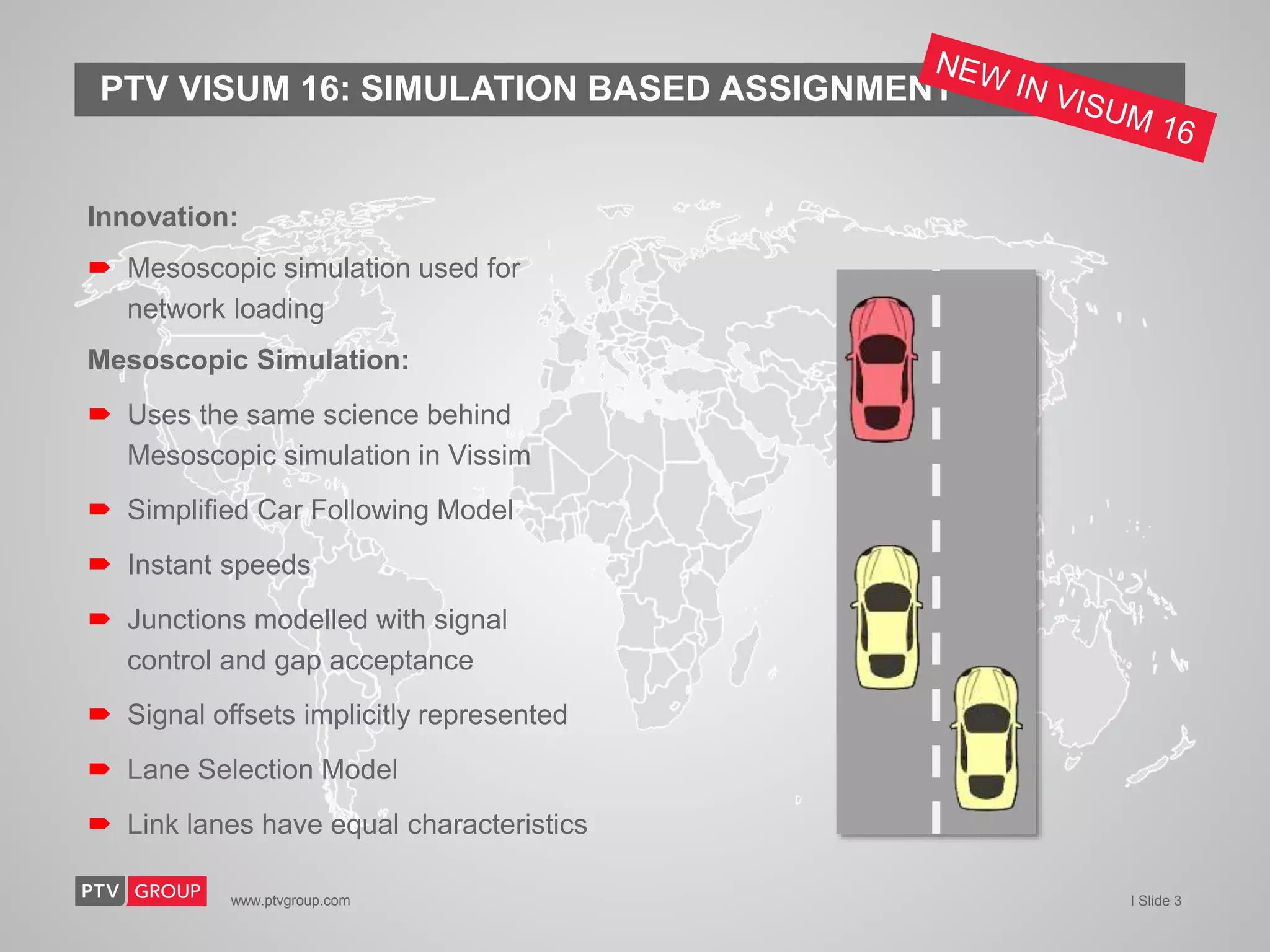
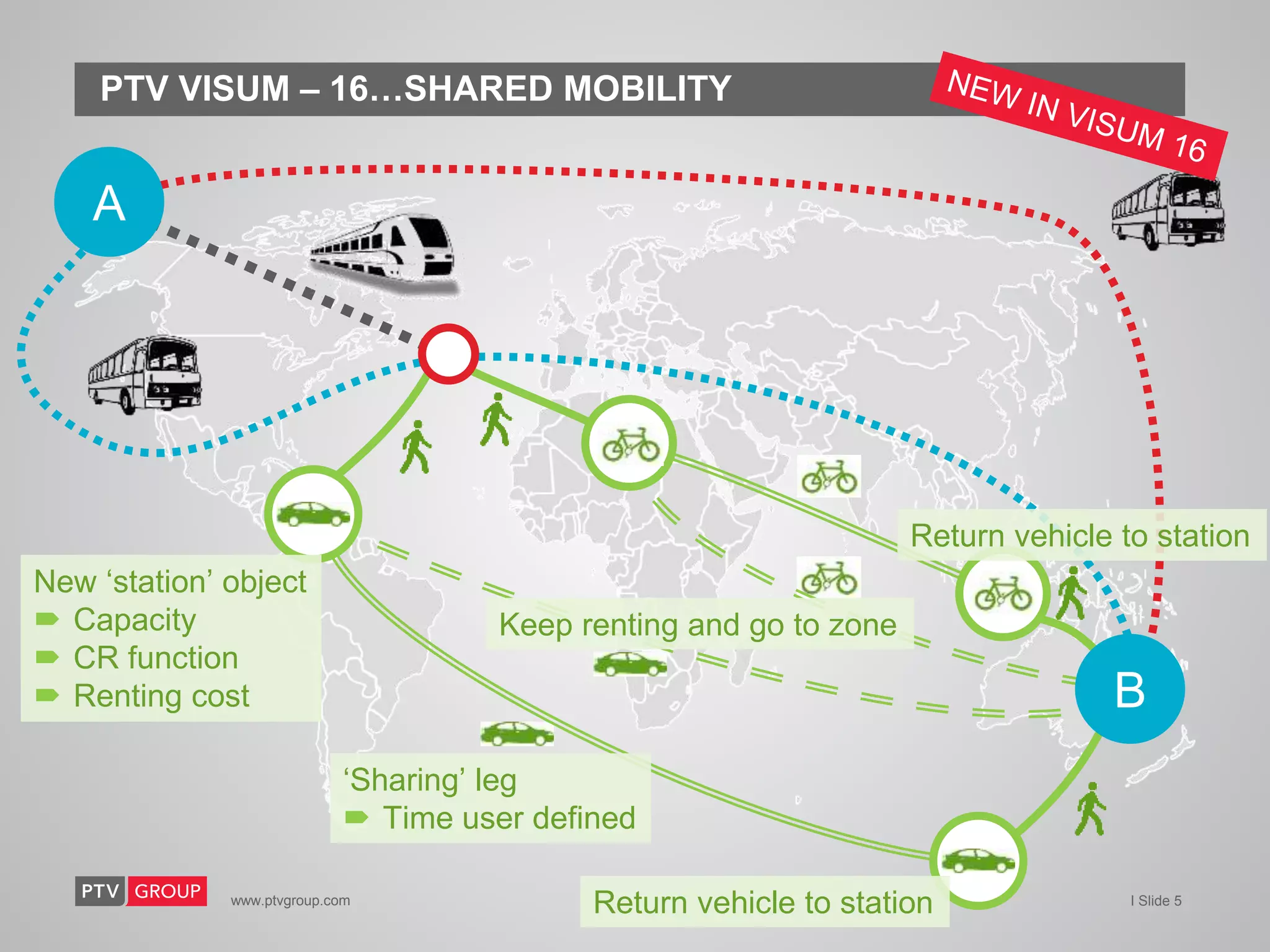
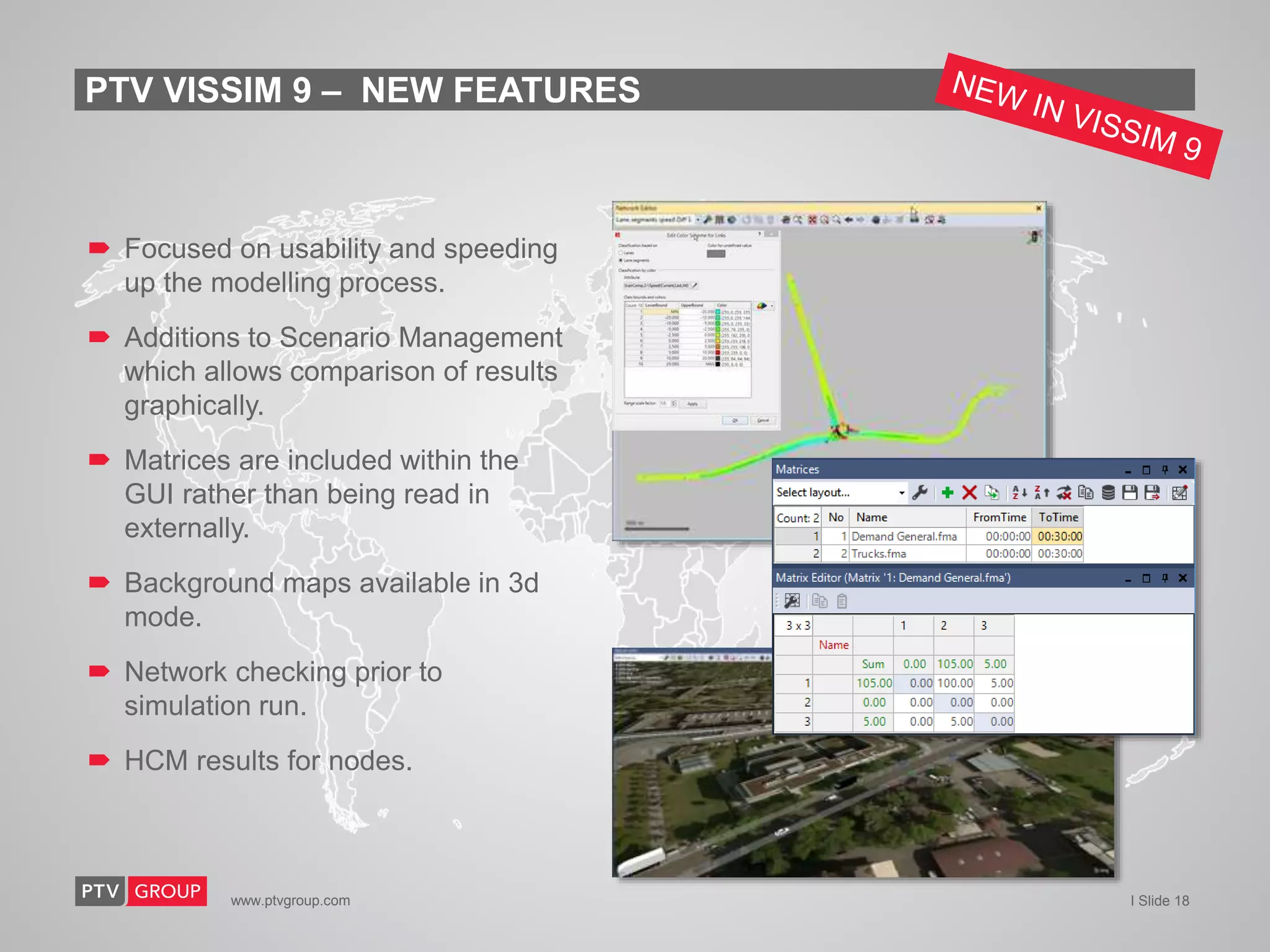
The document provides an overview of PTV Group's transportation modeling software and services. It highlights capabilities like microscopic pedestrian simulation, large-scale network modeling, traffic impact analysis, real-time traffic simulation fused with real data, online traffic signal control, and shared mobility modeling. It also summarizes case studies applying the software for autonomous vehicle modeling, urban cycling planning, and bridge closure impact analysis.