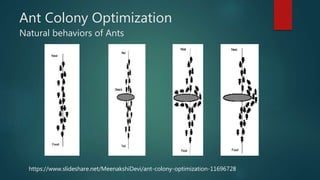
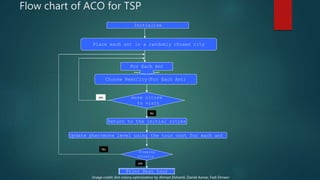
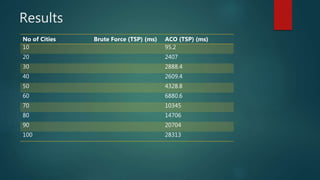
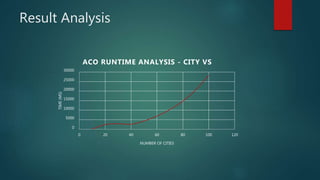
This document discusses using ant colony optimization to solve the travelling salesman problem. It first defines the travelling salesman problem as finding the shortest route for a salesman to visit all cities exactly once and return to the starting city with the minimum cost. It then explains that ant colony optimization is a probabilistic technique inspired by how real ants find food sources, and involves artificial ants laying pheromone trails between cities to probabilistically build solutions. The document provides pseudocode of the ant colony optimization algorithm and shows its results are faster than brute force solutions for solving the travelling salesman problem, with runtime scaling better as the number of cities increases.