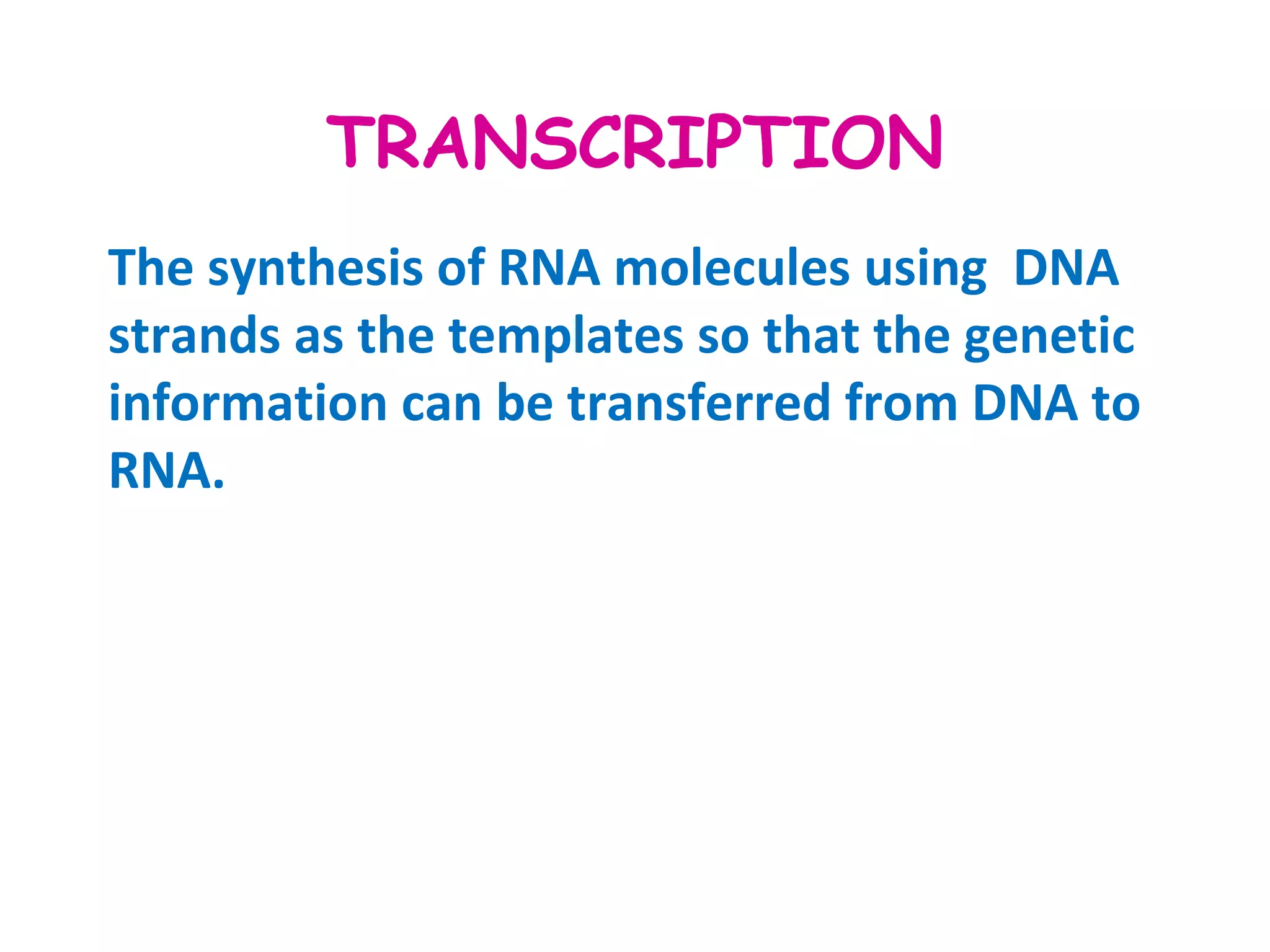
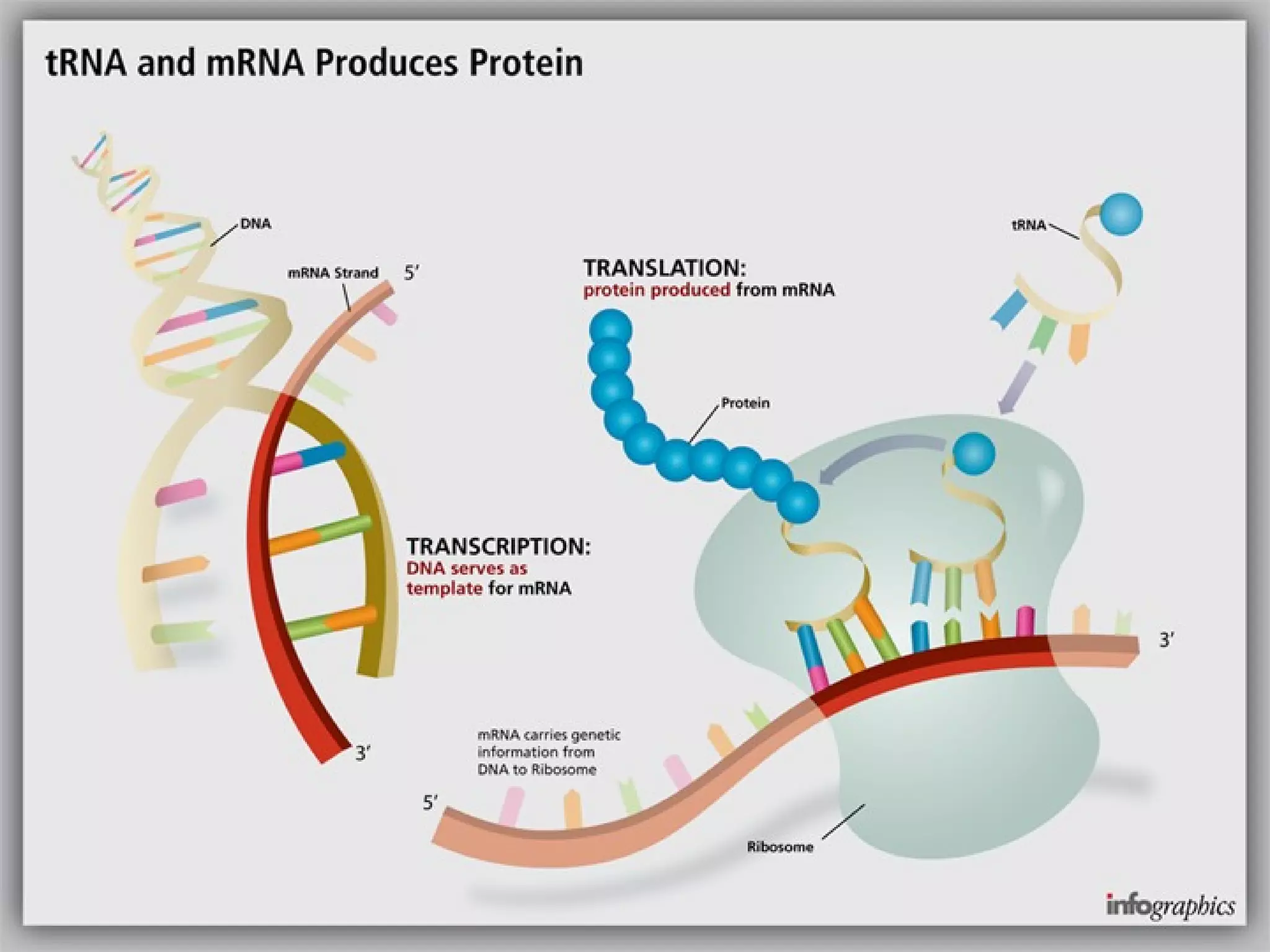
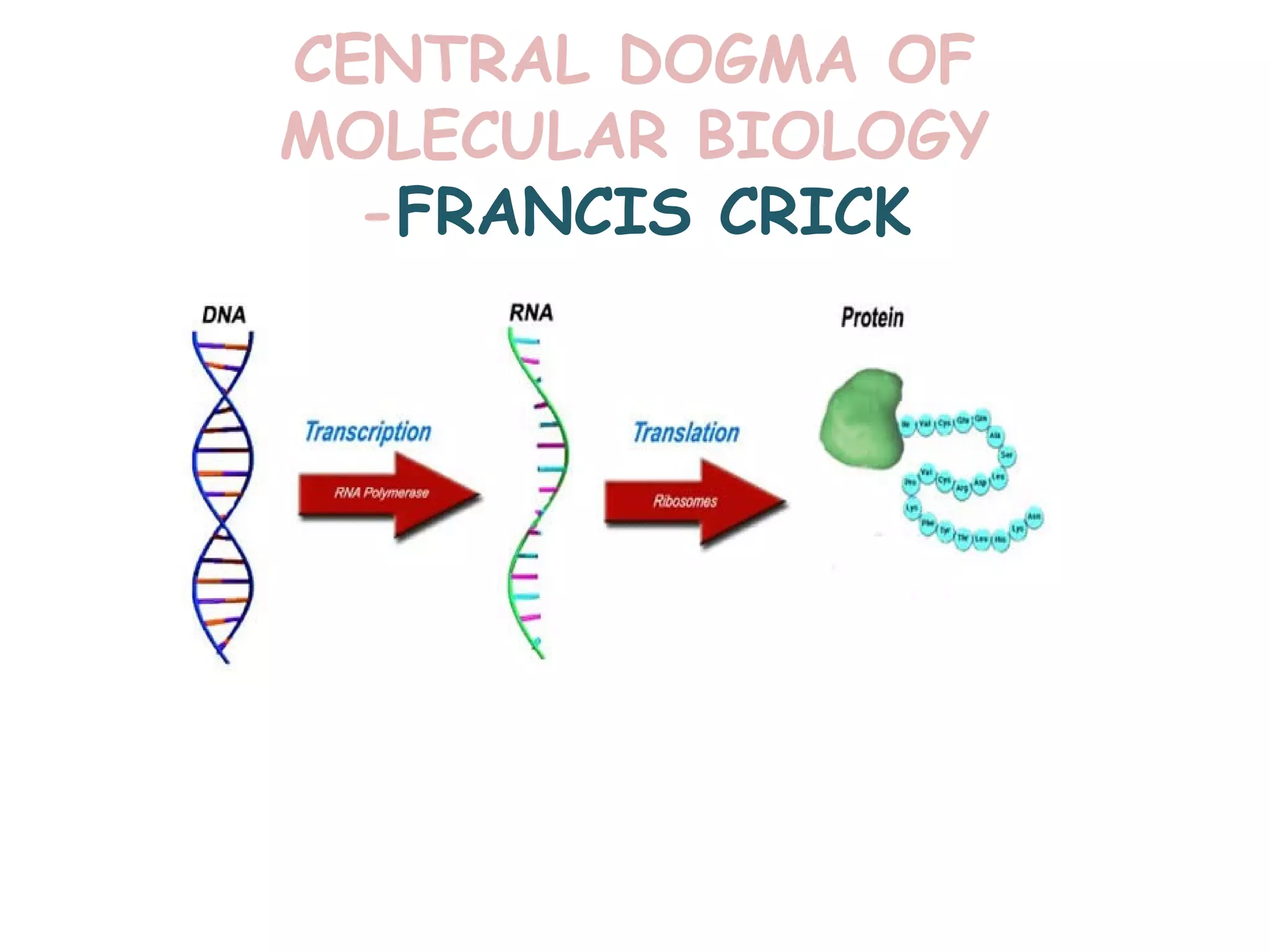
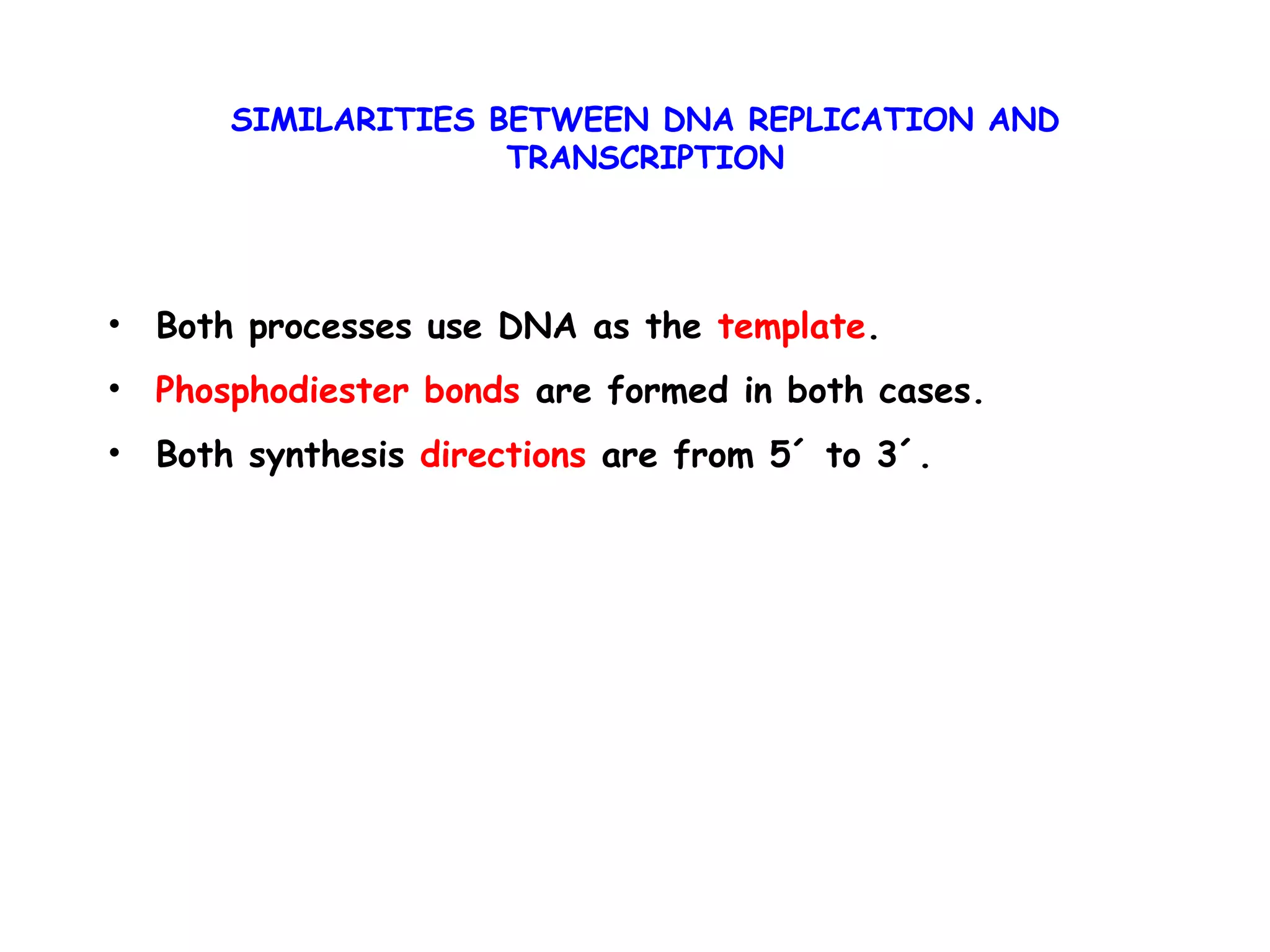
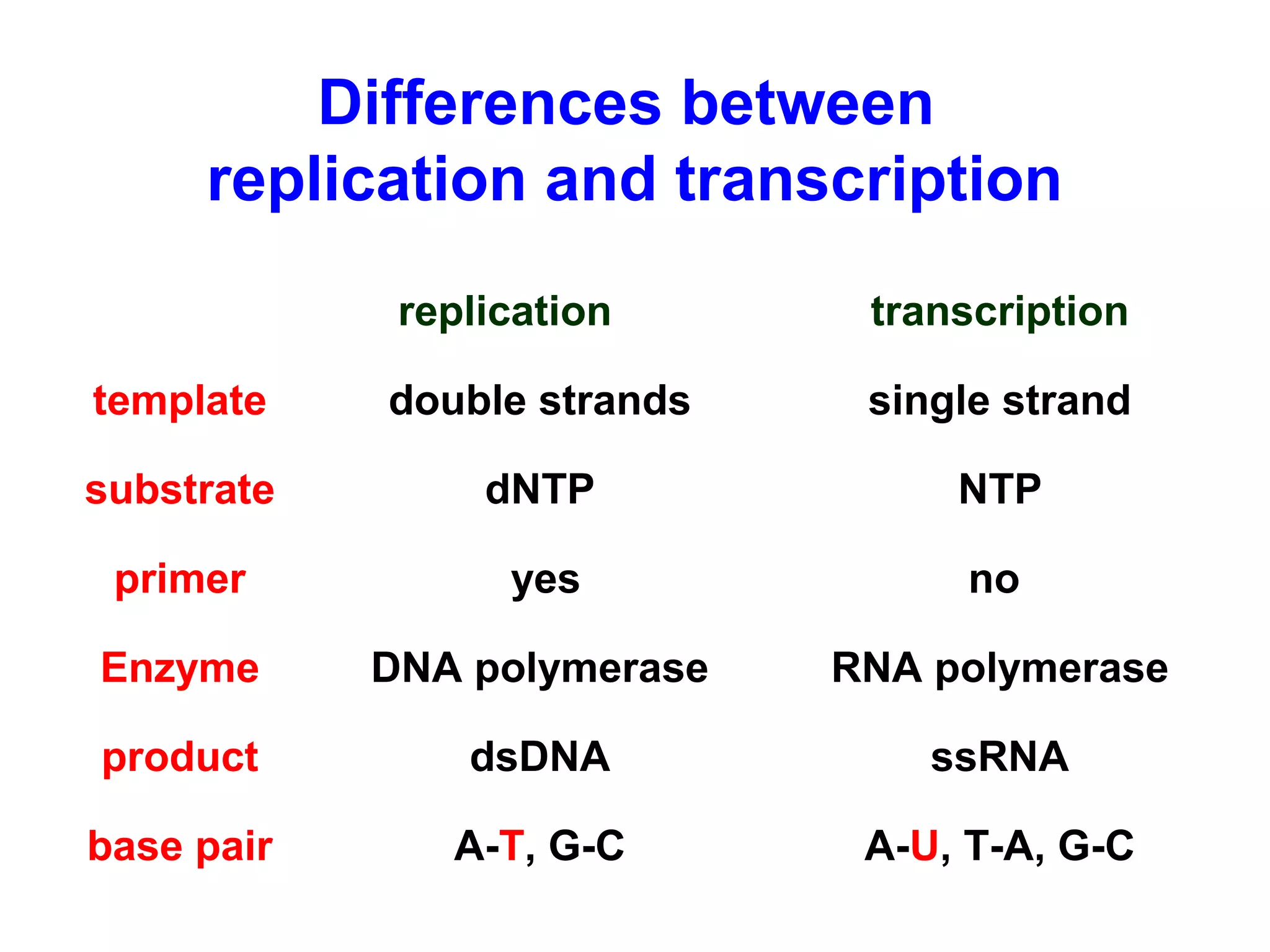
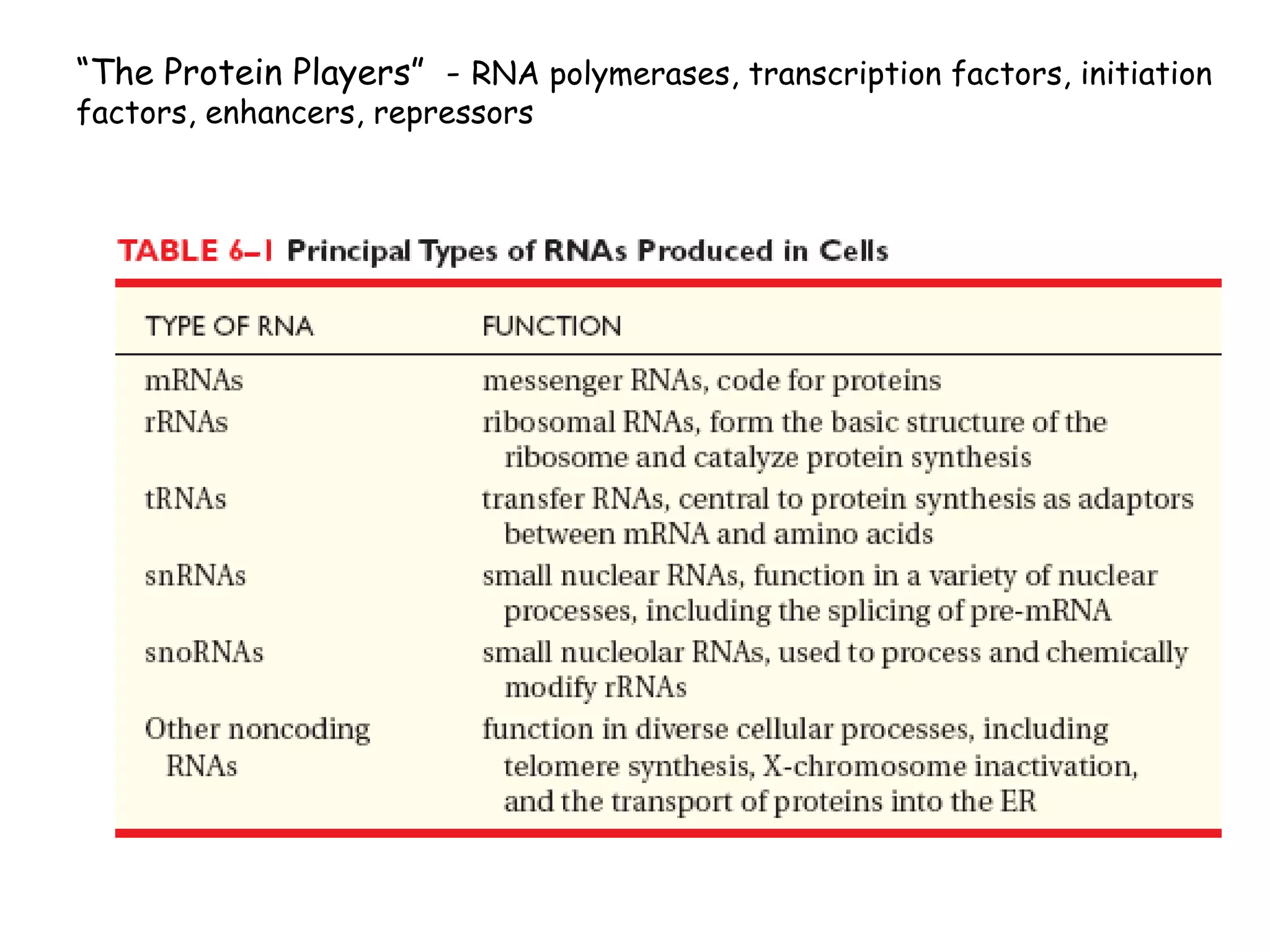
