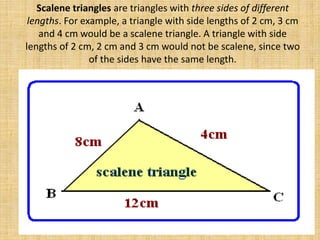
An acute triangle has all angles less than 90 degrees. An obtuse triangle has one angle greater than 90 degrees. A right triangle has one 90 degree angle. Triangles can also be classified based on their side lengths as equilateral (all sides equal), isosceles (two sides equal), or scalene (all sides unequal). The perimeter of a triangle is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. The area of a triangle is calculated using the formula Area = (base x height) / 2, where the base is the length of one side and the height is the length of the line drawn perpendicular to the base from the opposite vertex.