- People have choices for how to travel including transit, walking, biking, carpooling, motorcycling, or driving alone. Their mode choice depends on factors like availability of parking, income, availability and cost of transit, auto ownership, trip purpose, life stage, cost, safety, time, and cultural perceptions.
- Mode choice modeling uses numerical methods to describe how people select between transportation alternatives based on the characteristics of a given region. Models can separate choices by trip purpose.
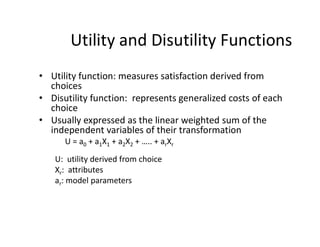
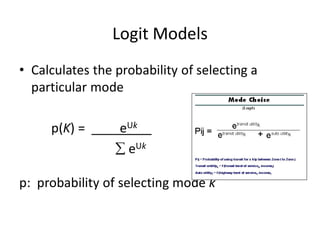
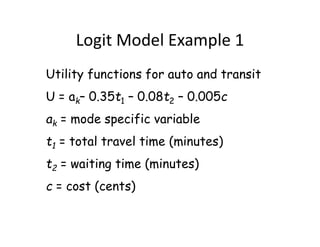
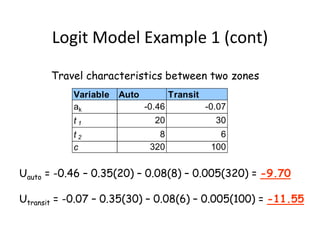
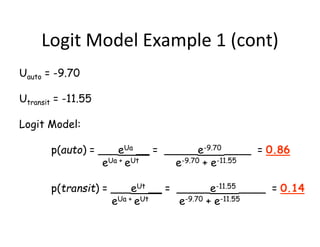
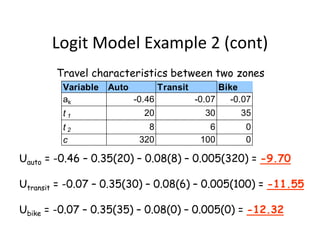
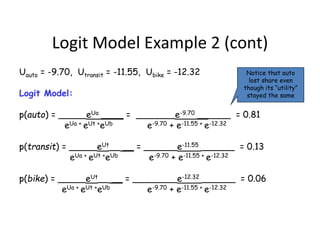
- Logit models calculate the probability of selecting a particular mode based on the utility and disutility of attributes like travel time, waiting time, and cost. Introducing new modes like improved biking infrastructure can shift mode shares