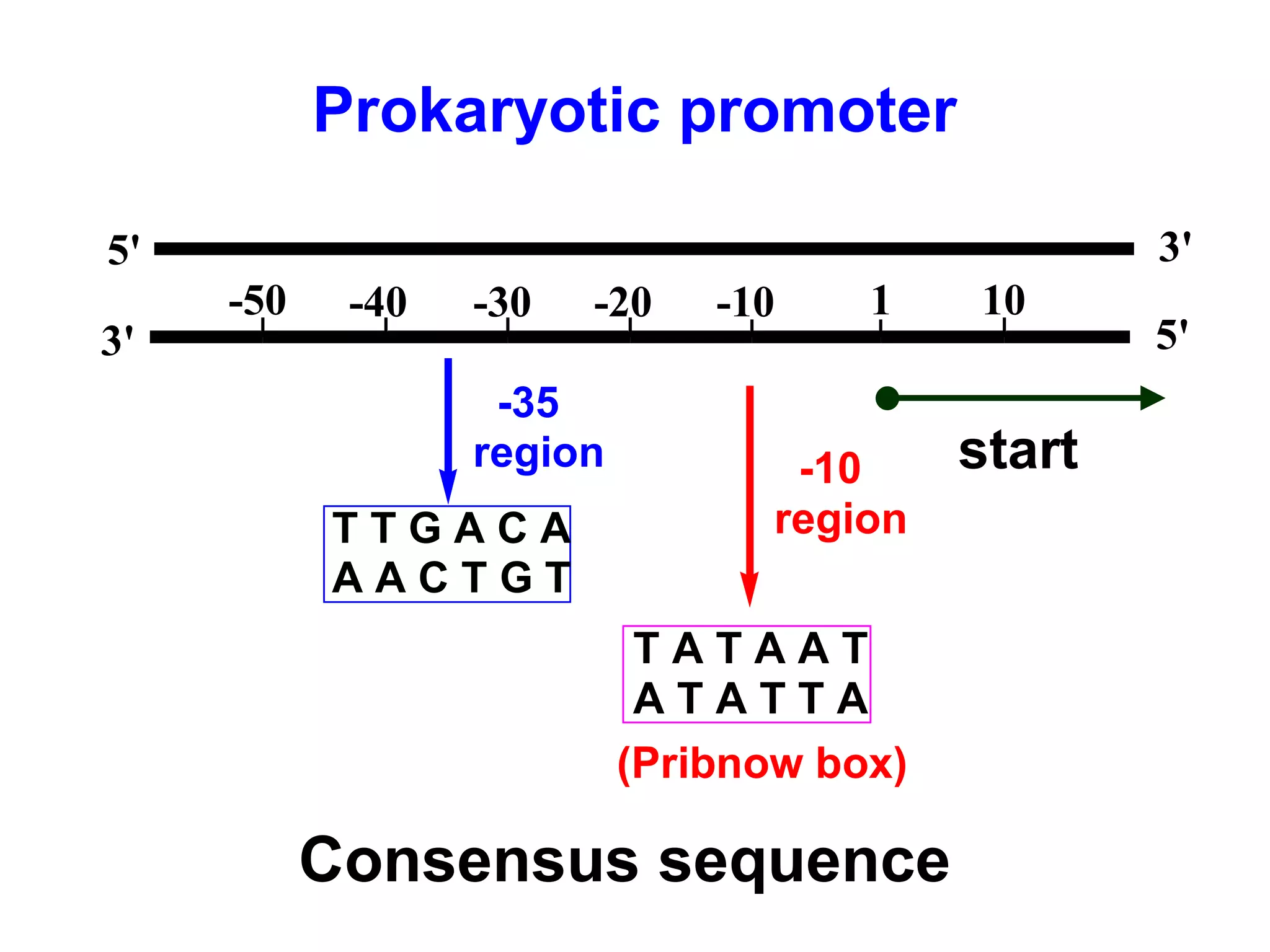
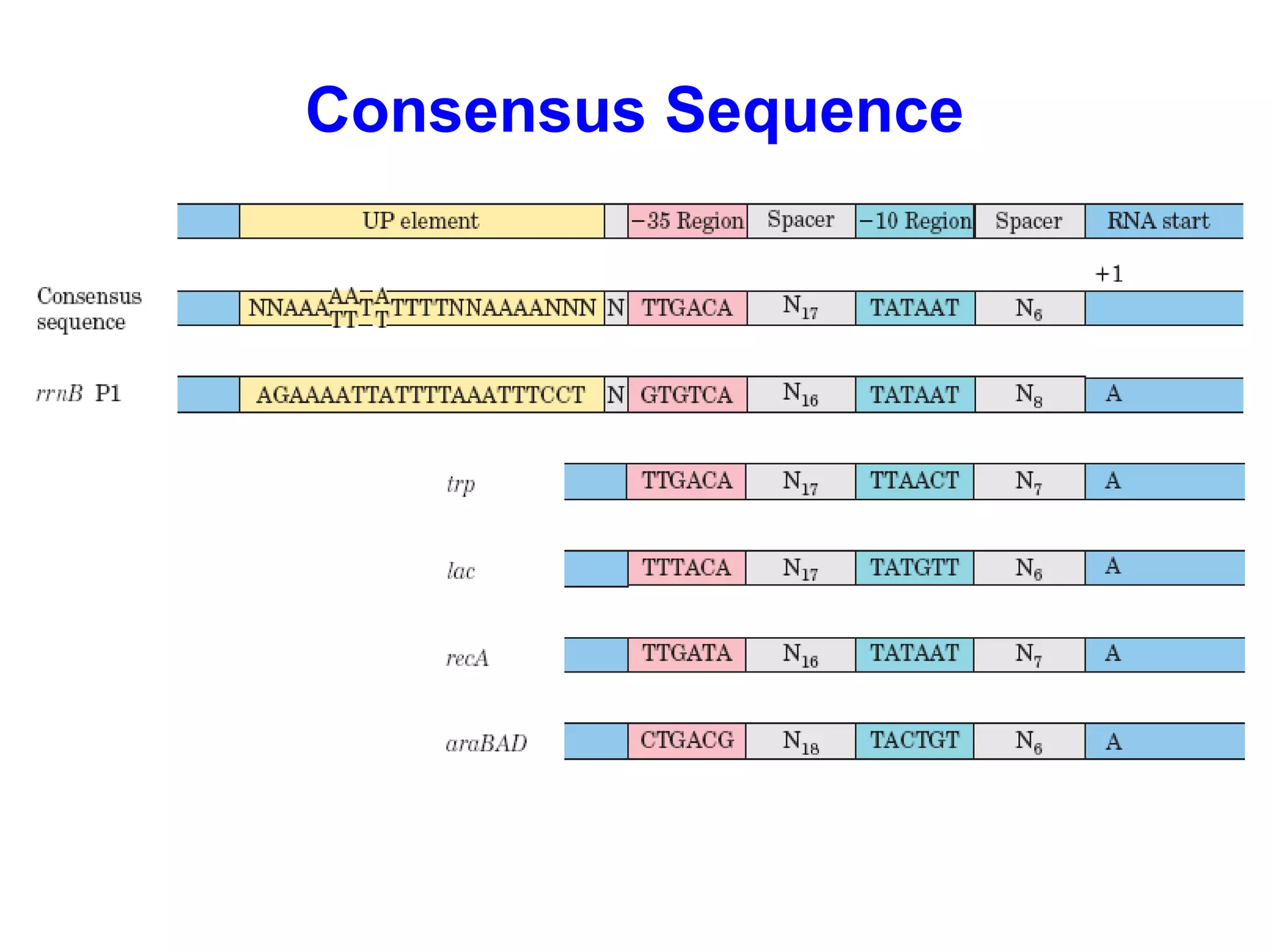
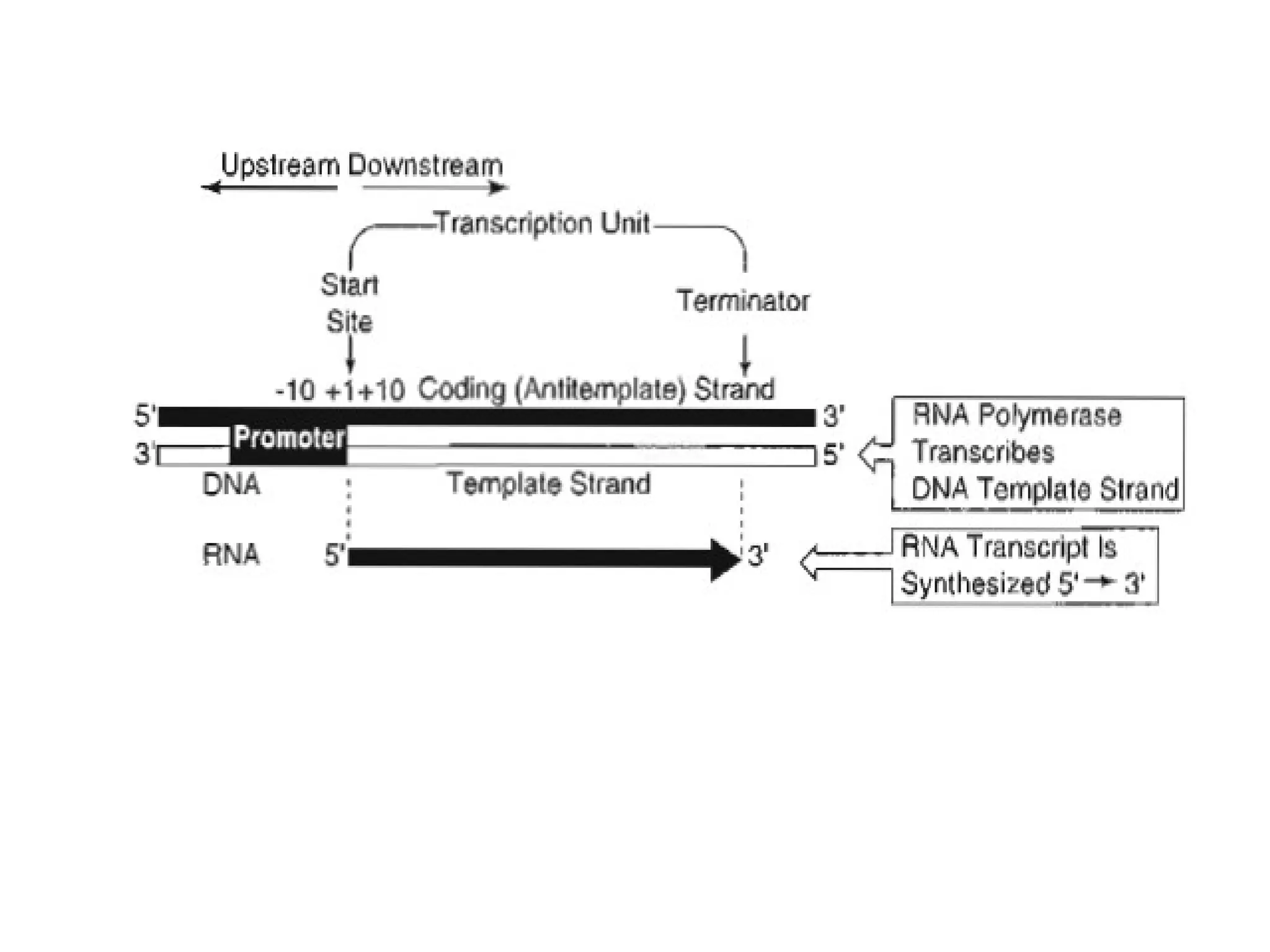
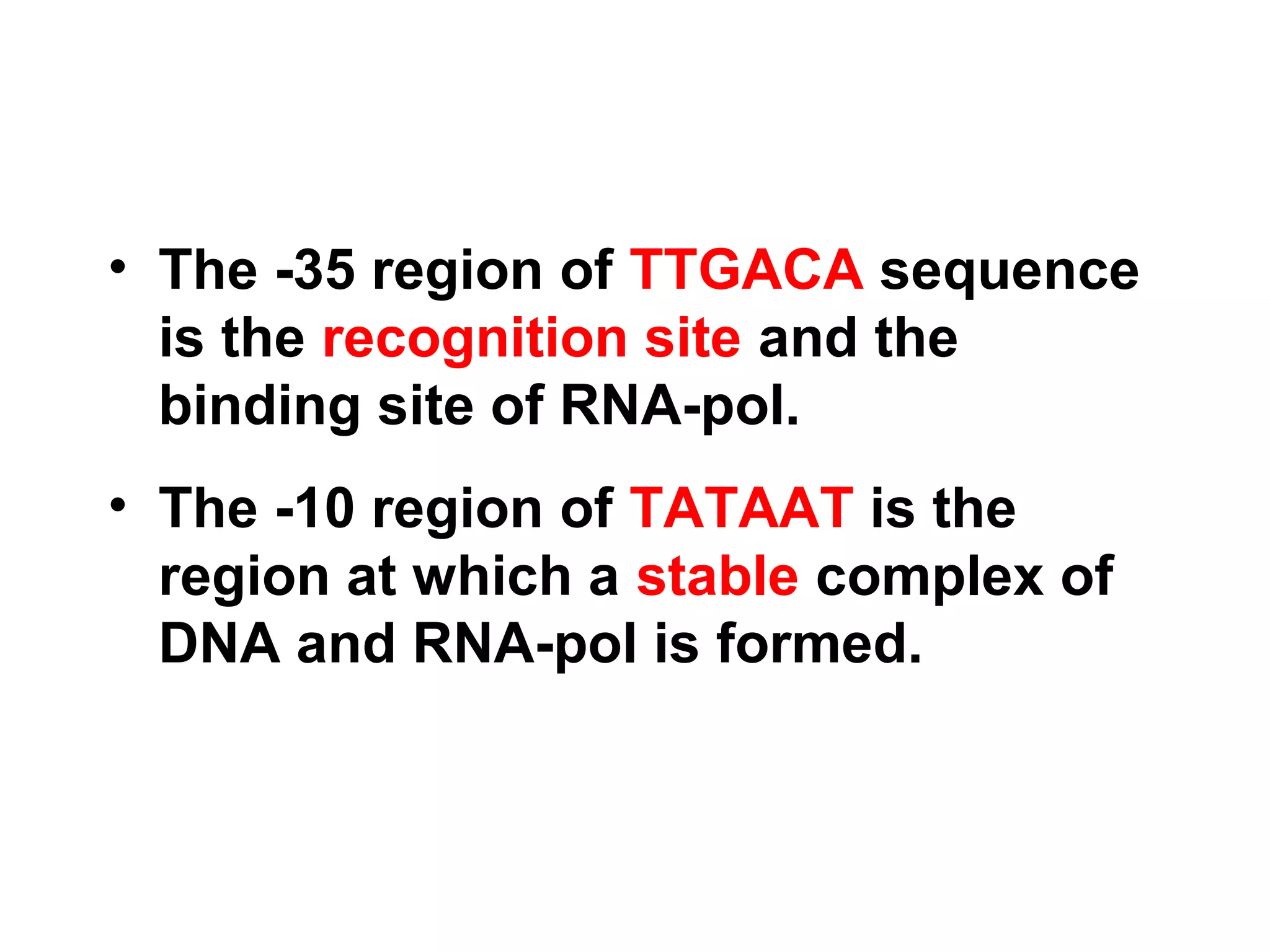
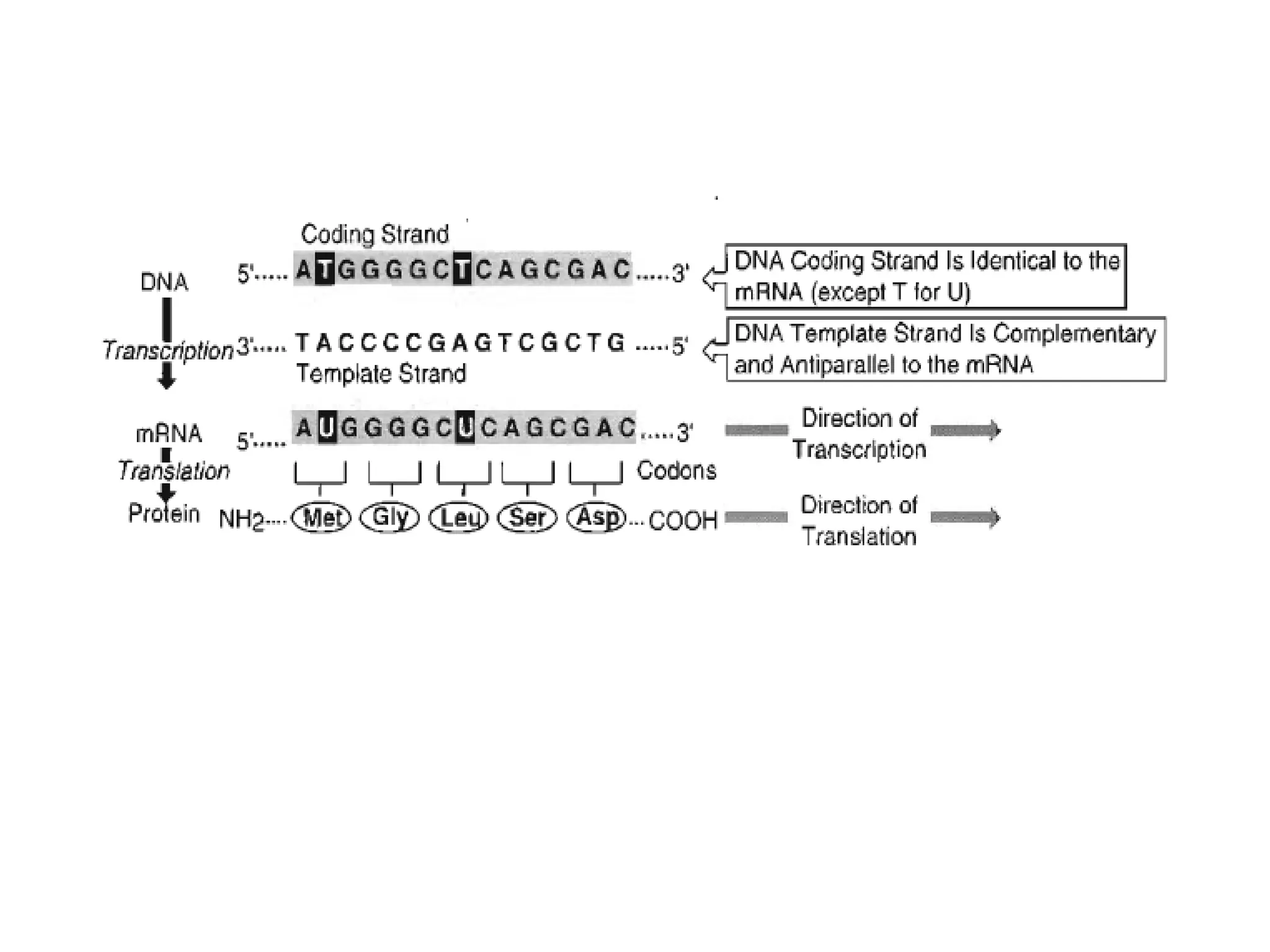
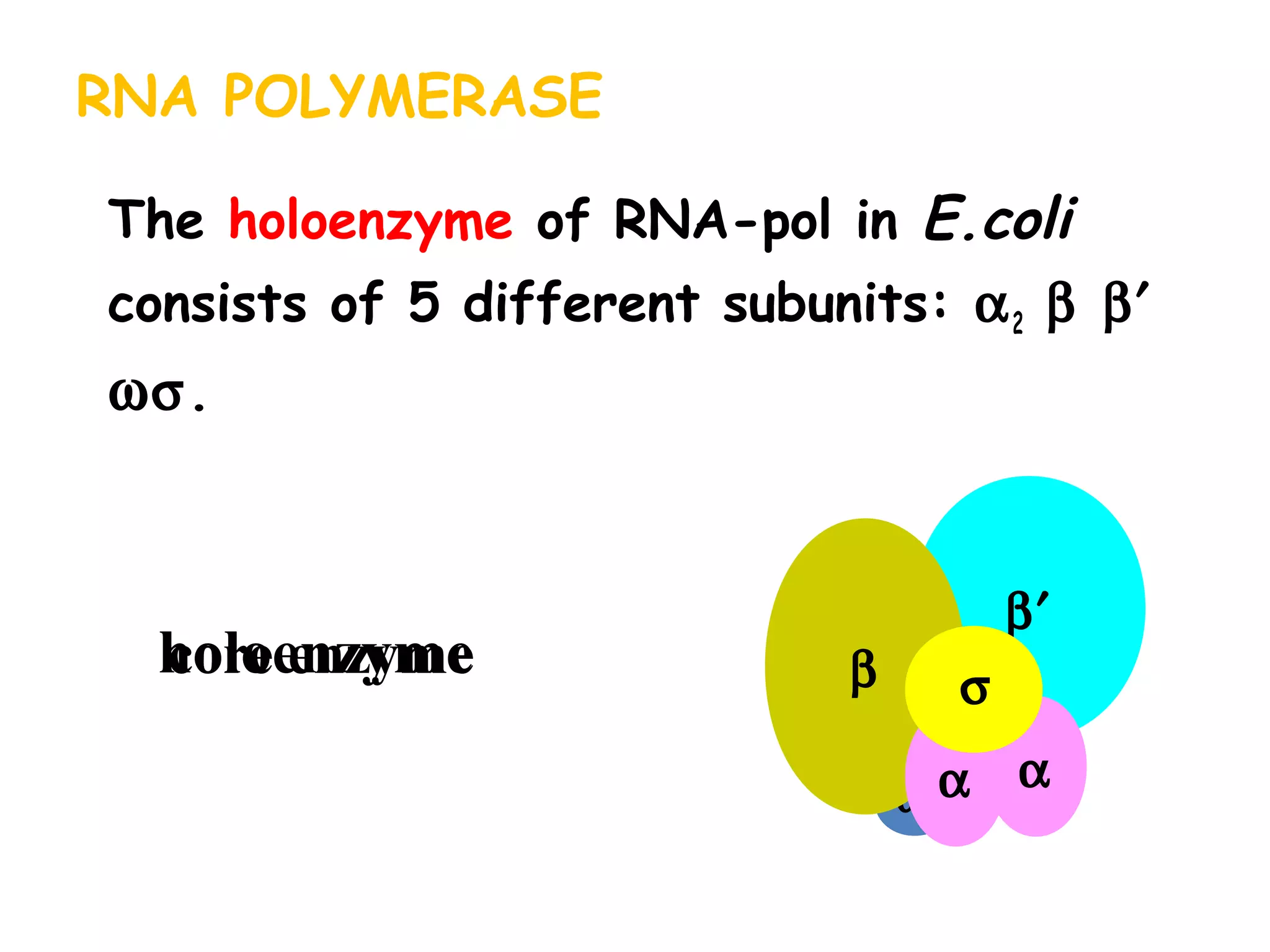
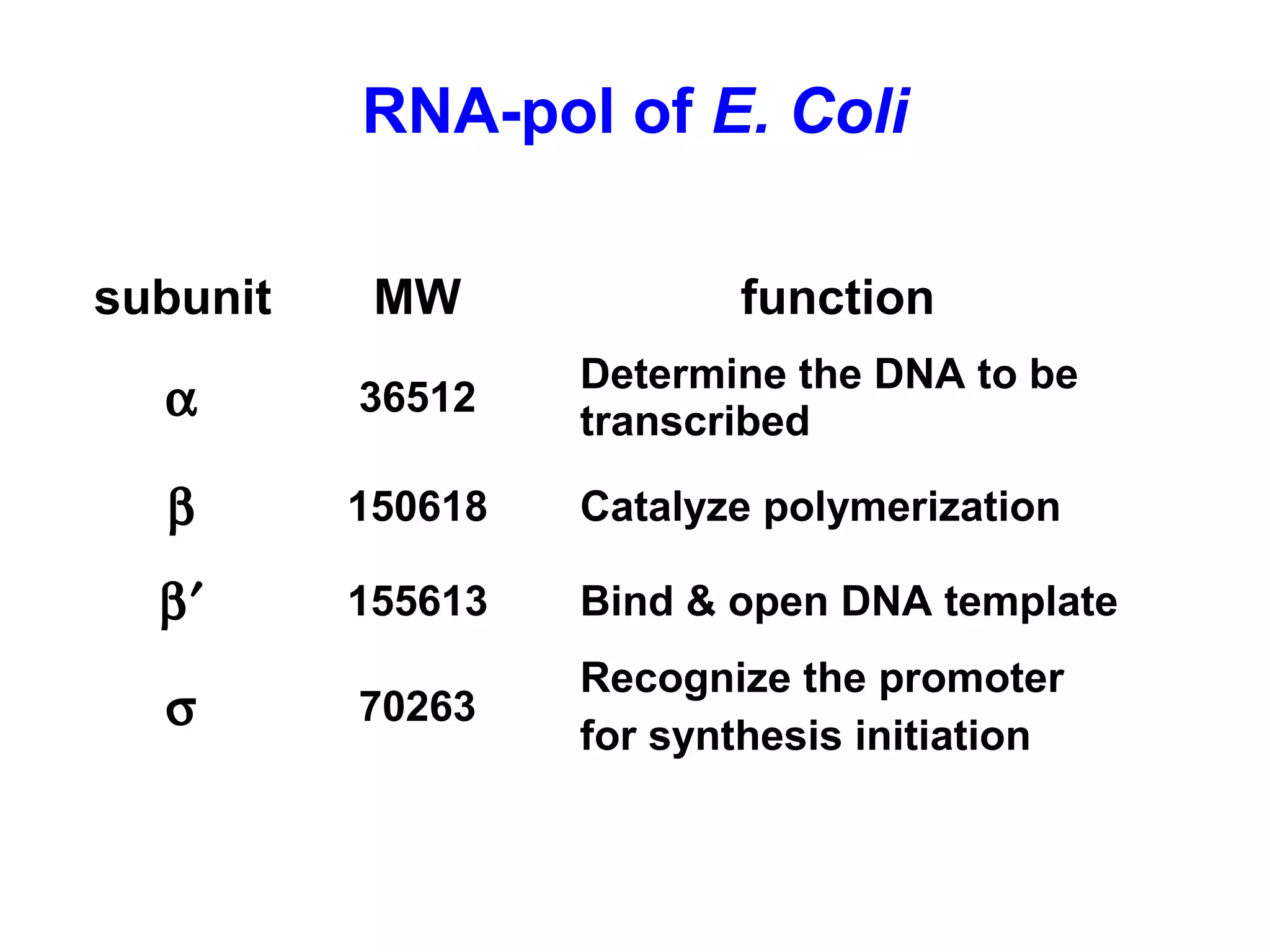
