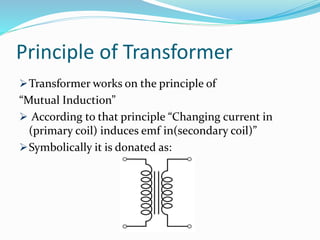
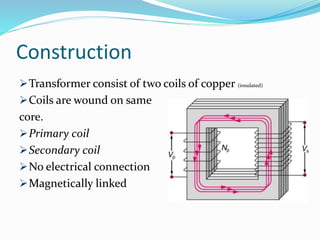
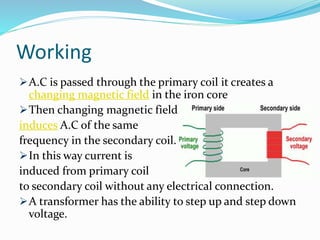
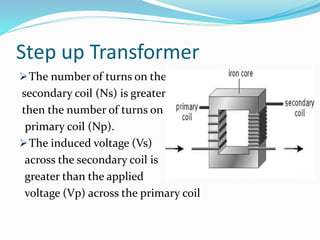
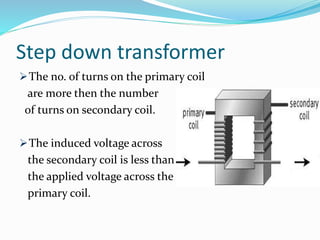
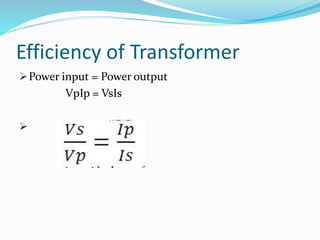
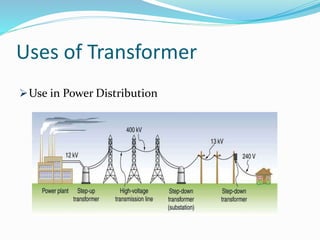
Transformers work on the principle of mutual induction to transform electrical energy from one circuit to another without a direct electrical connection. They consist of two coils wound around an iron core, with the primary coil connected to an alternating current source. As the current changes in the primary coil, it induces a changing magnetic field in the core which in turn induces an alternating current in the secondary coil. Transformers can step up or step down voltages depending on the ratio of turns in the primary and secondary coils. They are widely used in power distribution and electronics applications to efficiently transfer power or match voltages. However, some energy is lost through heat in the core and coils.