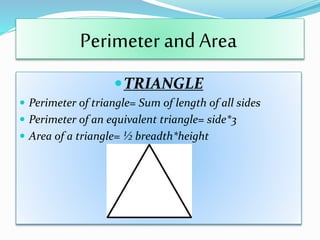
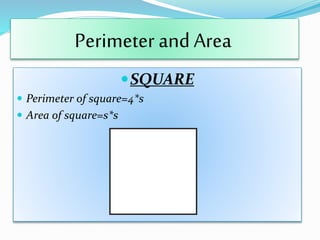
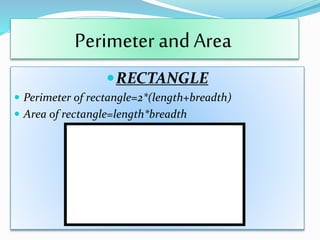
The document is a presentation on the topic of mensuration, which is the branch of mathematics that deals with the measurement of geometric figures. It covers the origins of mensuration, its two main parts—plane mensuration and solid mensuration—and includes formulas for calculating the perimeter and area of different shapes. The author expresses gratitude to their math teacher for guidance and support in preparing the presentation.