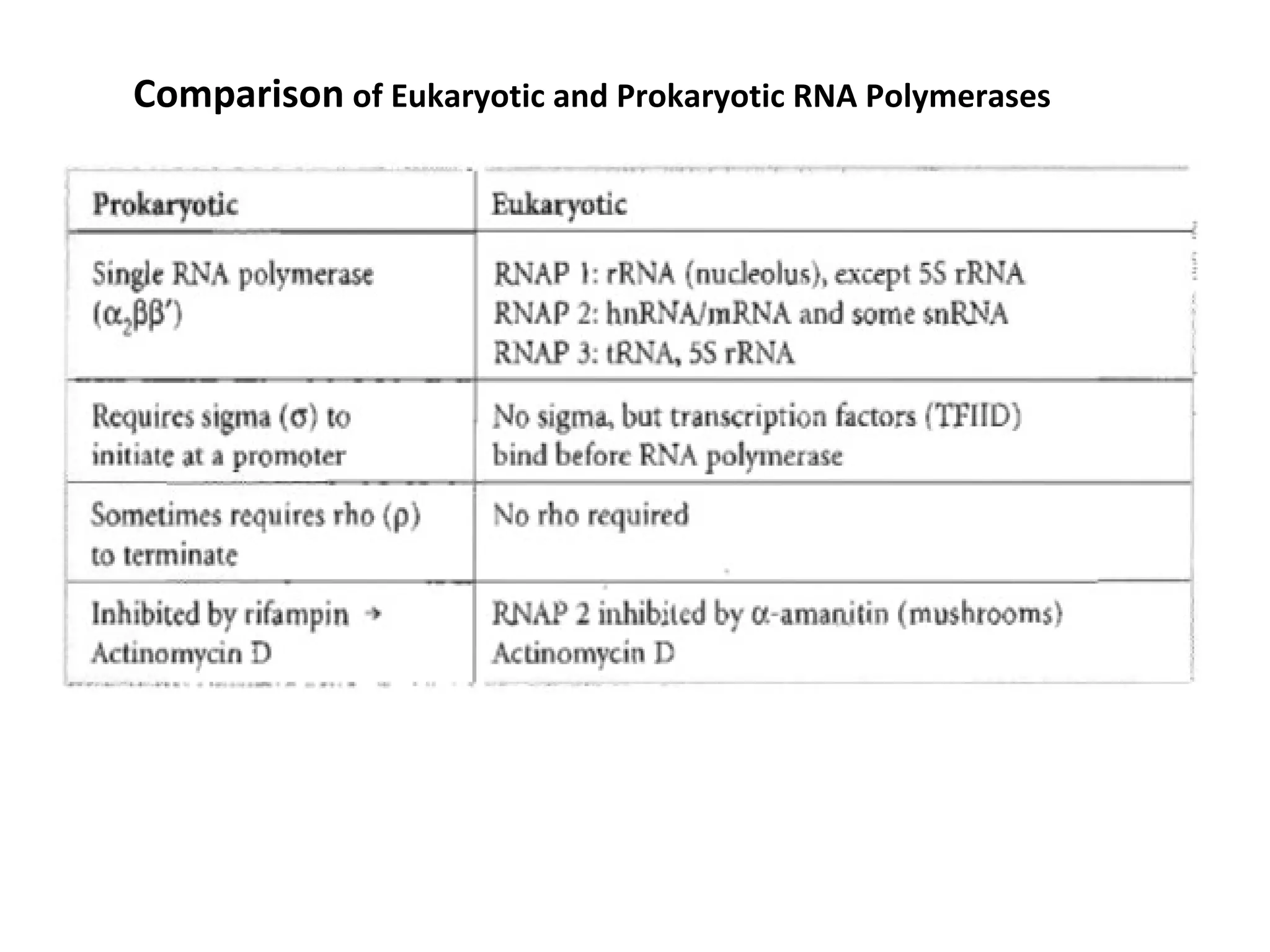
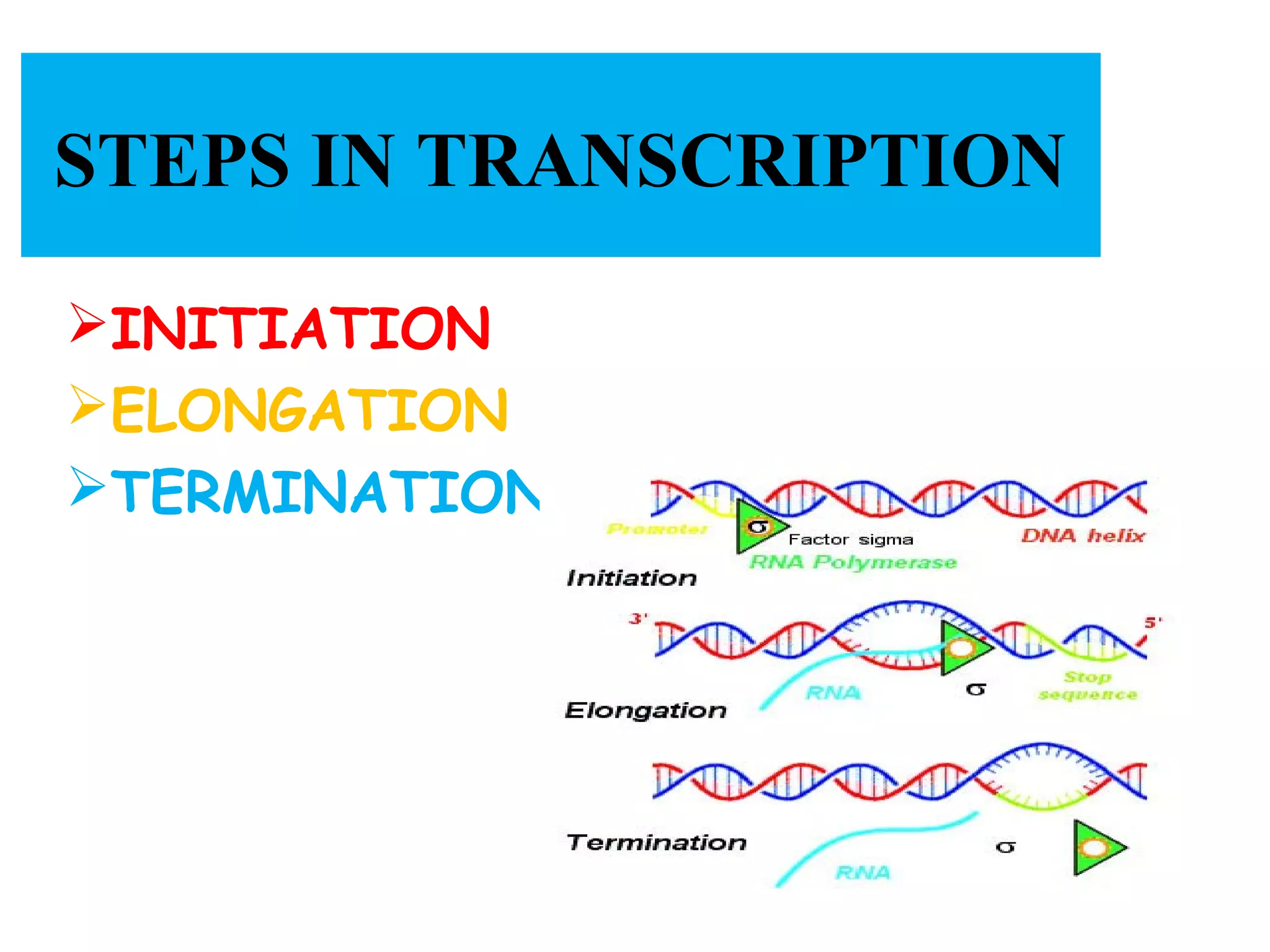
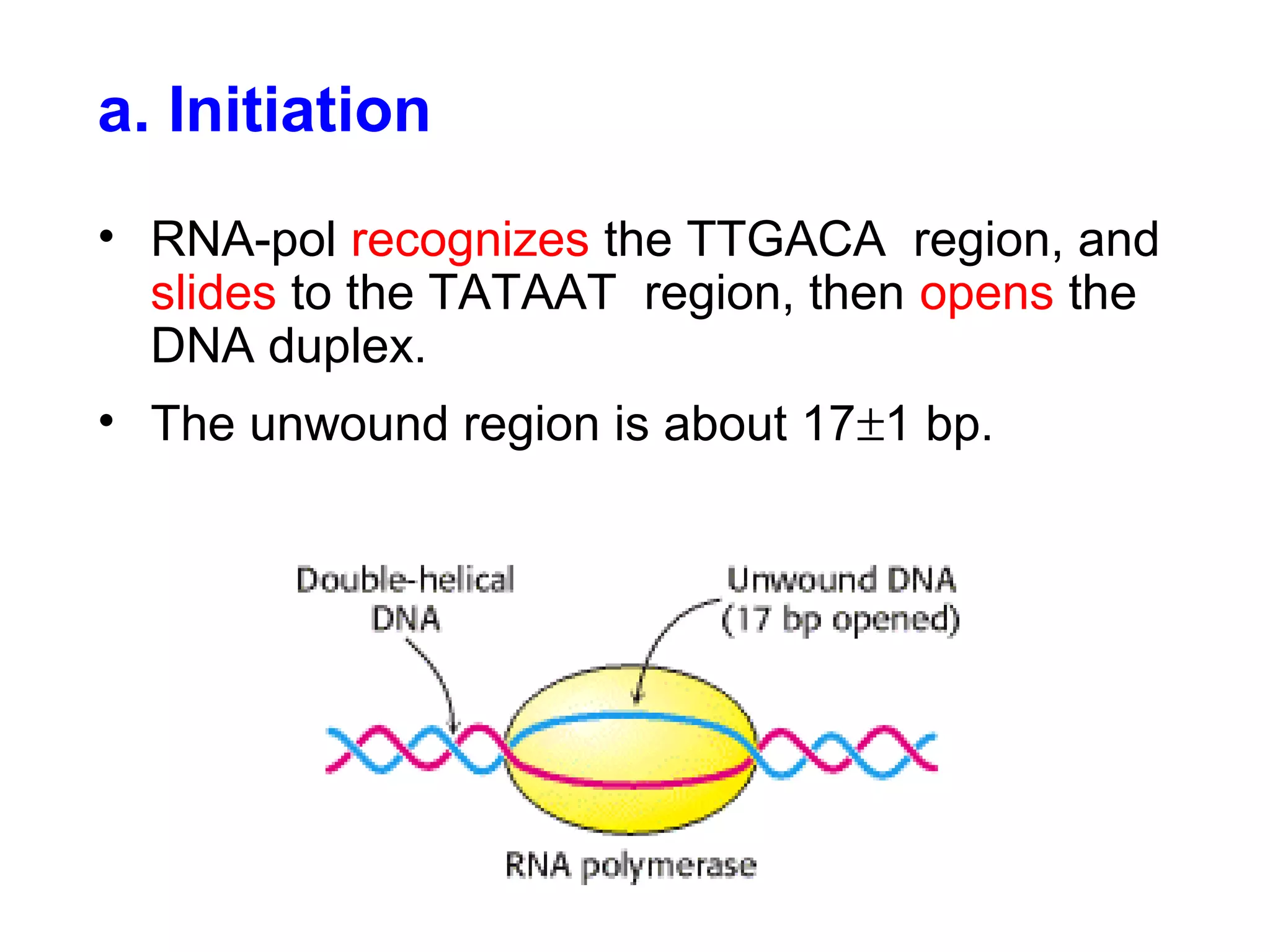
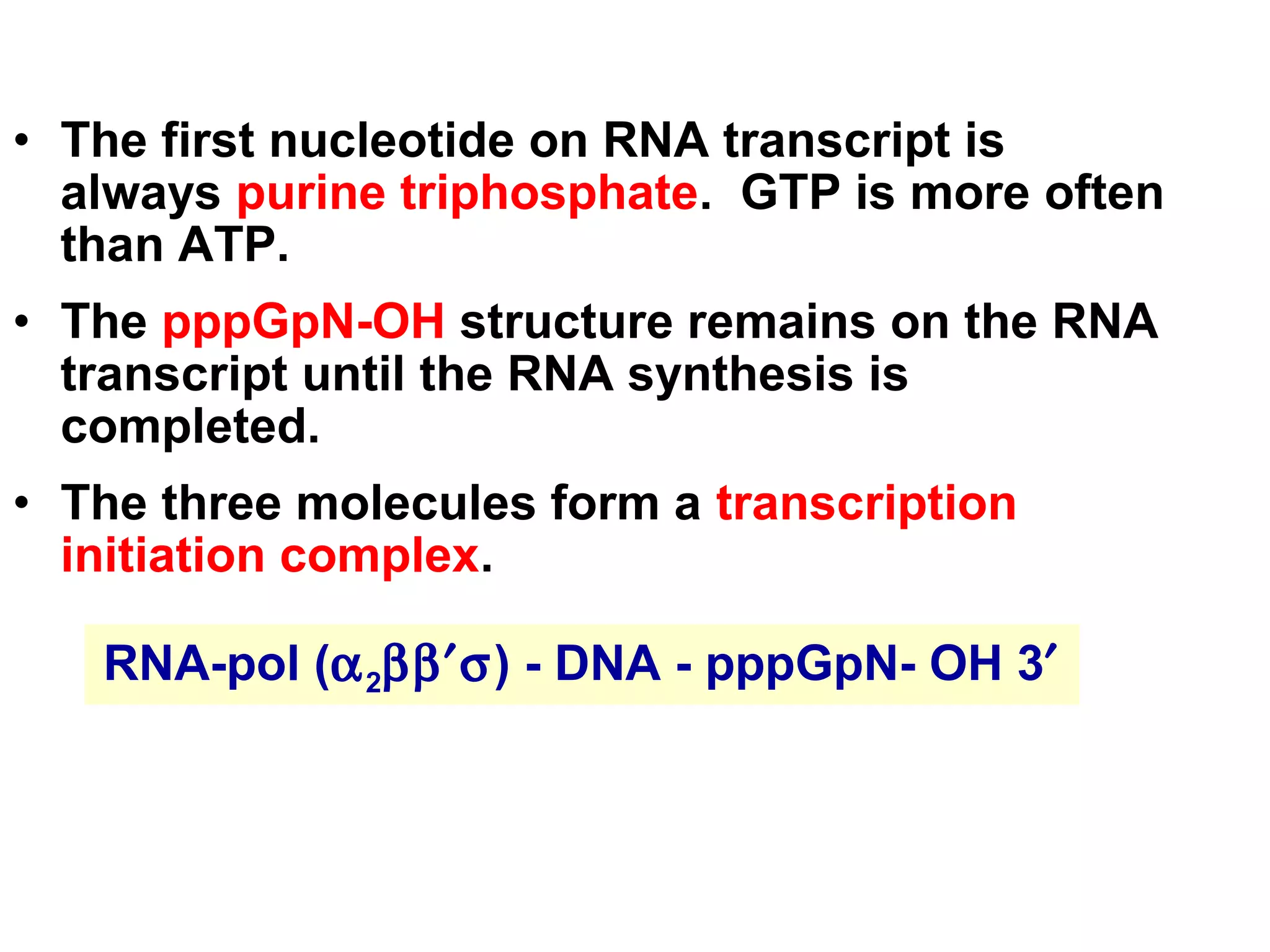
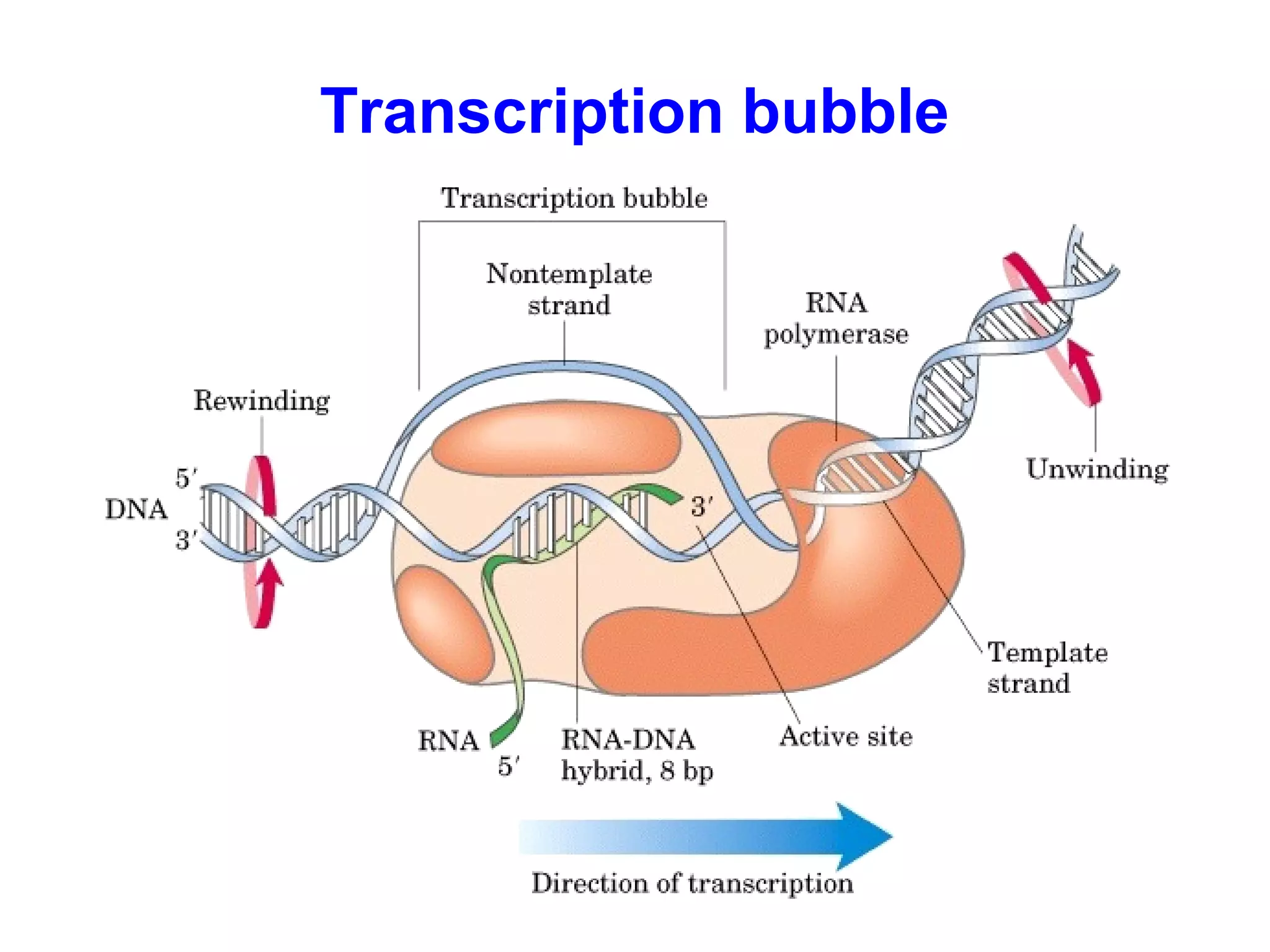
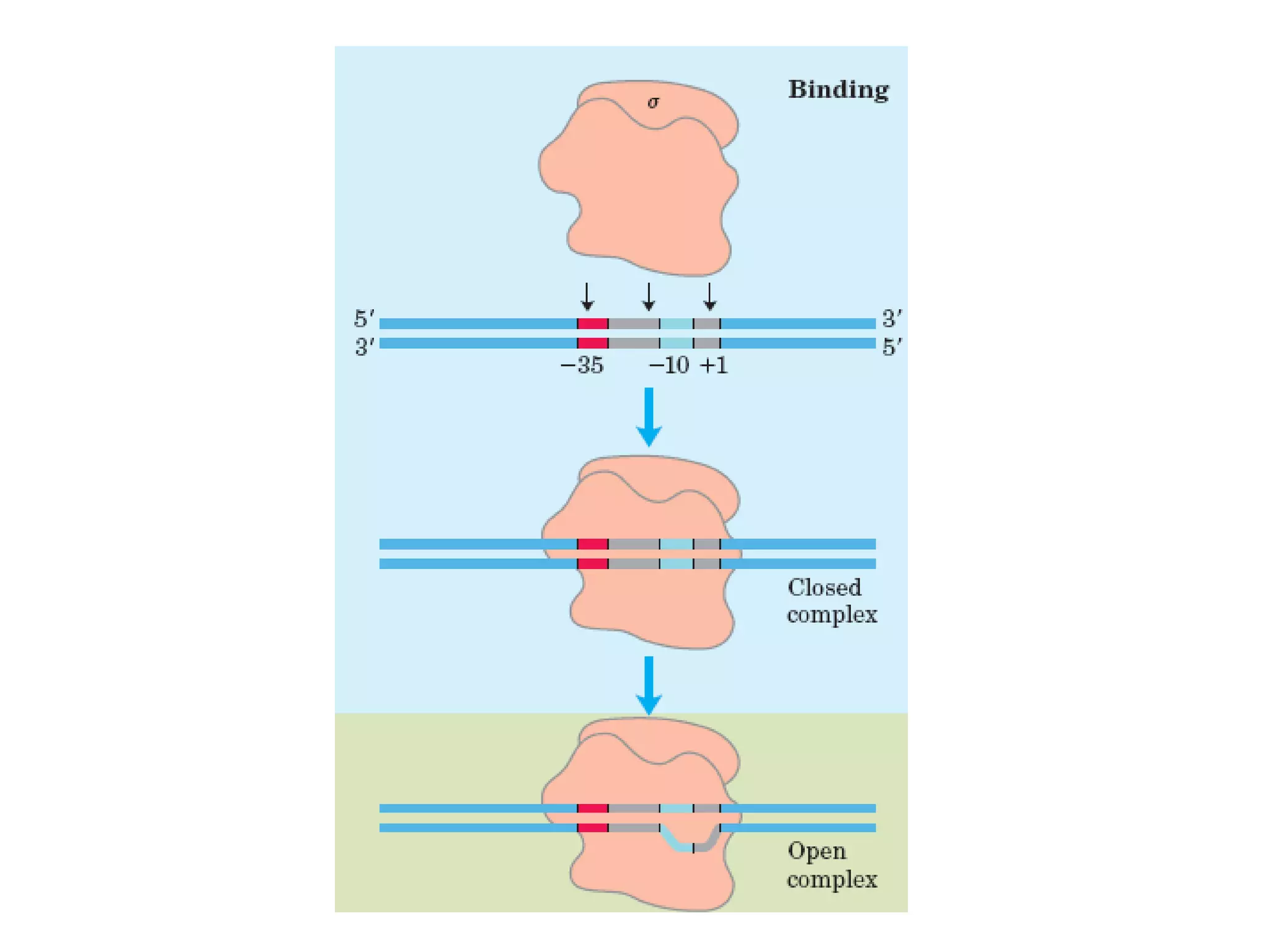
