This document discusses various mechanisms of transport across plasma membranes, including:
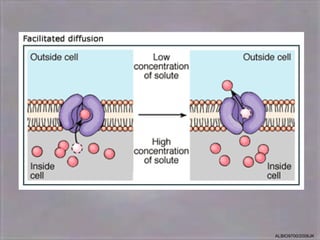
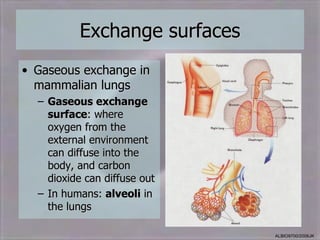
1) Diffusion and facilitated diffusion, which involve the passive movement of substances down their concentration gradients, or through membrane protein channels.
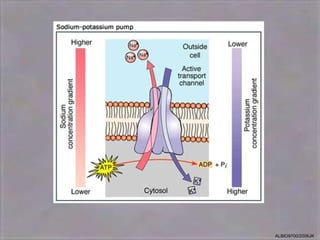
2) Active transport, which uses energy to transport substances against their gradients via carrier proteins.
3) Bulk transport processes like endocytosis and exocytosis that move large quantities of material into and out of cells.
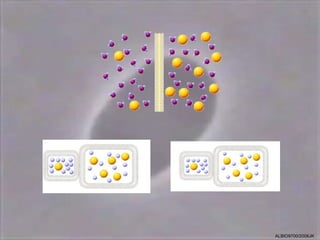
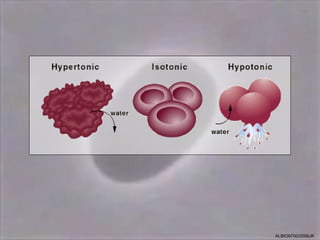
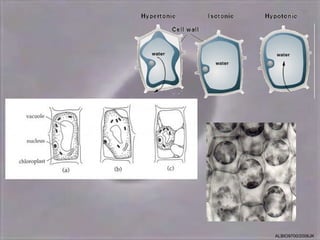
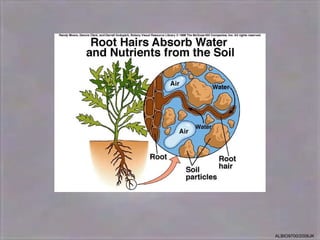
4) Osmosis, the passive movement of water through semi-permeable membranes down its concentration gradient, influenced by solute concentrations and pressure potentials.