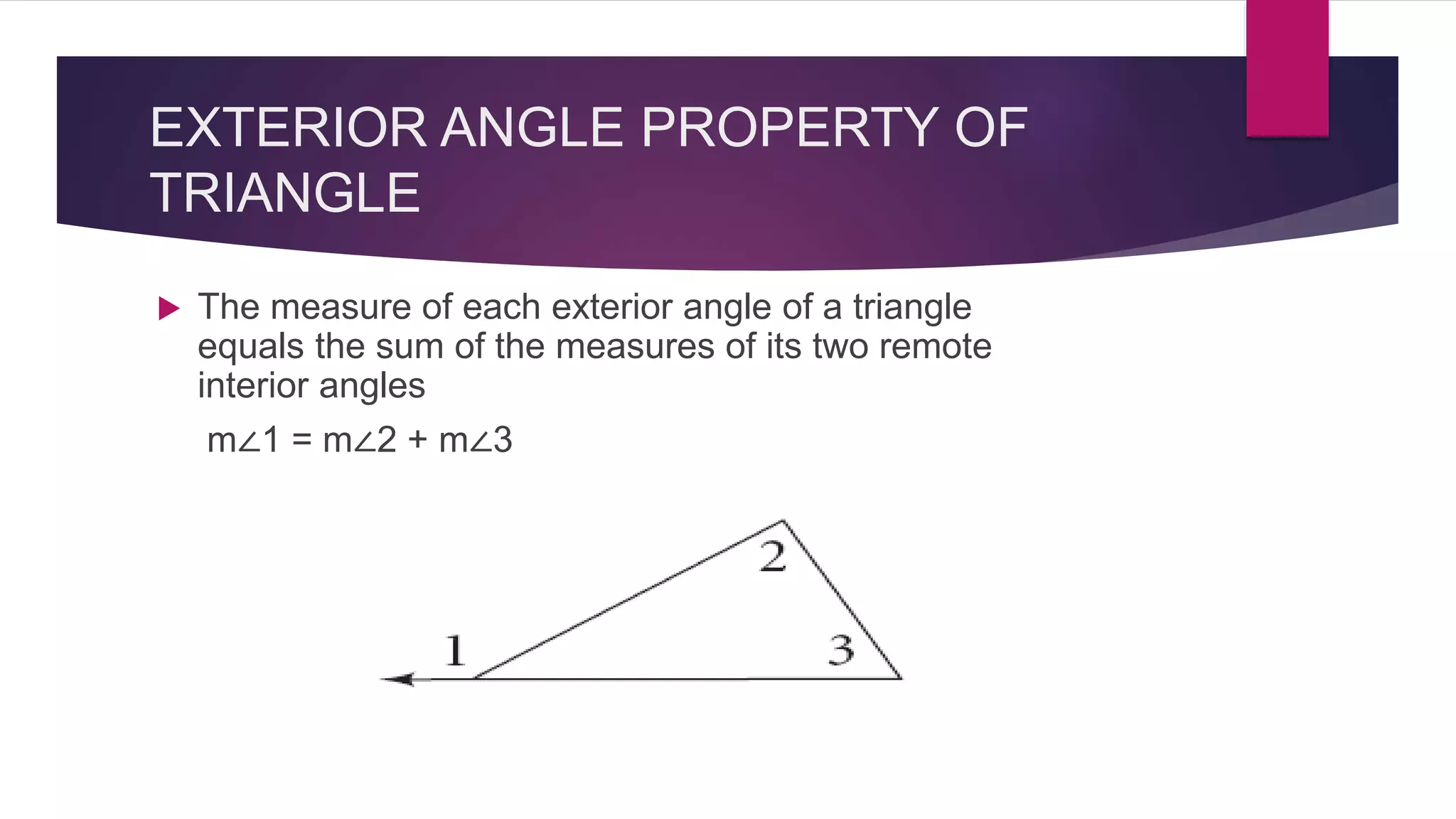
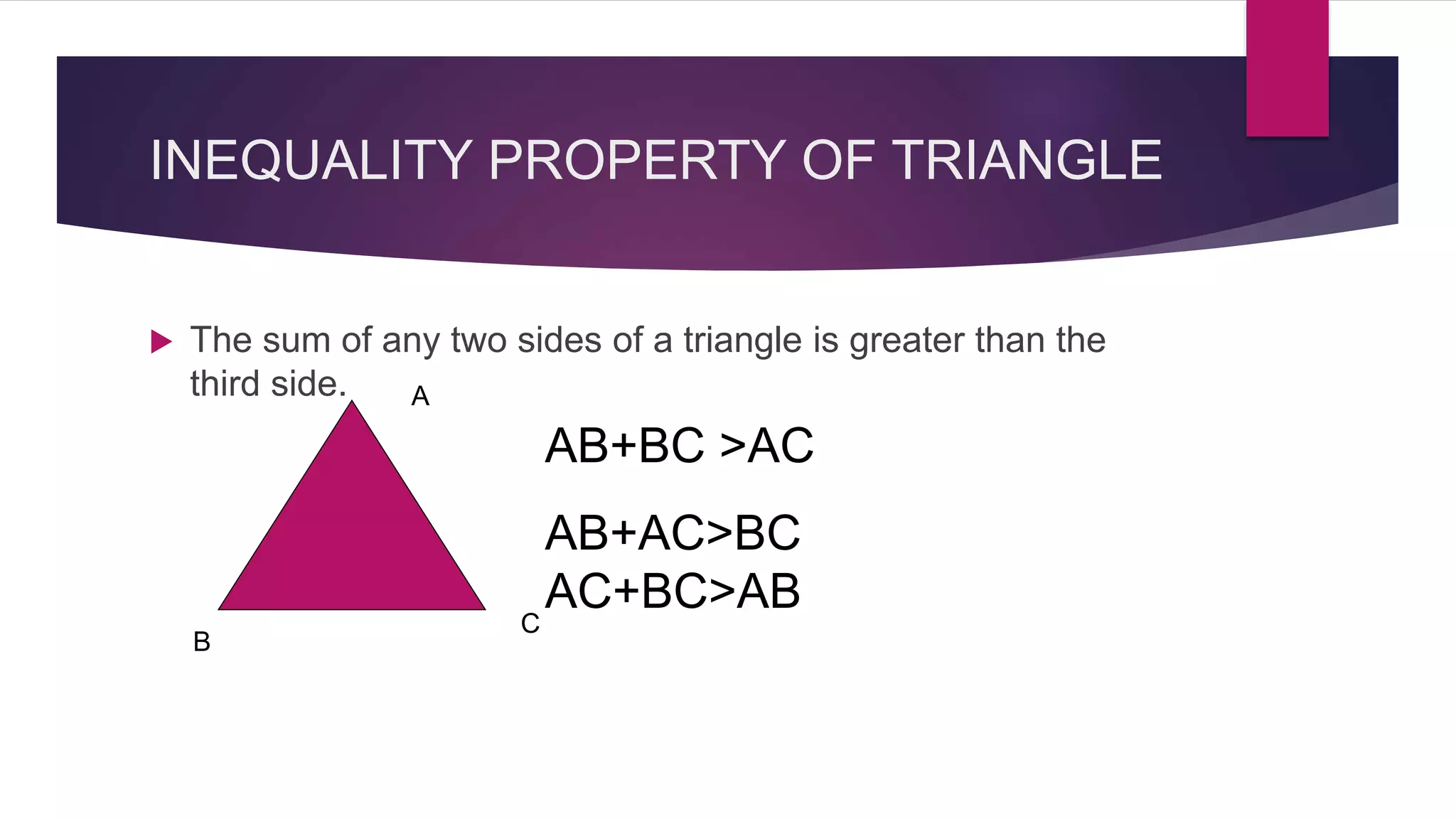
