This document discusses and compares different types of transmission media:
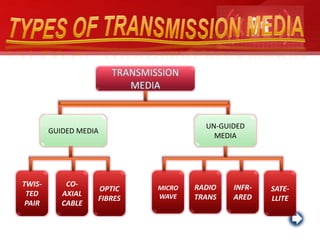
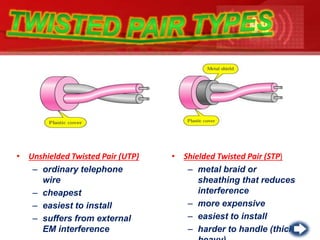
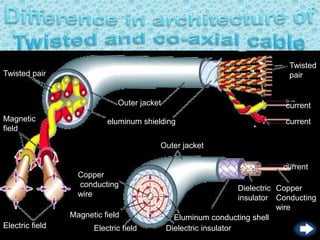
- Guided or wired media include twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and optical fiber cable. These employ physical conductors to transmit data.
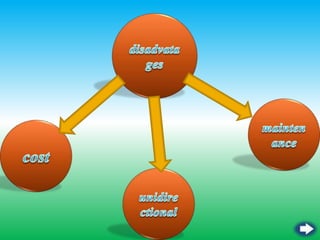
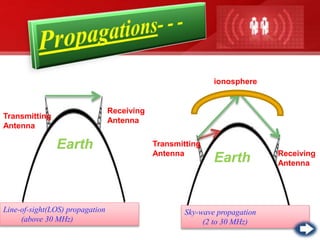
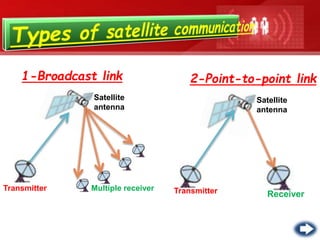
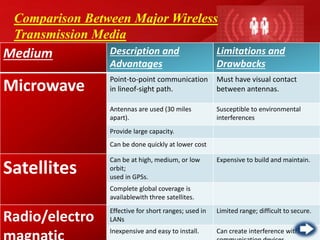
- Unguided or wireless media transmit data using electromagnetic waves without a physical conductor. These include radio transmission, microwave transmission, and satellite transmission.
- Each media type has advantages like capacity, cost, and limitations like range or susceptibility to interference that make some more suitable for different transmission needs. Optical fiber provides the greatest bandwidth potential over the longest distances.