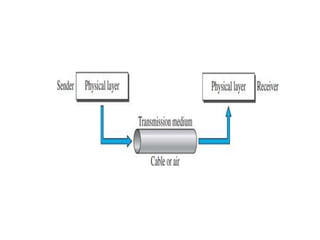
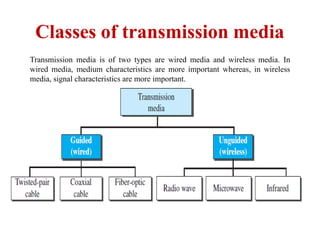
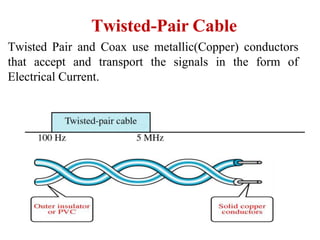
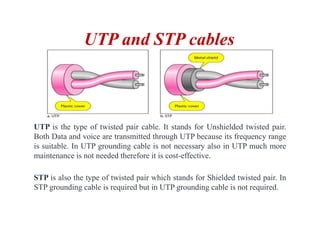
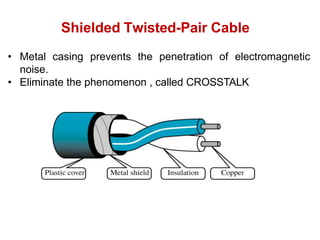
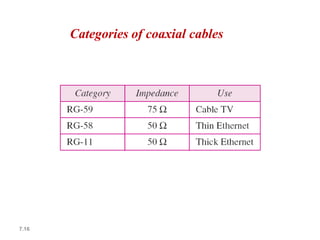
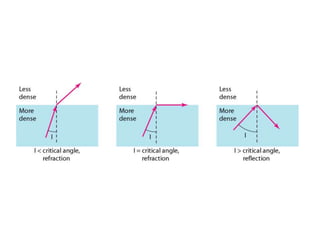
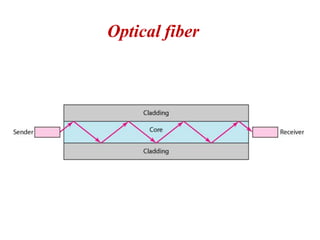
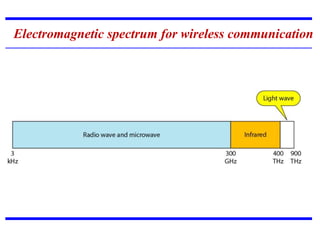
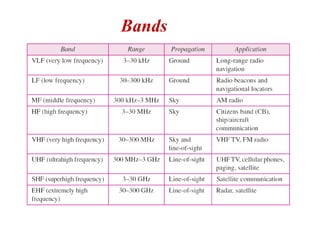
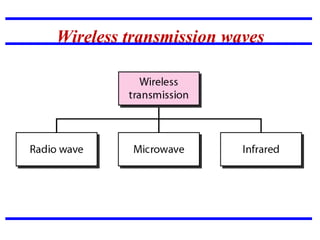
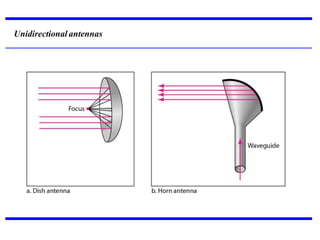
Transmission media carries information between sender and receiver using electromagnetic signals. It supports the physical layer in OSI models. Wired transmission media like twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber optics use copper or glass to transmit electrical or light signals. Wireless transmission media transmits signals through radio waves, microwaves, or infrared without physical connections. Factors like bandwidth, transmission impairments, and interference affect signal quality over different transmission media.