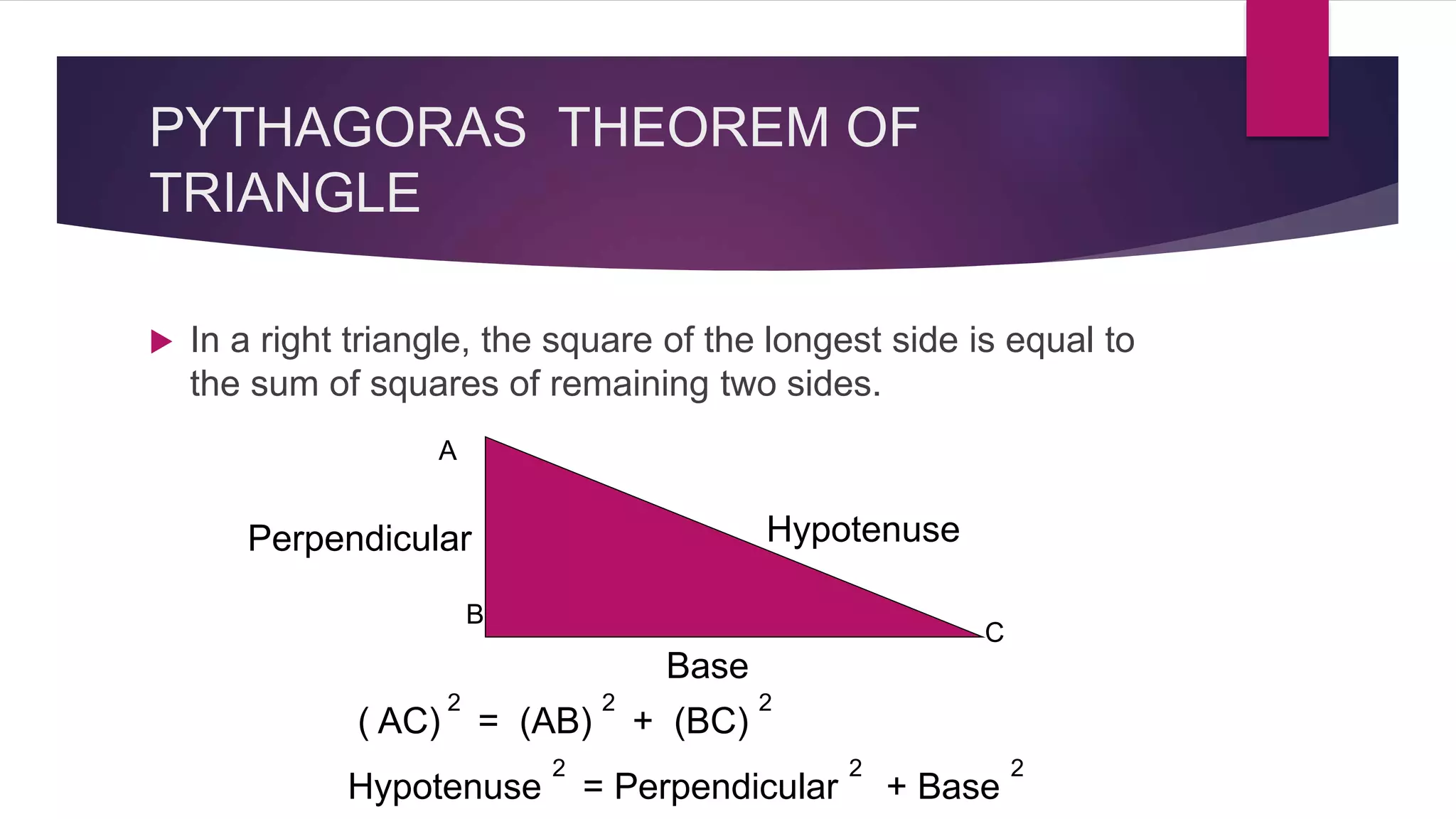
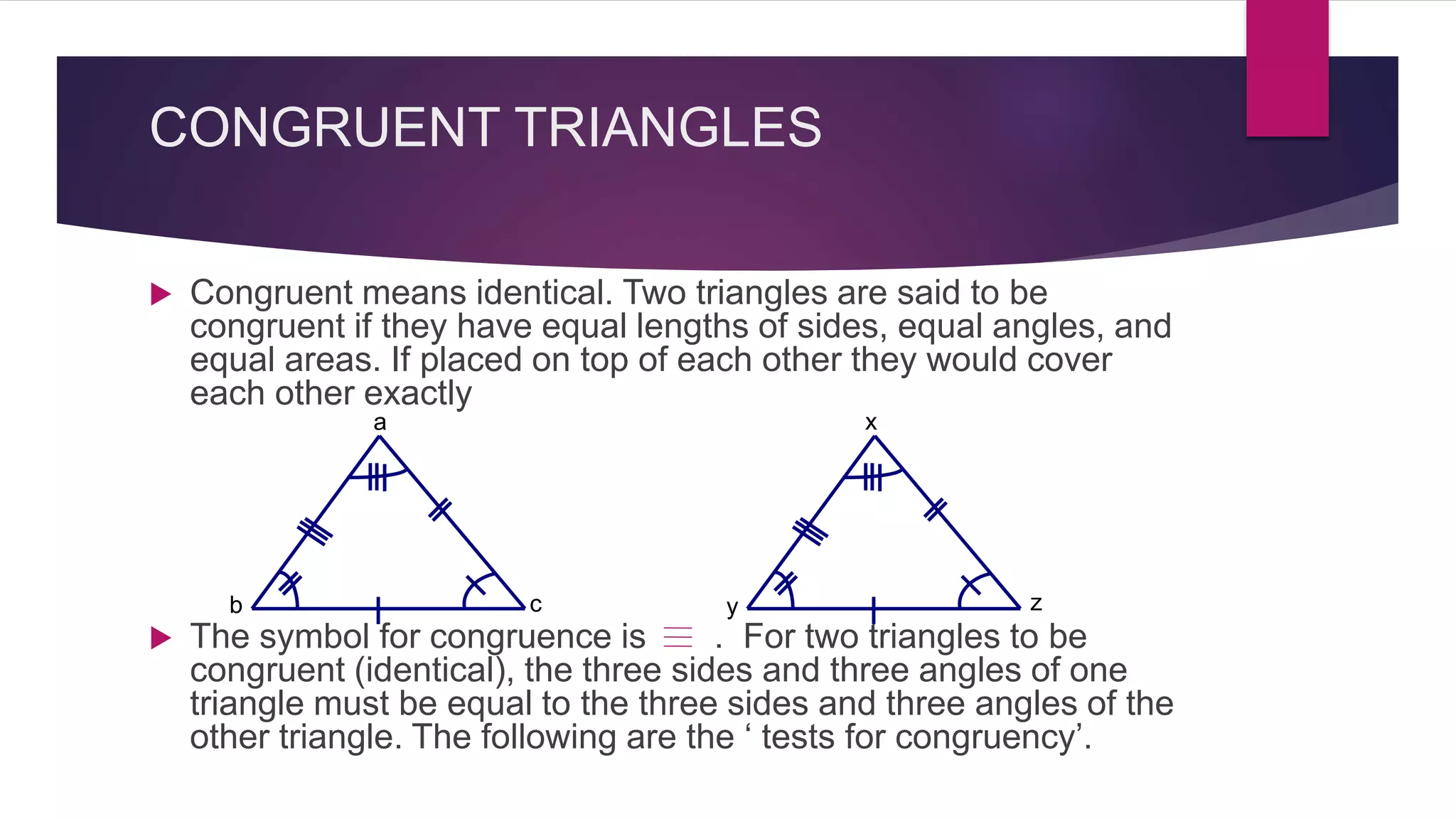
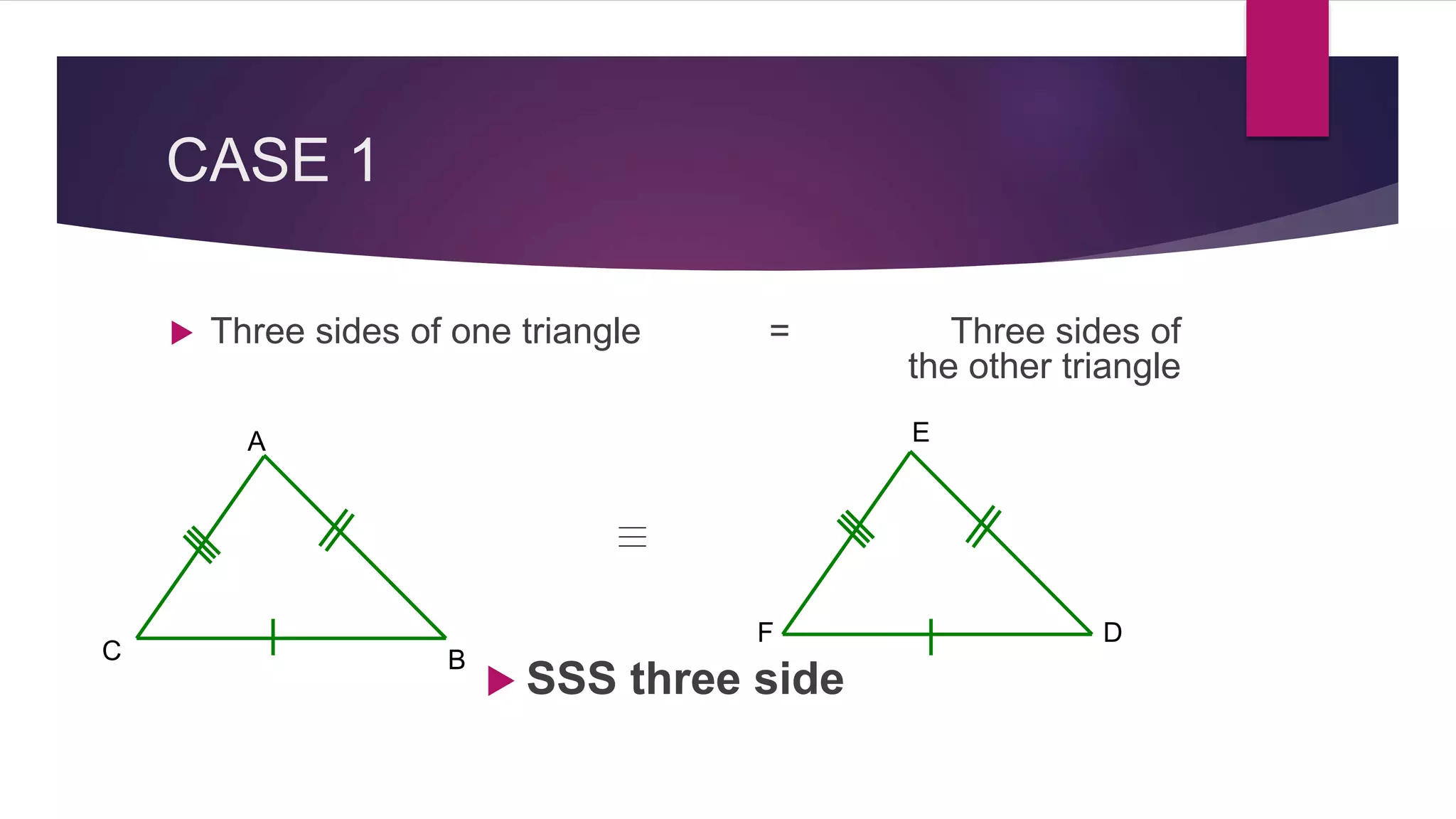
