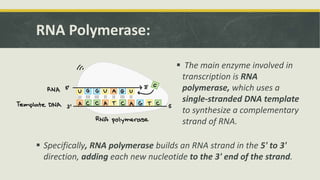
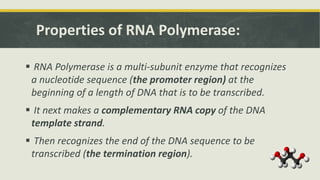
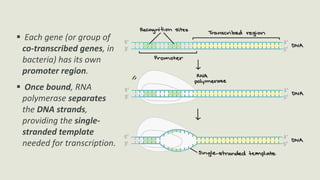
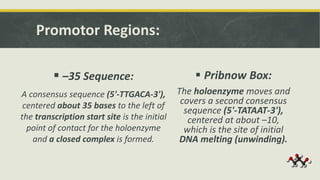
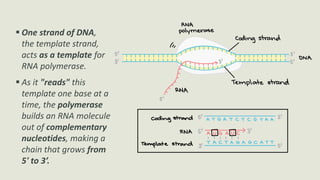
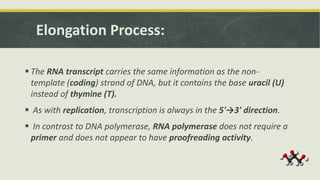
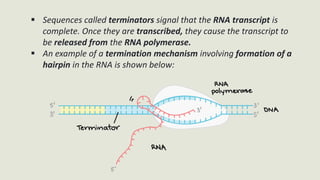
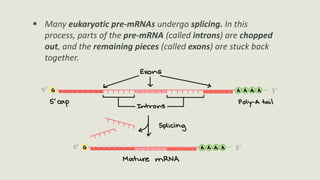
Transcription is the process by which a DNA strand is copied into RNA. It involves three main phases - initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation begins when RNA polymerase binds to the promoter region of DNA and separates the strands to form a transcription bubble. Elongation then occurs as RNA polymerase reads the template strand and builds a complementary RNA chain. Termination happens when a termination signal is reached, causing the RNA transcript to detach from the polymerase. The main enzyme involved is RNA polymerase, which synthesizes RNA using a DNA template.