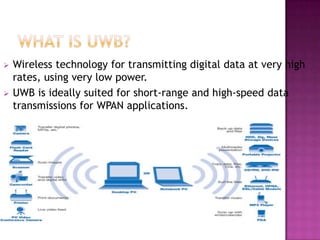
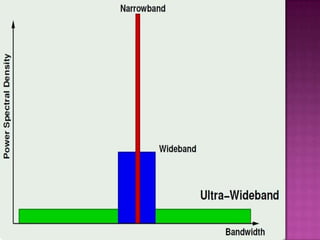
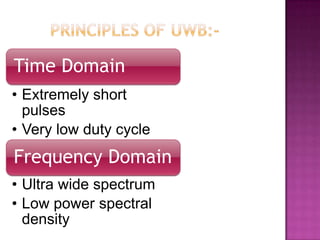
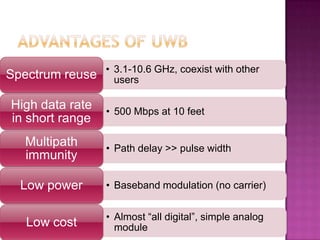
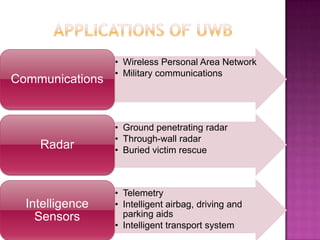
This document provides an overview of ultra-wideband (UWB) technology. It discusses what UWB is, its principles and characteristics in both the time and frequency domains. Key advantages of UWB include high data rates over short ranges, multipath immunity, low power and cost. Applications discussed include wireless personal area networks, military communications, ground penetrating radar and sensors. Challenges of UWB are also noted, as well as its future potential and comparison to other technologies.