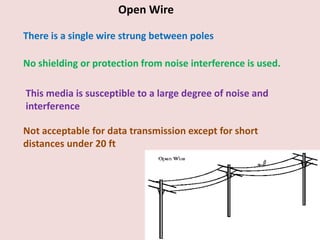
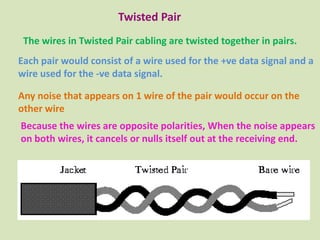
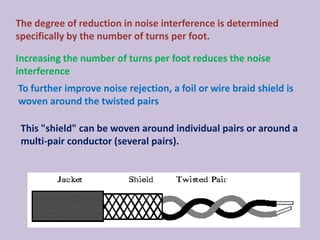
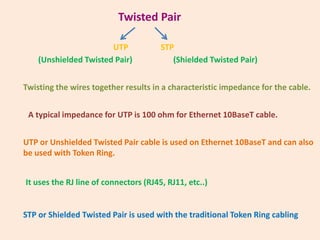
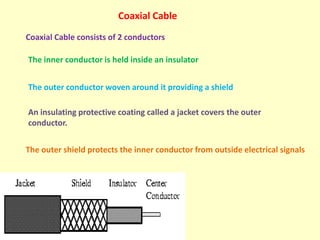
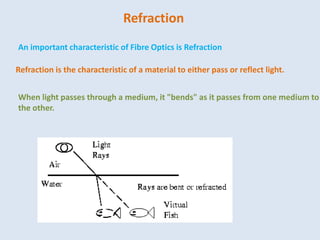
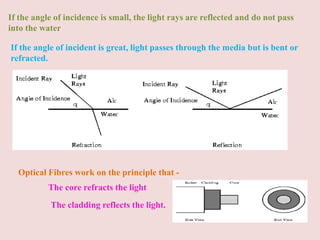
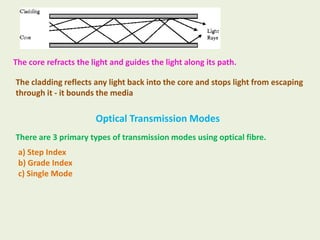
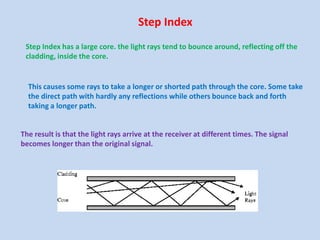
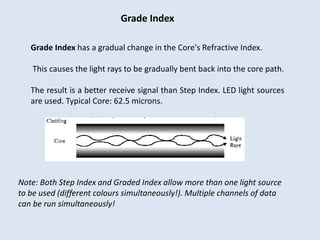
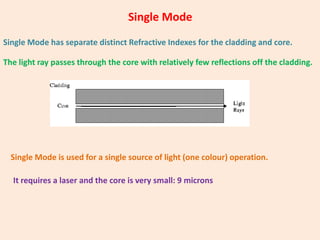
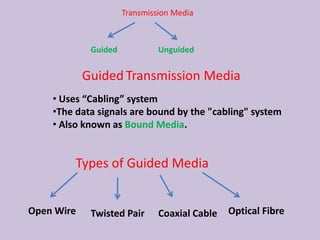
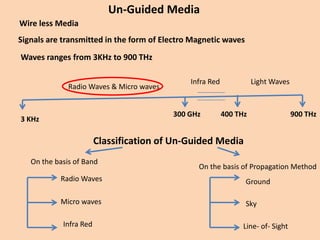
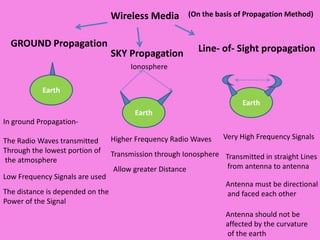
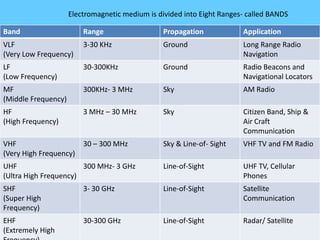
Guided transmission media uses cabling to bind data signals, also known as bound media. Types include open wire, twisted pair, coaxial cable, and optical fiber. Unguided media transmits signals as electromagnetic waves via radio waves, microwaves, or infrared light. It can propagate through the ground, sky, or line-of-sight. The electromagnetic spectrum is divided into bands like VLF, LF, MF, HF, VHF, UHF, SHF, and EHF that determine the propagation method and applications.