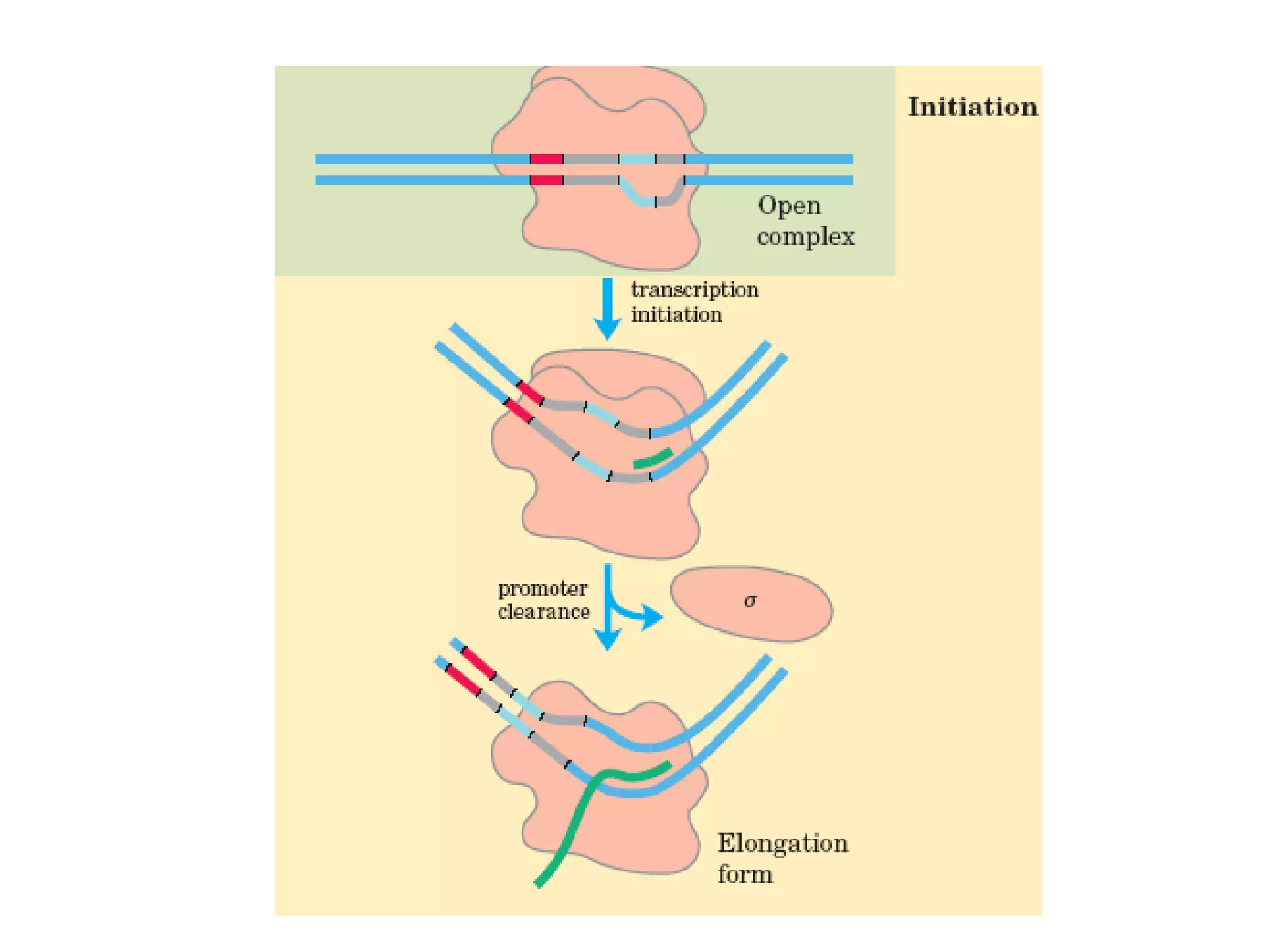
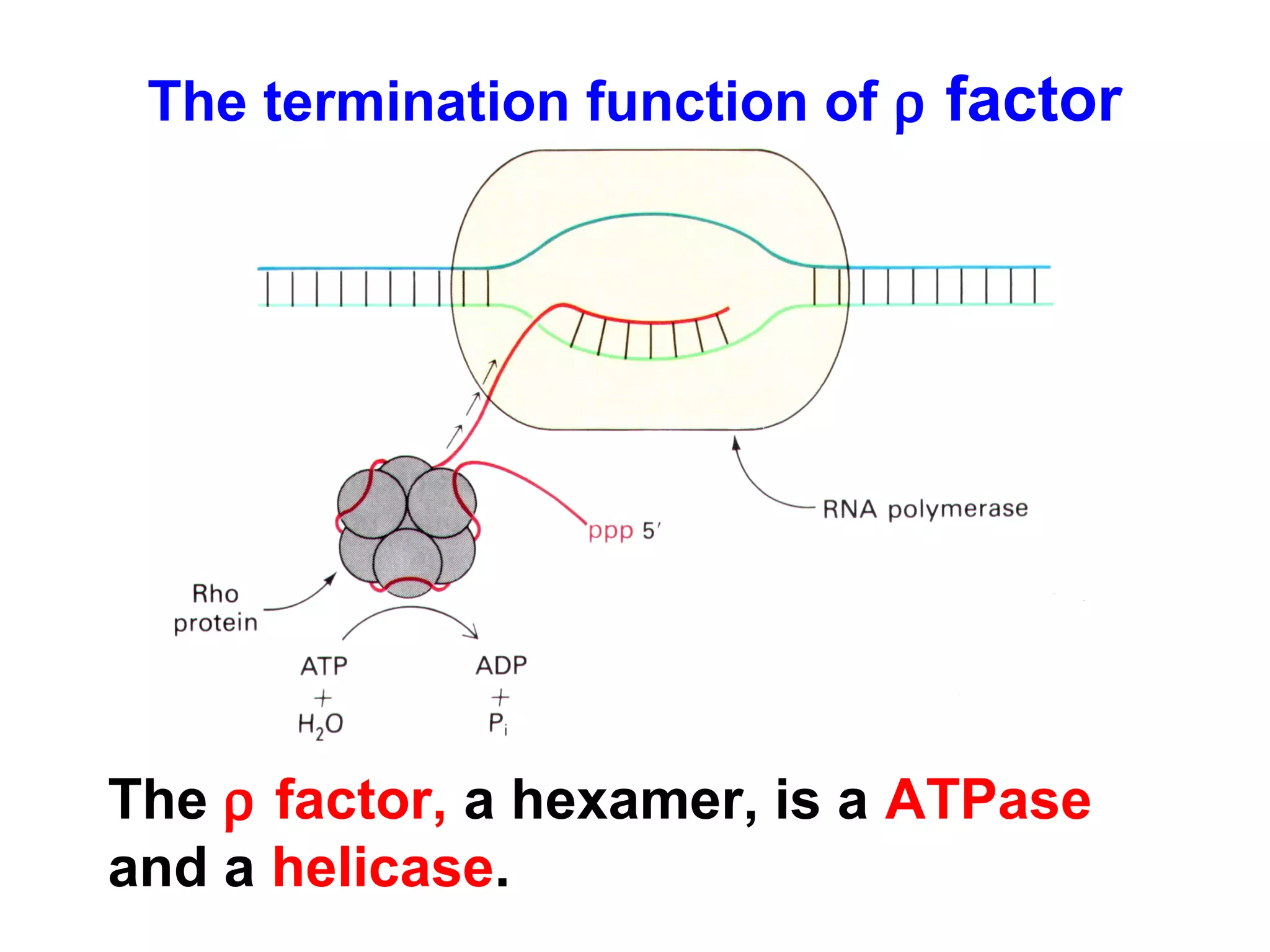
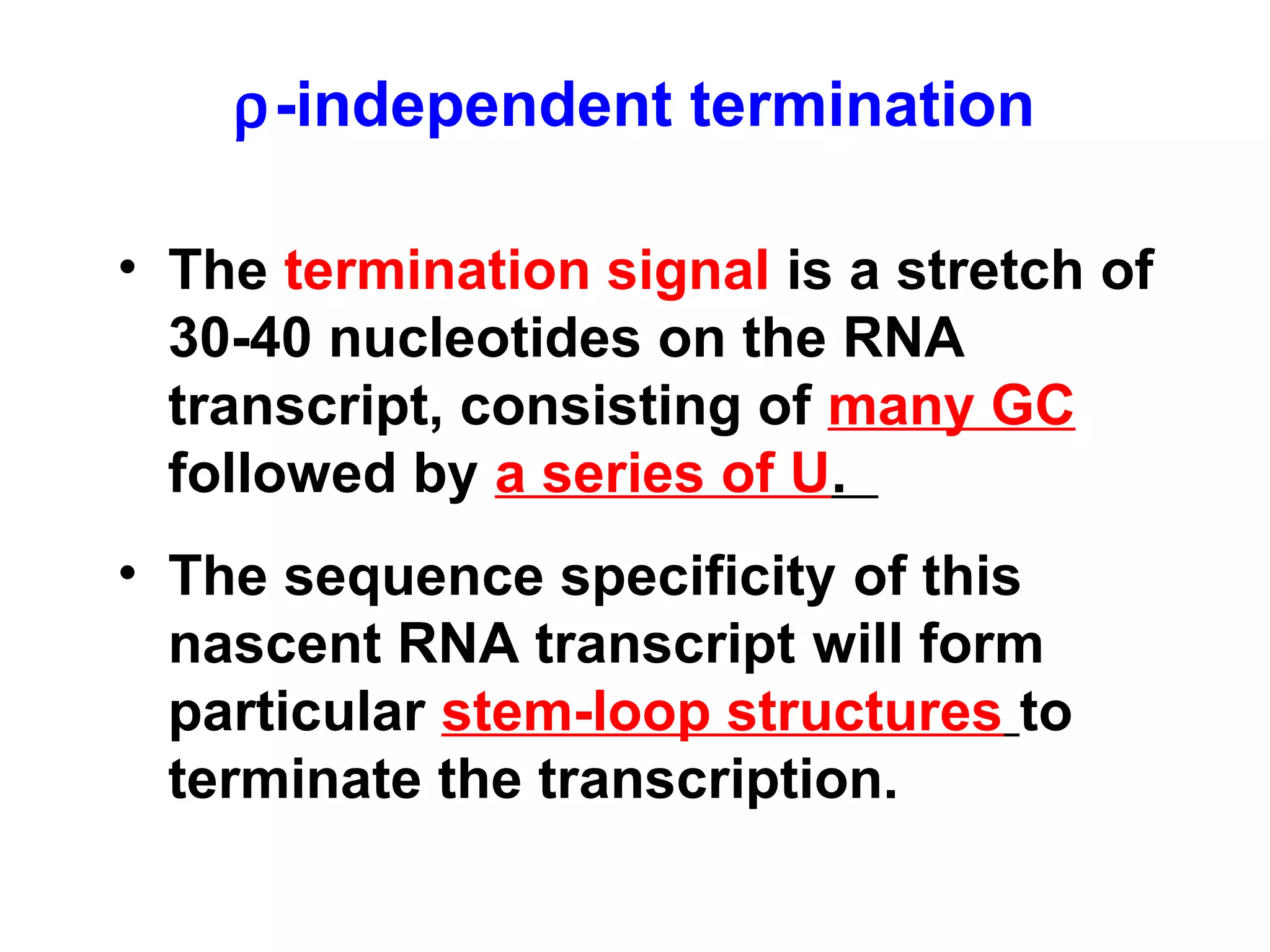
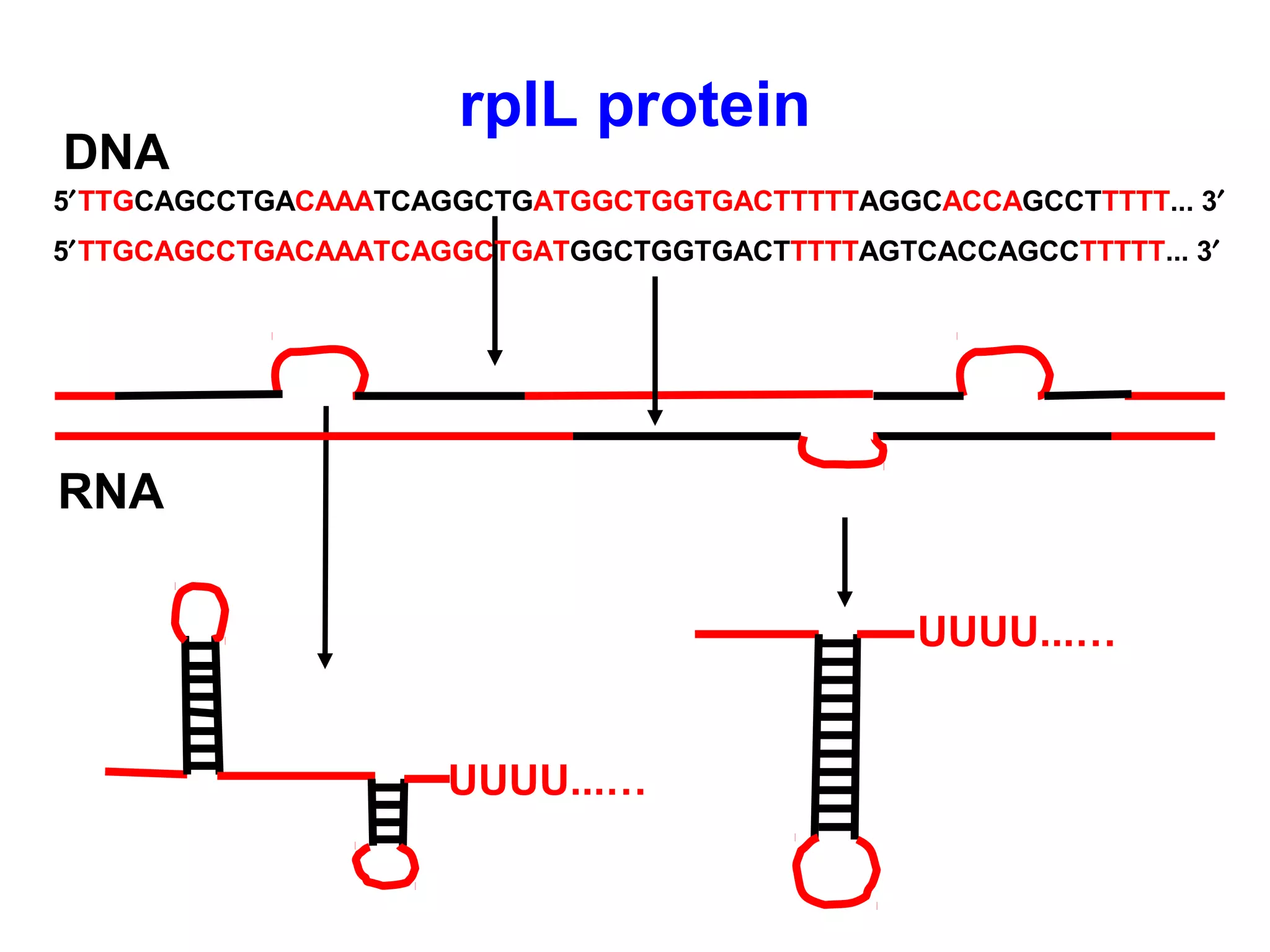
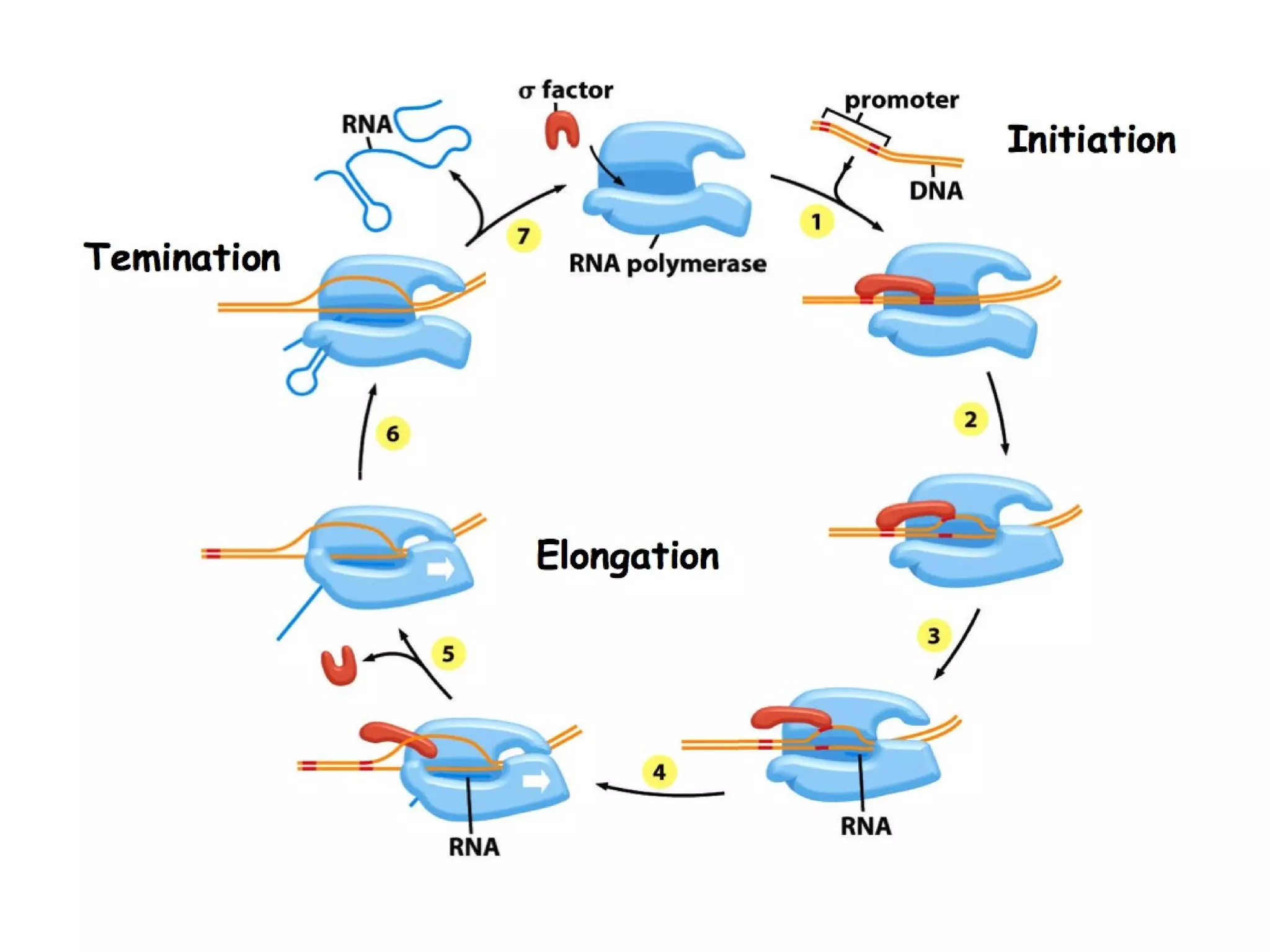
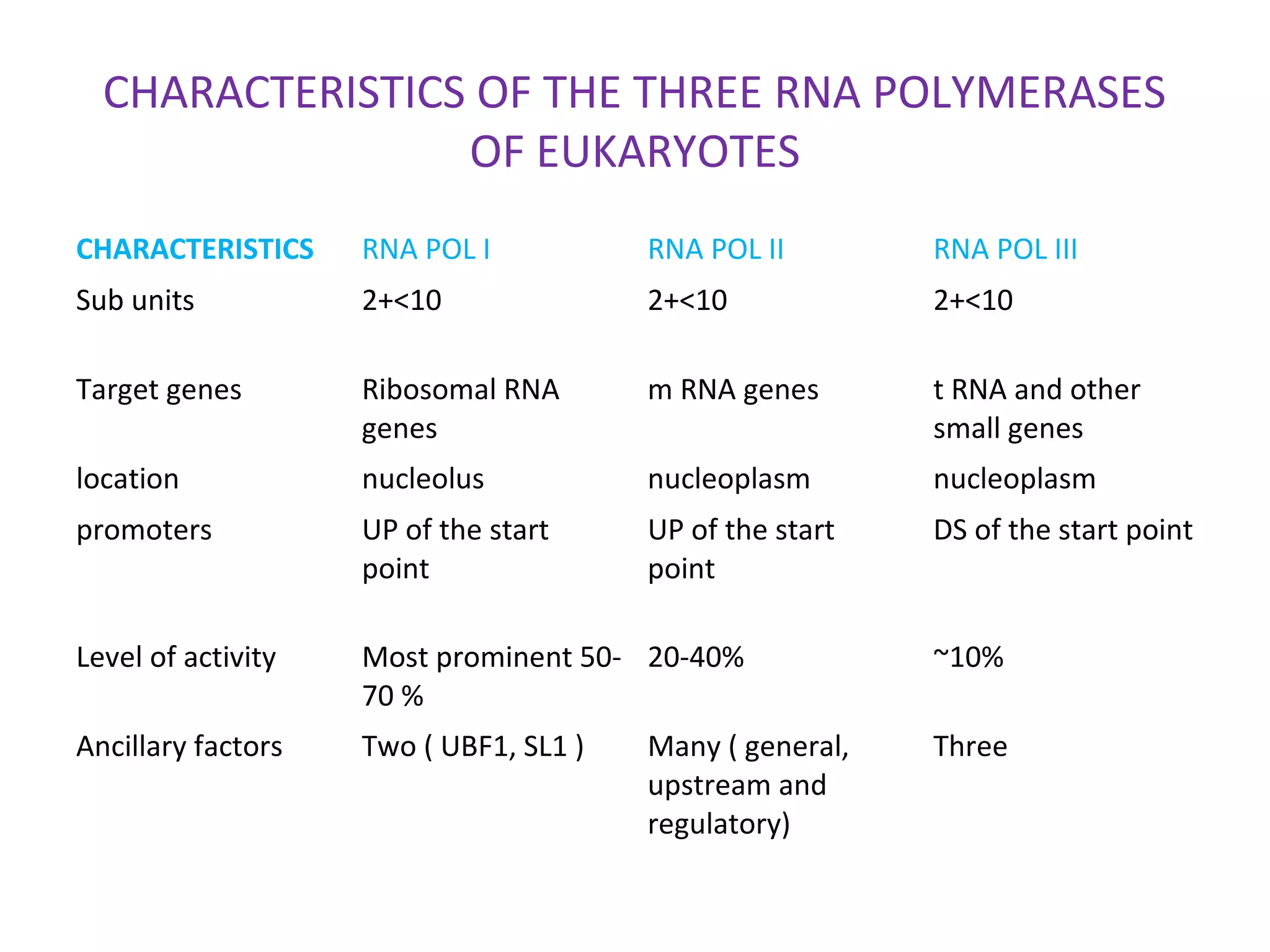