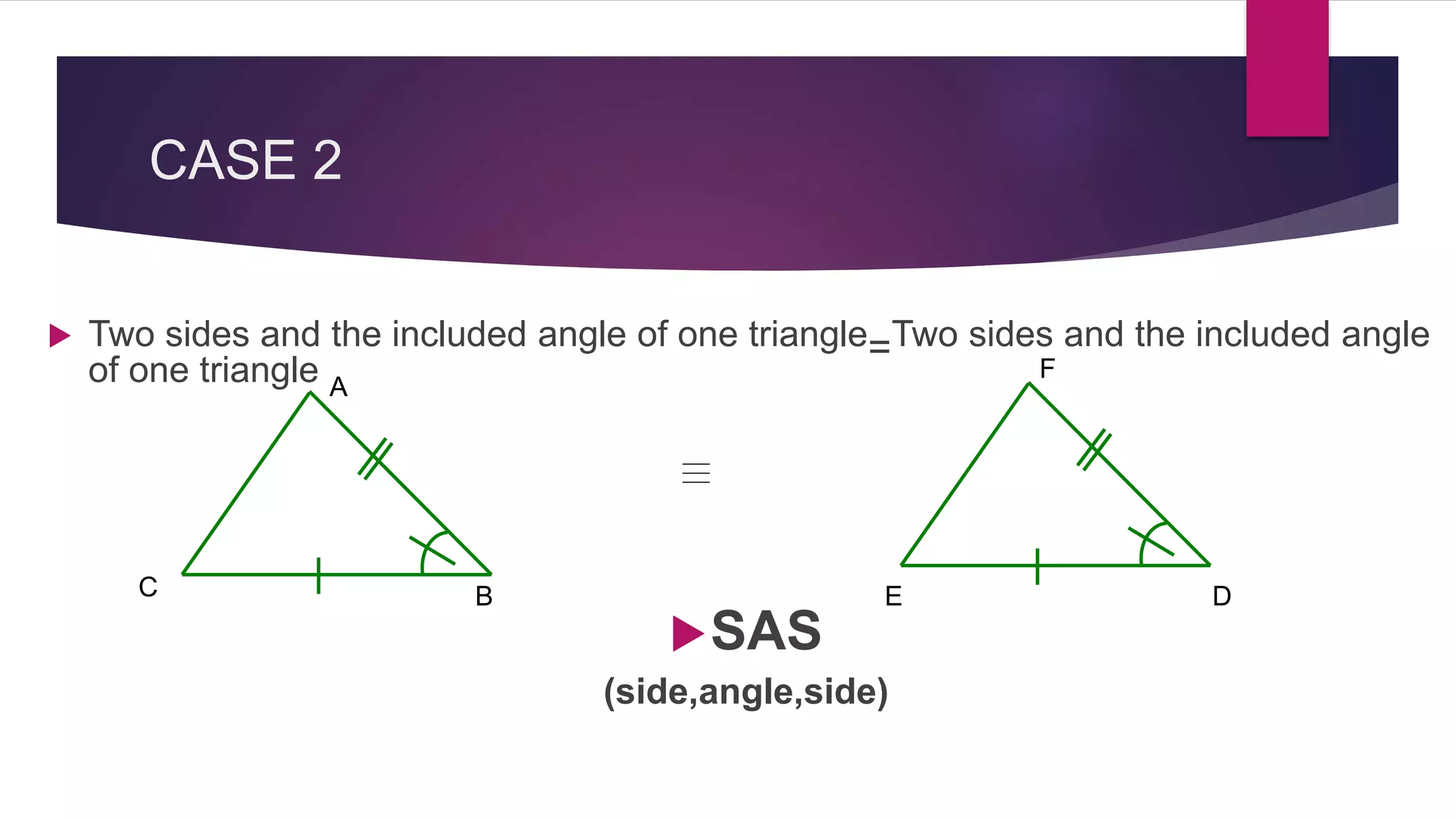
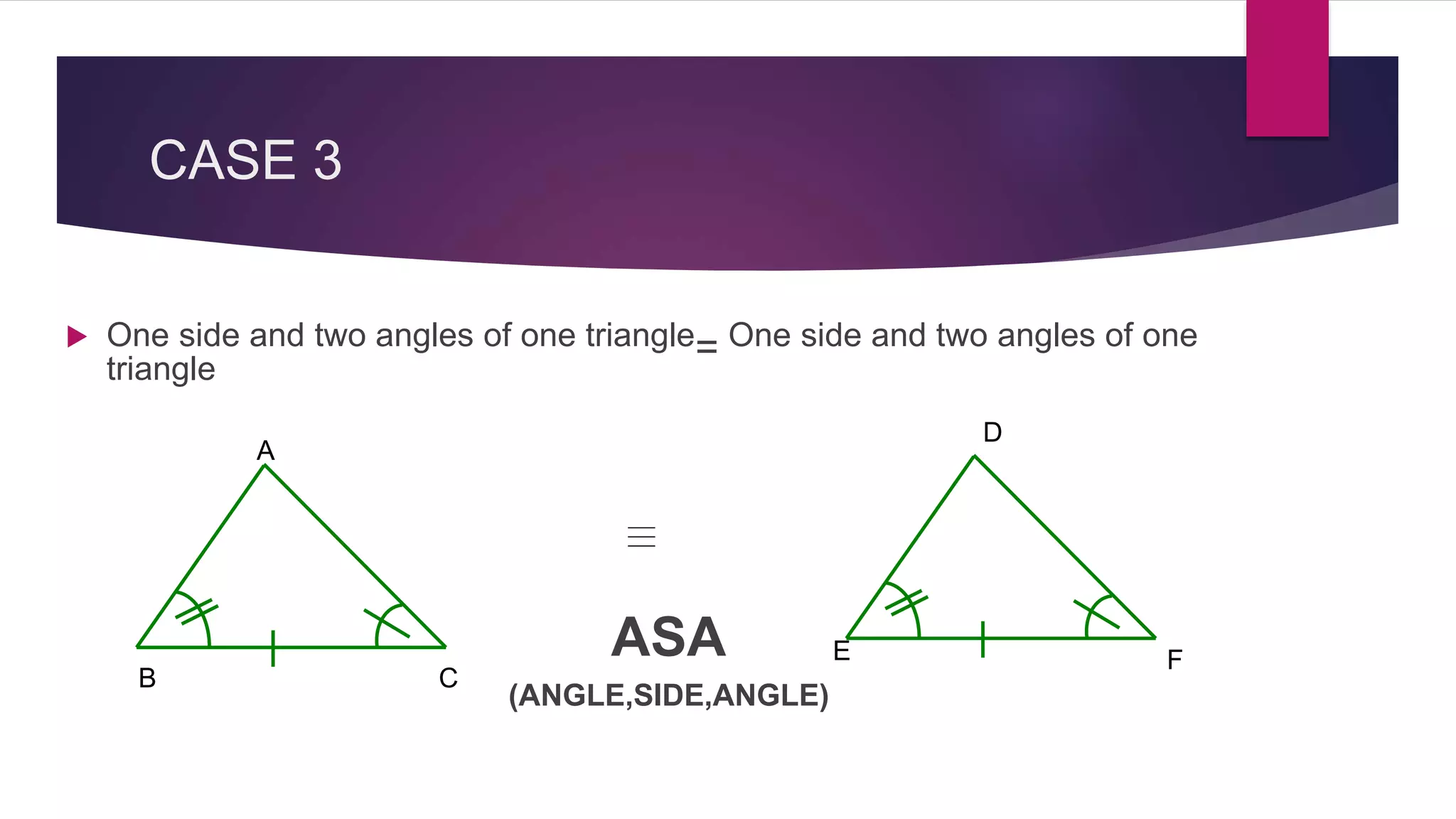
