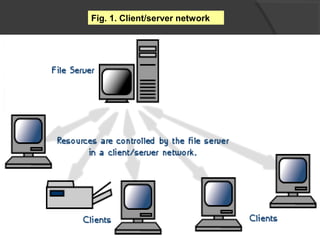
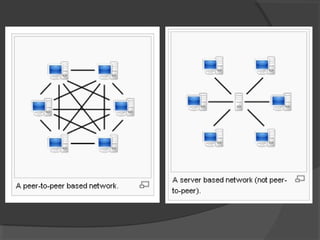
The document discusses two main network architectures: client/server and peer-to-peer. In a client/server network, one computer acts as a centralized server that provides services to other client computers on the network. A peer-to-peer network does not have a centralized server; instead, all computers on the network have equal capabilities to share resources directly with each other. The key differences between the architectures are that client/server networks have higher cabling costs but are easier to manage, while peer-to-peer networks are cheaper but harder to manage.