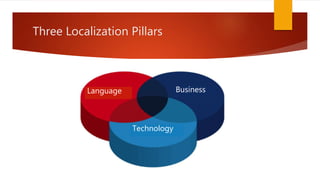
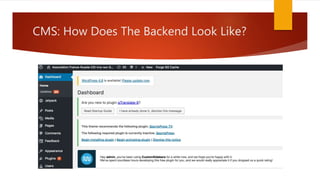
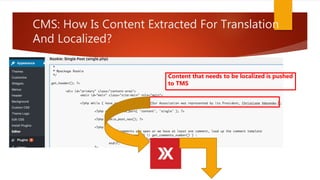
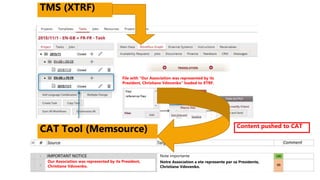
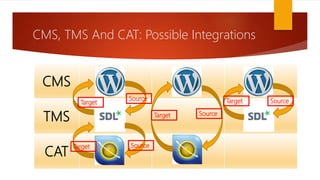
The document outlines the importance of localization in translation, emphasizing its role in making products culturally appropriate for diverse markets, particularly in the technology-driven environment. It discusses various aspects of localization including tools for language management, game and content localization, and the integration of machine translation, while highlighting the skills needed for translators to succeed in the modern market. The text culminates in the idea that successful translation combines artistry with technological proficiency and business acumen.