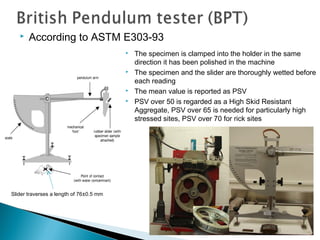
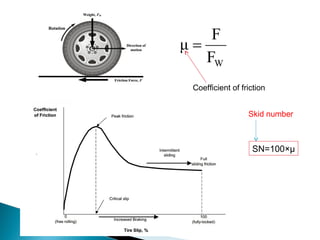
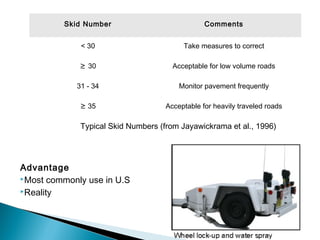
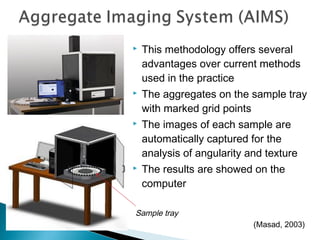
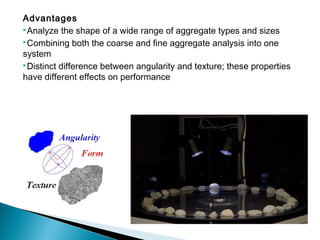
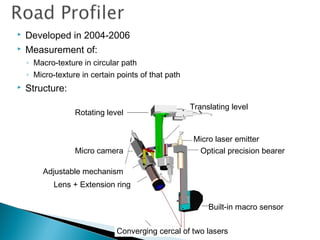
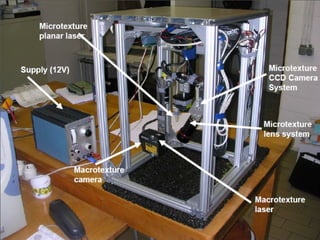
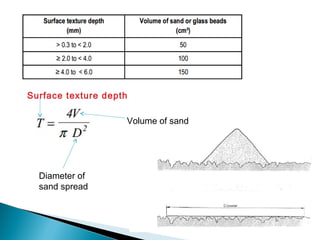
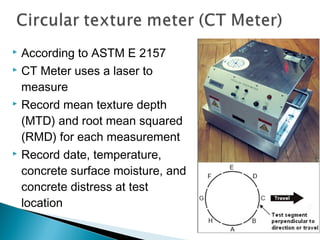
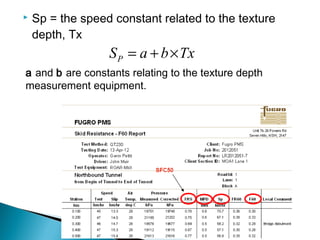
This document discusses various methods and standards for measuring pavement surface characteristics like skid resistance and texture. It covers topics like factors that influence skid resistance, methods for measuring micro-texture and macro-texture, standards for measuring polished stone value, and devices for measuring skid resistance at different speeds. The summary provides an overview of the key methods and standards discussed in the document.