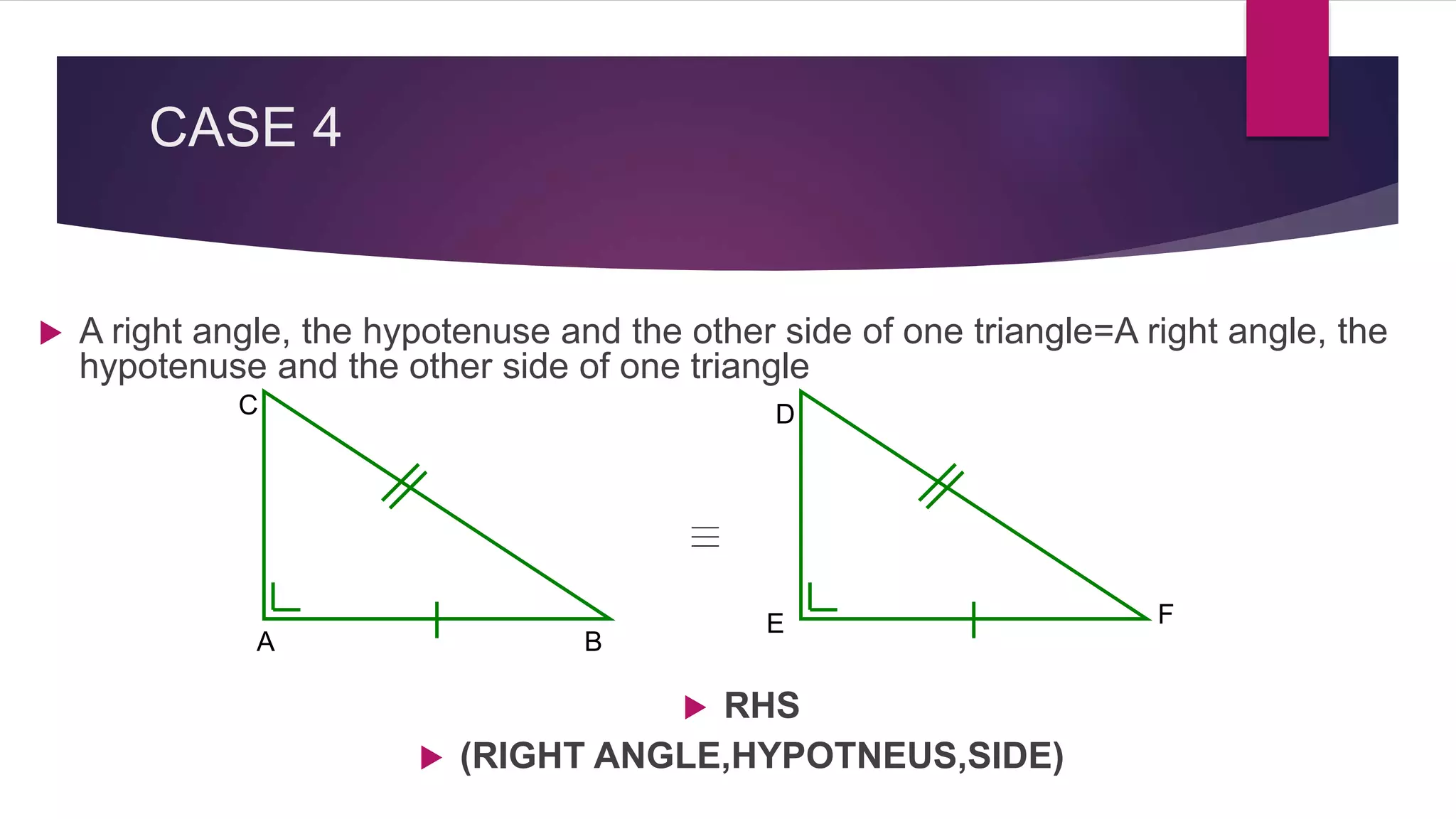
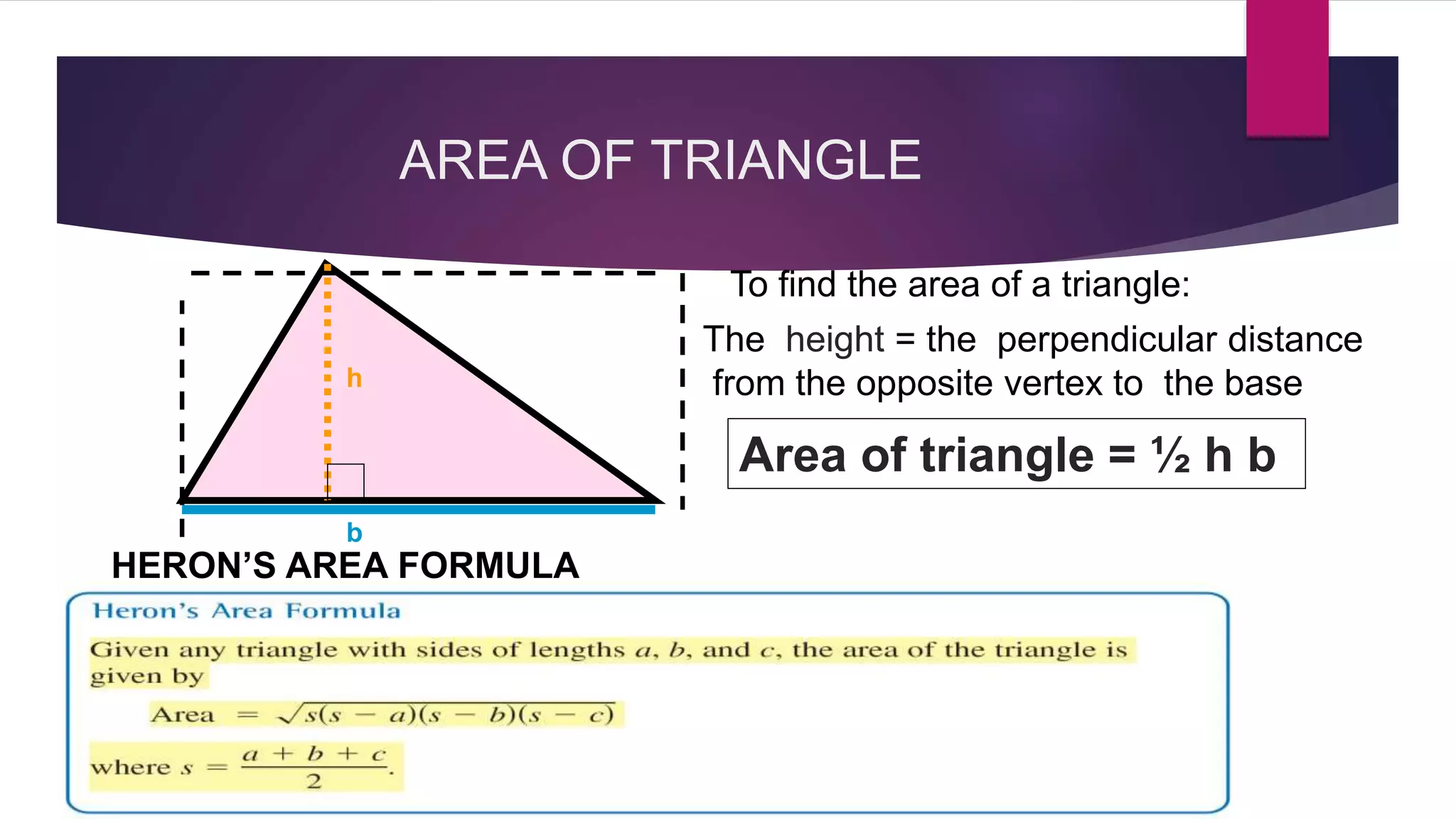
The document provides an overview of triangles, detailing their definition, types based on sides and angles, and key properties such as the angle sum property and the Pythagorean theorem. It also explains congruence in triangles, outlining tests for congruency, and presents formulas for calculating the area of triangles. Overall, the document serves as a foundational guide to understanding the properties and classifications of triangles.