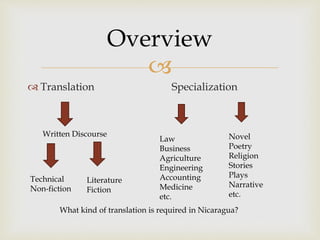
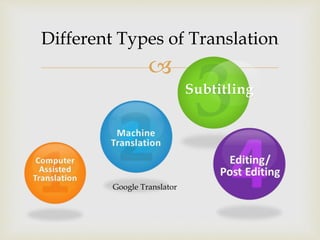
Rolando Tellez specializes in various types of translation, emphasizing the importance of computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools for efficiency and accuracy. He discusses the nuances of translation, including the editing process and requirements for professional translators in Nicaragua. Additionally, Tellez highlights the need for practical experience and resources to improve translation skills.