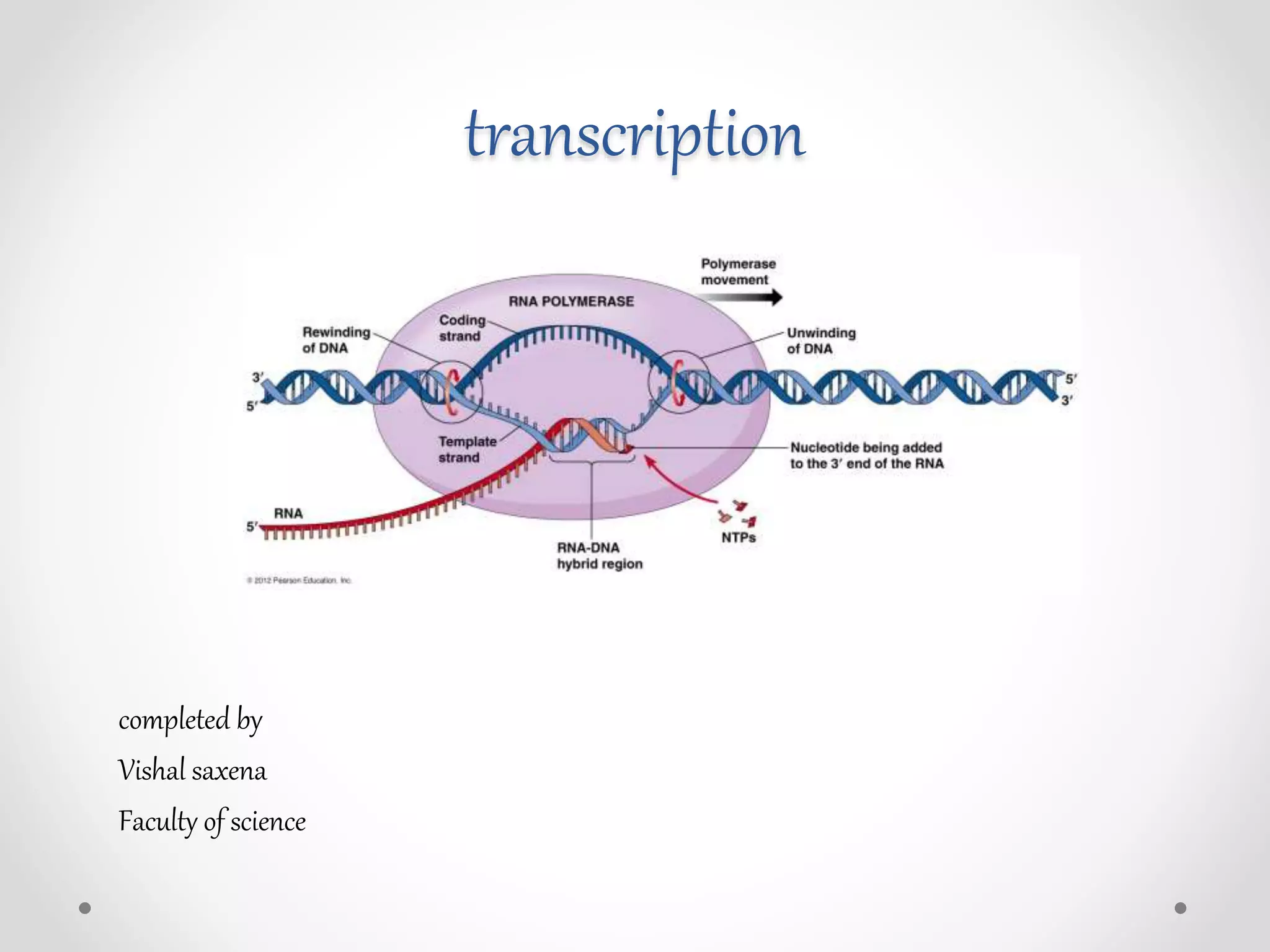
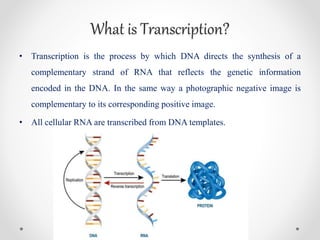
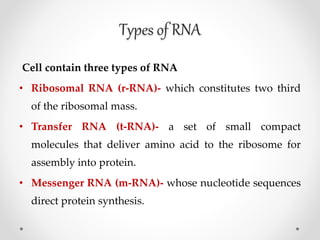
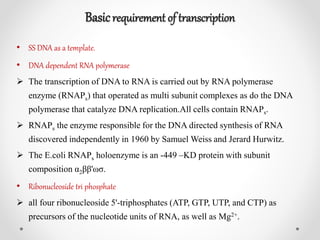
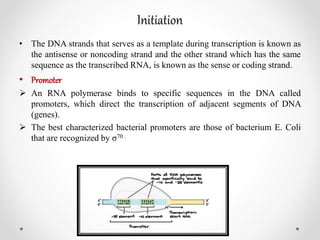
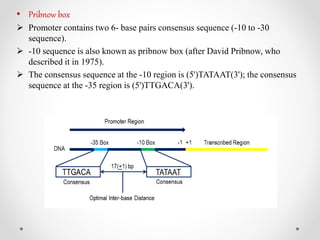
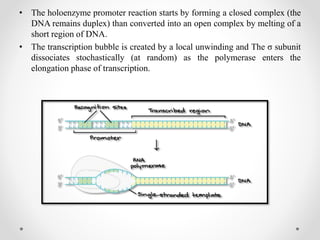
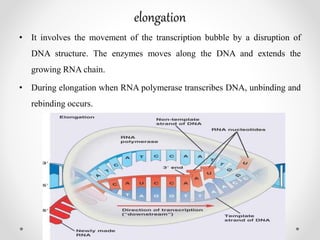
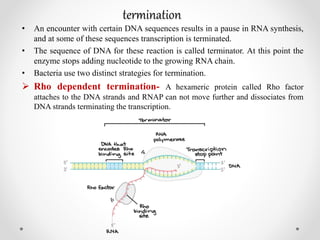
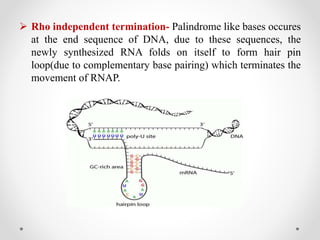
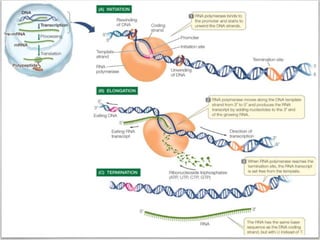
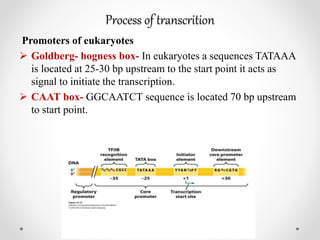
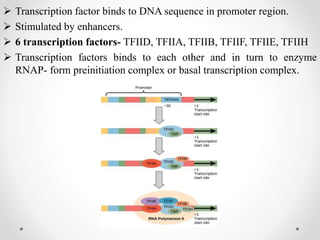
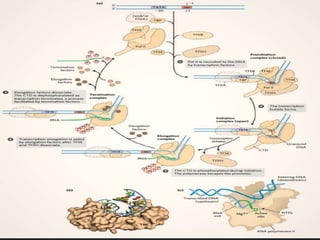
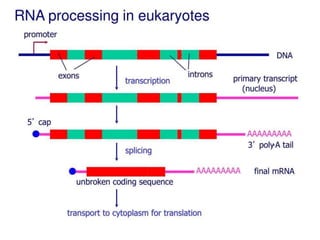
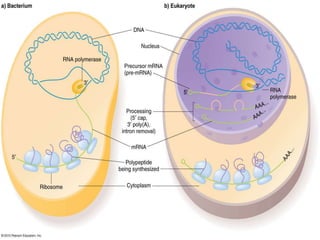
Transcription is the process by which DNA directs the synthesis of RNA, involving three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. In prokaryotes, RNA polymerase binds to specific DNA sequences called promoters, while eukaryotes utilize multiple RNA polymerases and transcription factors for this process. Post-transcriptional modifications in eukaryotes include 5' capping and the addition of a poly A tail, which stabilize mRNA and facilitate translation.