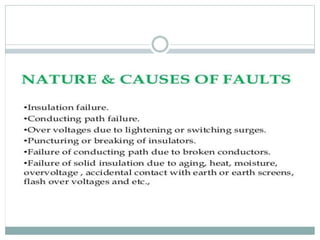
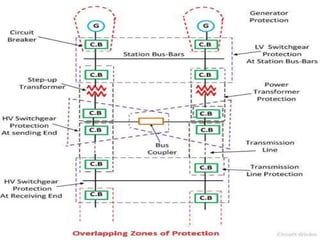
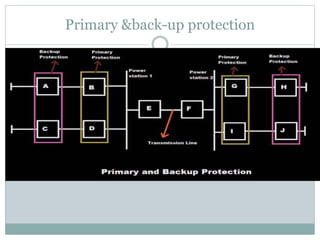
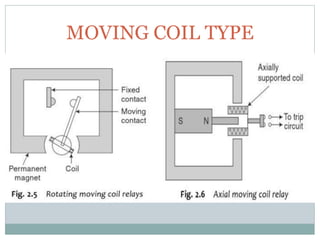
This document provides an overview of the power system protection course including the modules, objectives, and key topics. Module 1 covers the introduction to power system protection including the need for protective schemes, types of faults, zones of protection, essential qualities of protection, and classification of protective relays. It also discusses relay construction and operating principles, focusing on electromechanical, static, and numerical relays. Overcurrent protection is introduced as one of the key protective schemes.