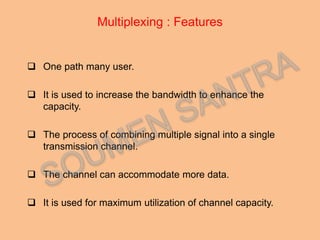
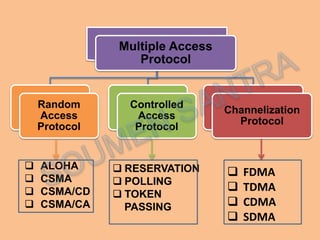
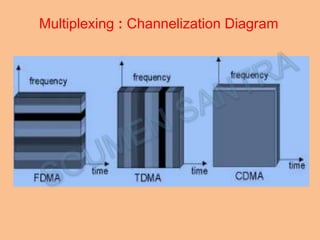
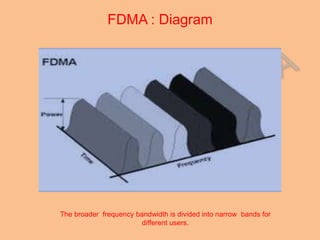
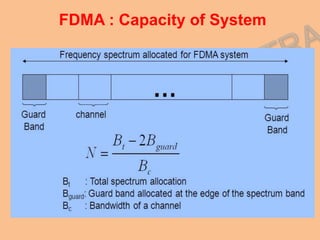
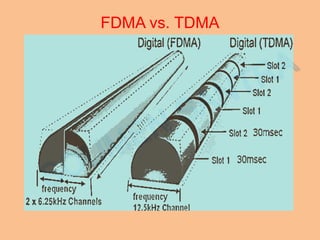
Frequency Division Multiplexing Access (FDMA) is essential for wireless communication, allowing simultaneous data transmission between mobile stations and base stations using a shared link. It divides the frequency spectrum into narrow bands for different users, maintaining continuous transmission and avoiding timing issues, though it incurs higher transceiver costs. While FDMA provides specific frequency allocations, Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) is often considered more efficient due to its flexibility and reduced waste in bandwidth.