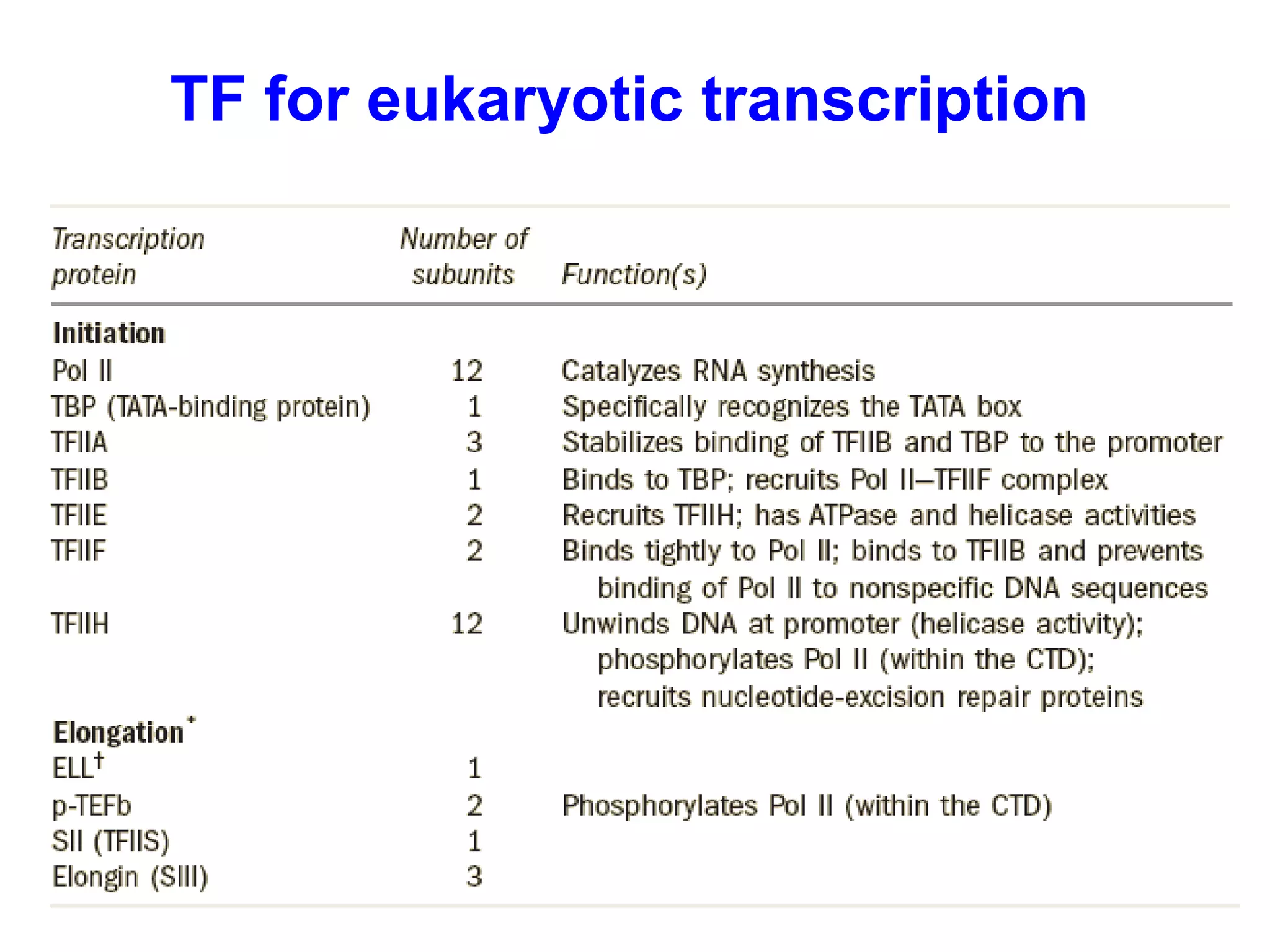
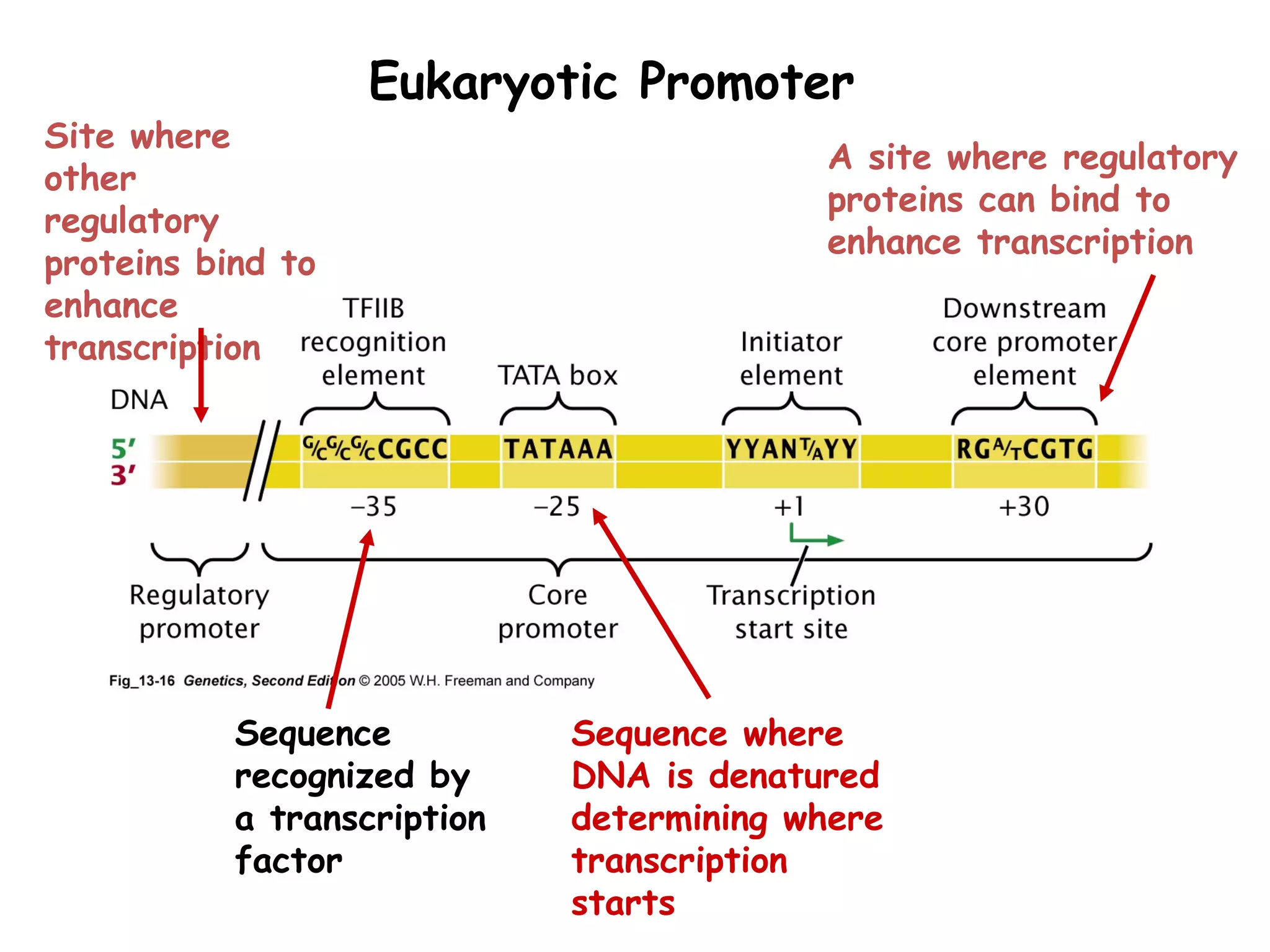
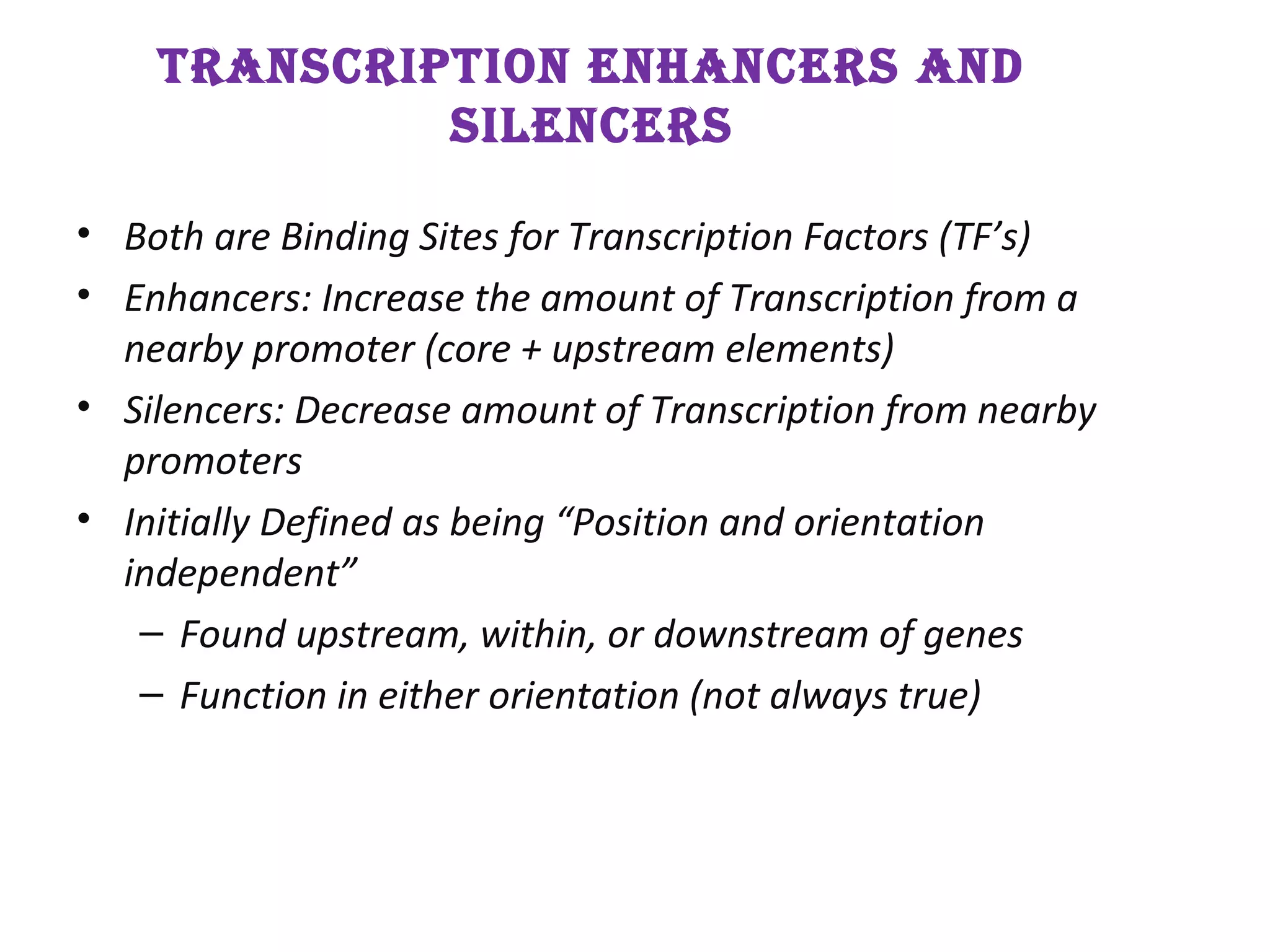
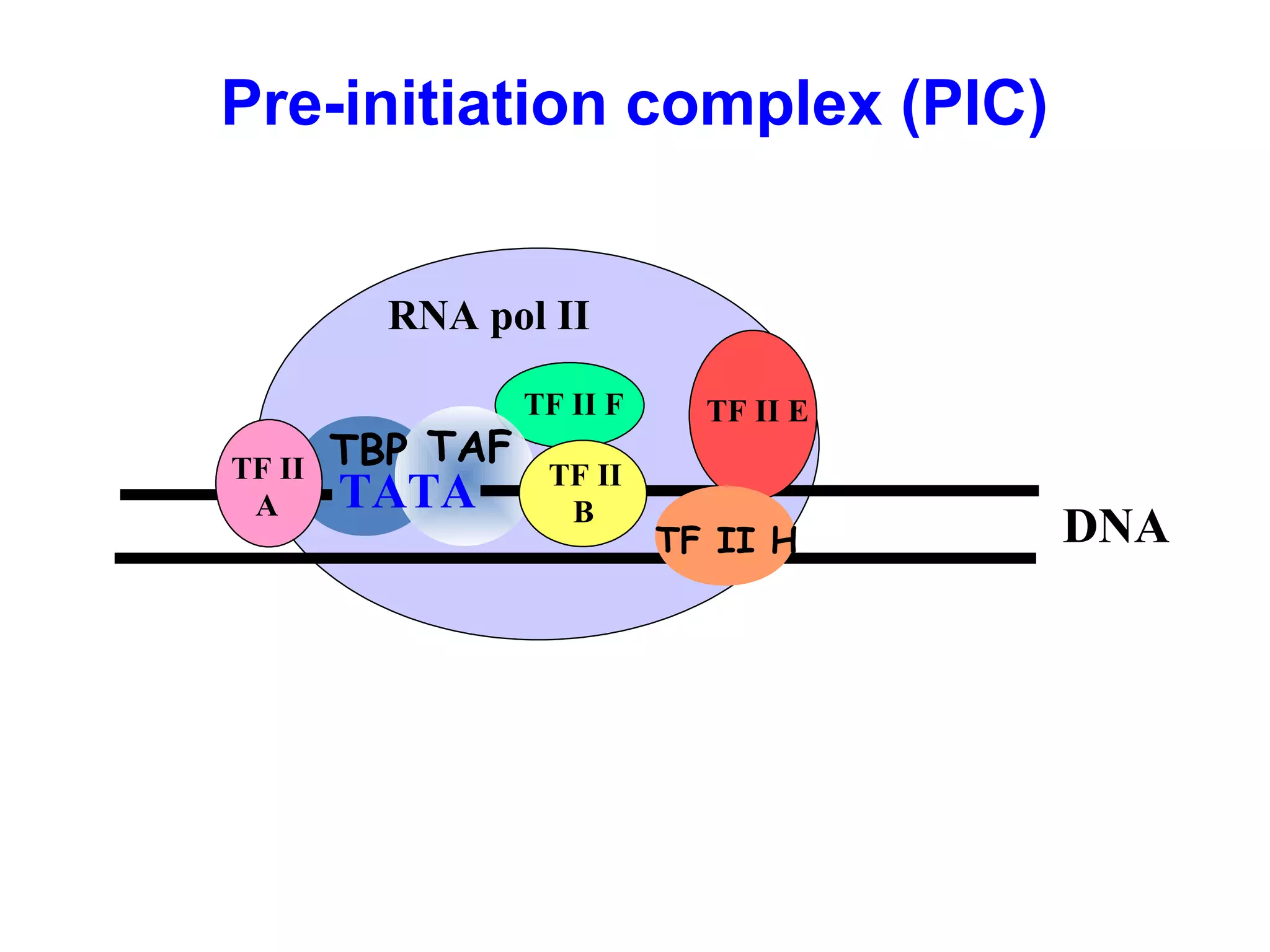
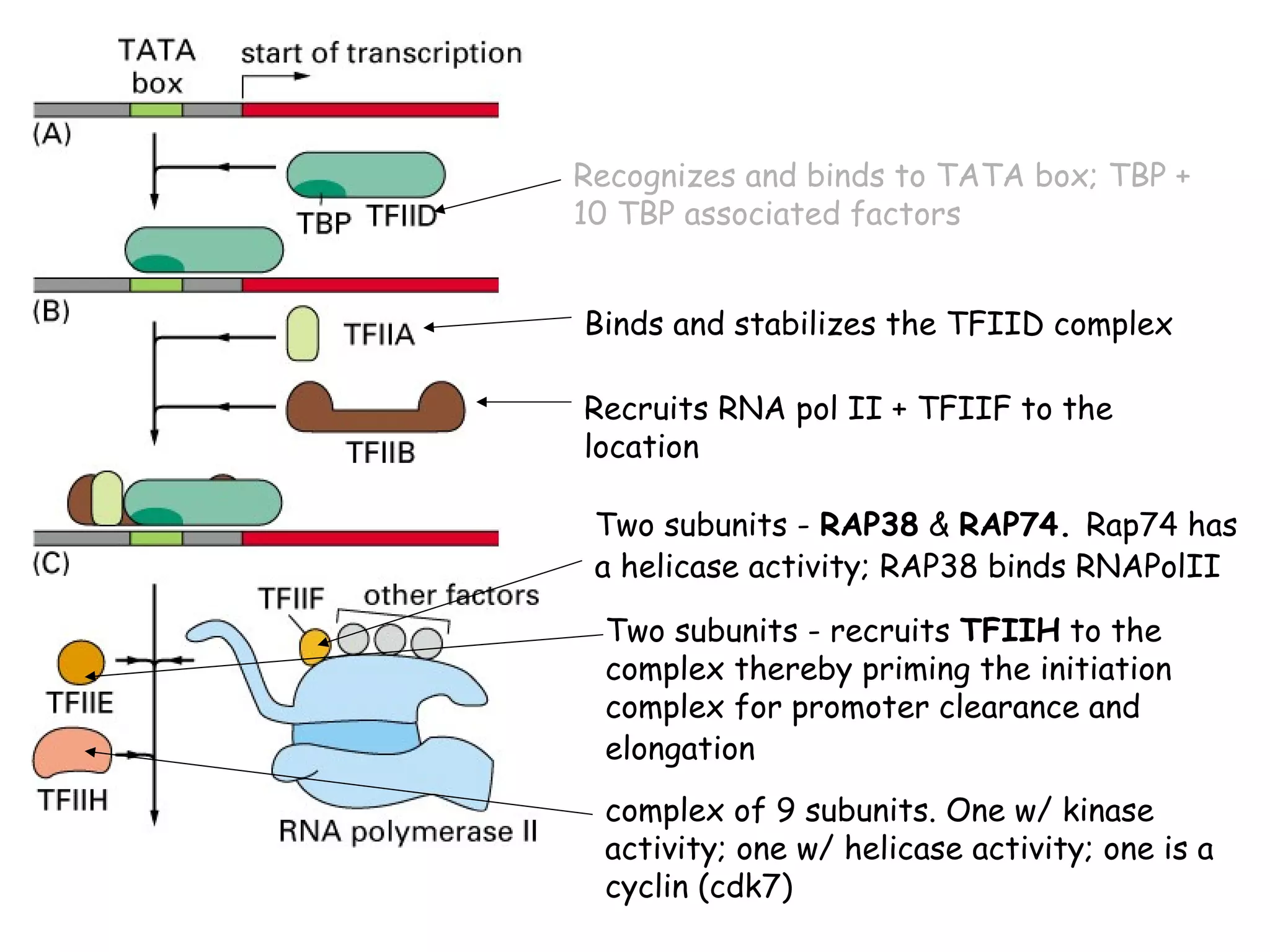
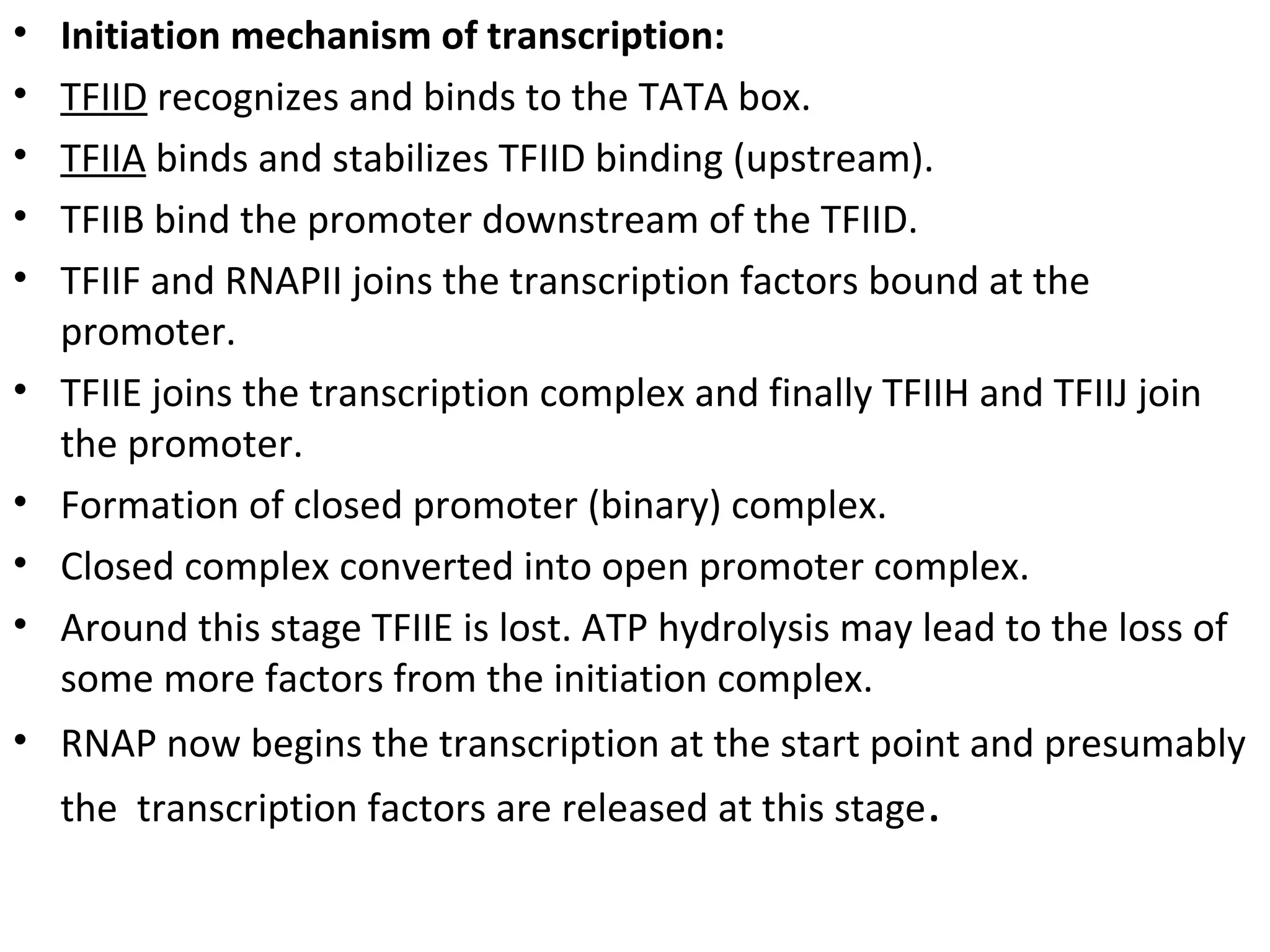
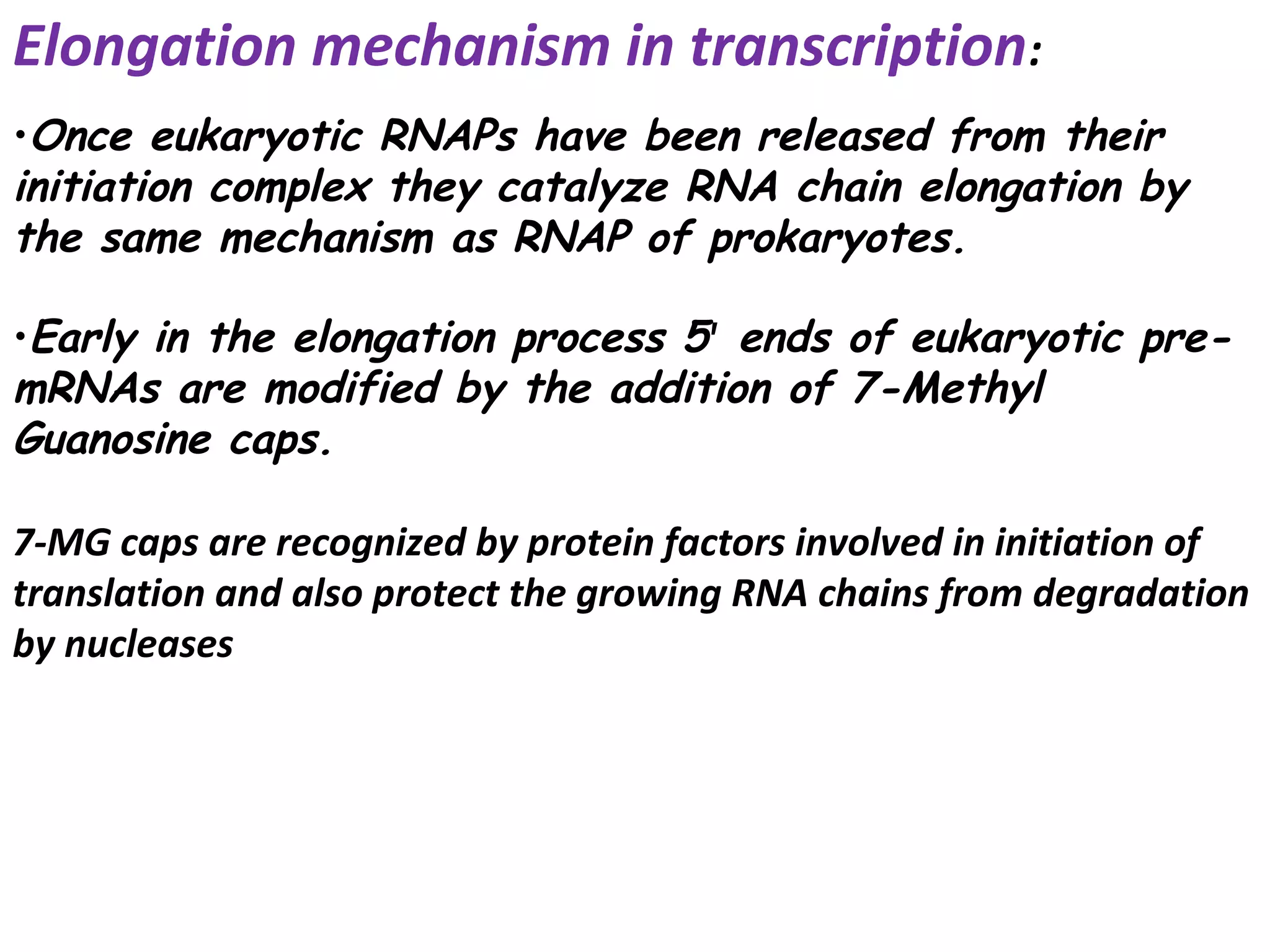
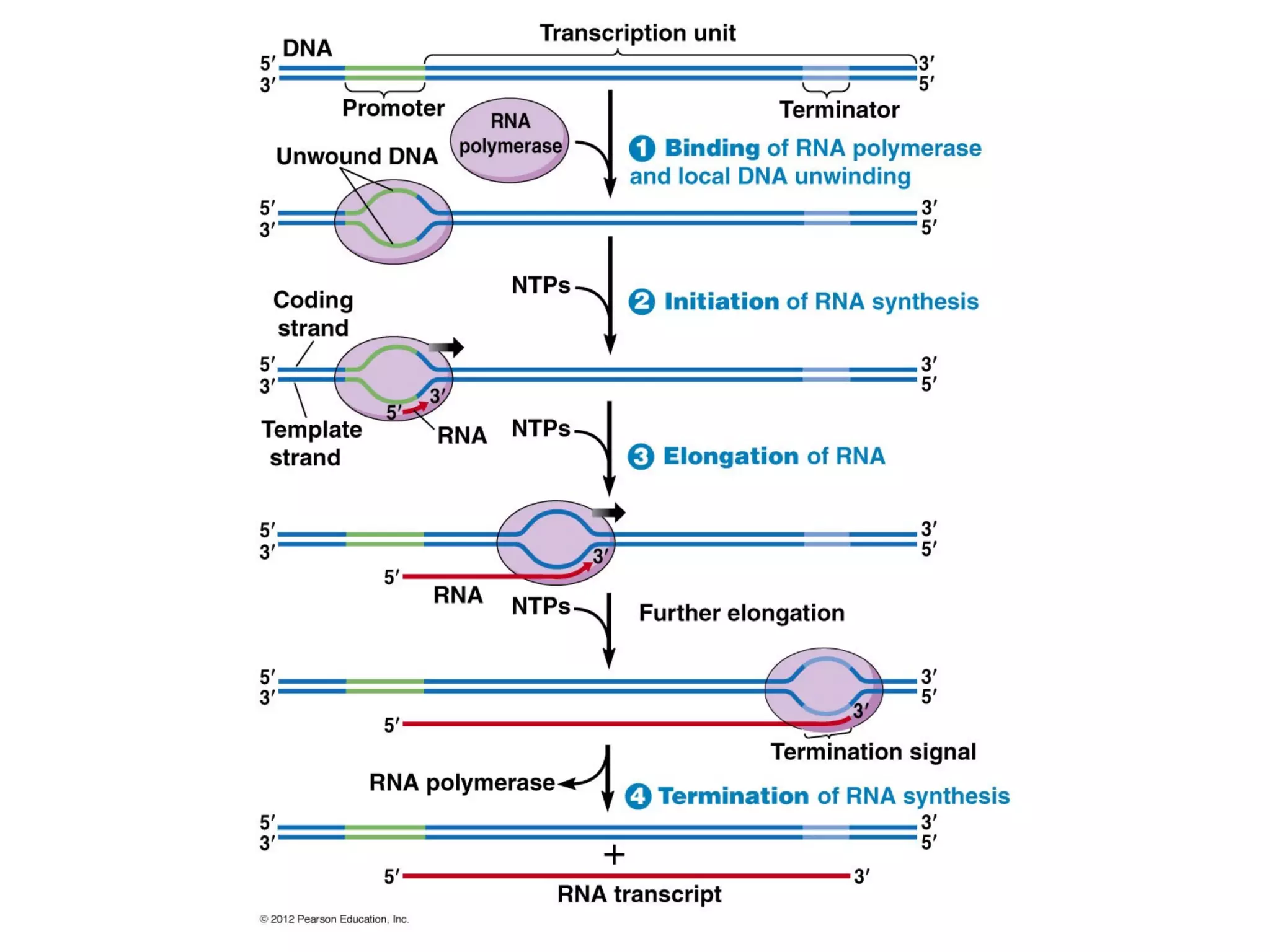
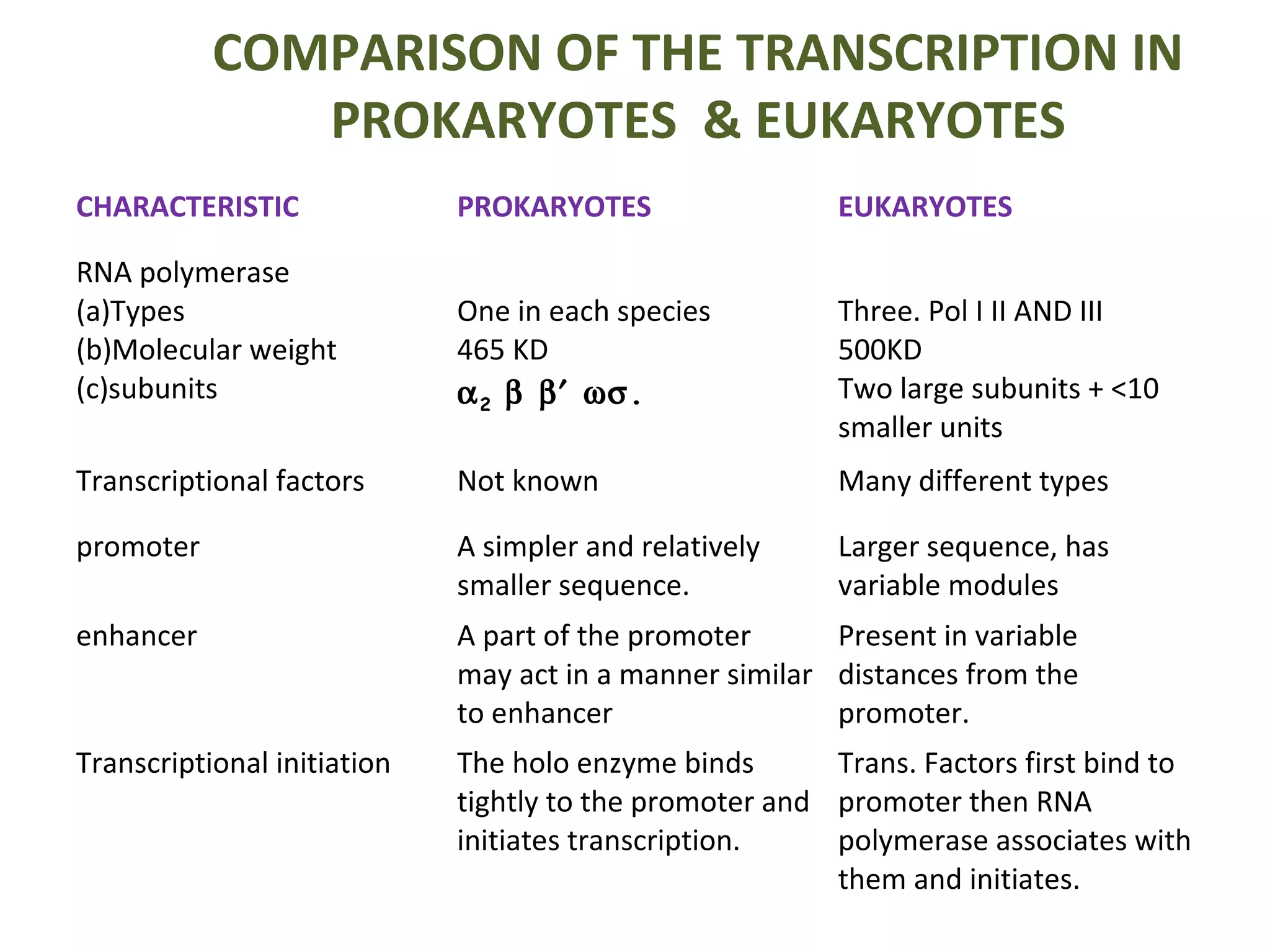
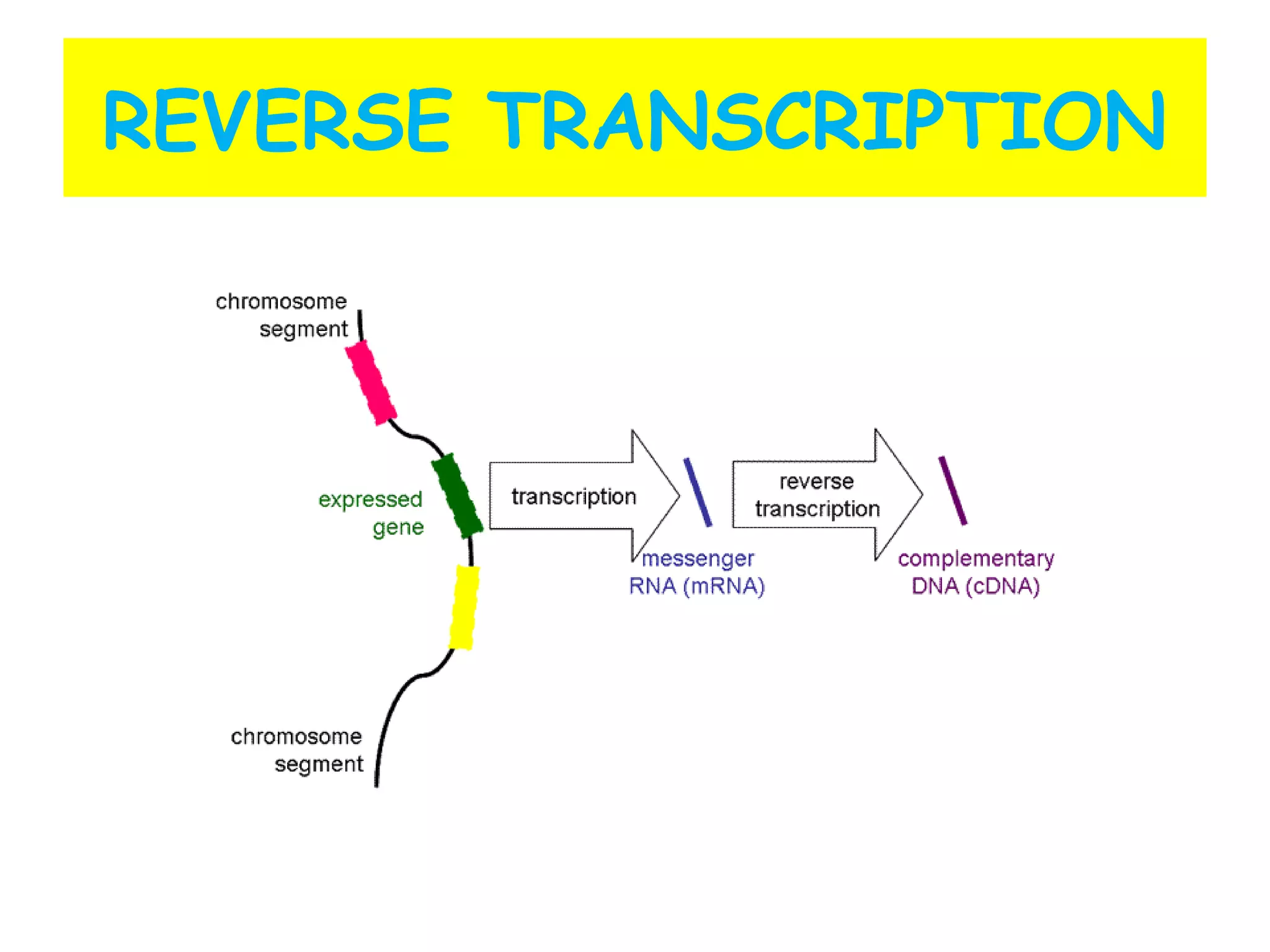
Transcription is the process by which RNA is synthesized from a DNA template. It involves three main steps - initiation, elongation, and termination. In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase binds directly to the promoter region of DNA and initiates transcription. Eukaryotes require various transcription factors to help RNA polymerase bind to the promoter. The transcription process is similar between prokaryotes and eukaryotes, but eukaryotes have three types of RNA polymerase and more complex regulation. Reverse transcription is the process by which DNA is synthesized from an RNA template using the enzyme reverse transcriptase.