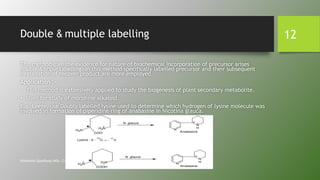
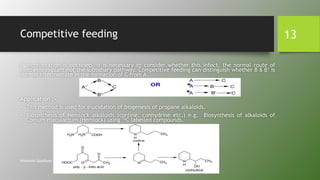
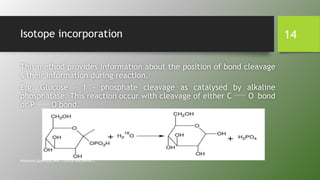
Tracer techniques involve using labeled compounds, such as radioactive isotopes, to trace intermediates and steps in biosynthetic pathways in plants. Labeled precursors are introduced into plants and their movement and incorporation into products is tracked over time. This allows investigation of precursor-product relationships, localization of compounds, and elucidation of biosynthetic sequences. Tracer techniques have various applications, including studying the biosynthesis of secondary metabolites, photosynthesis, and mineral uptake in plants.



![What is labelled compound ?
• The labelled compound can be prepared by use of two types of isotopes.
- Radioactive isotopes
- Stable isotopes
• Radioactive isotopes :- (e.g.- 1H, 14C, 24Na, 42K, 35S, 35P, 131I decay with emission of radiation)
- for biological investigation – carbon and hydrogen
- for metabolic studies – S, P, alkali and alkaline earth metals are used.
- for studies on protein, alkaloids and amino acid – labelled nitrogen atom give more specific
information.
- 3H compound is commercially available.
• Stable isotopes :- (e.g.- 2H, 13C, 15N,18O)
- used for labelling compounds as possible intermediates in biosynthetic pathways.
- usual method of detection are :- MASS spectroscopy [ 15N,18O ]
- NMR spectroscopy [ 2H, 13C ]
Himanshu Upadhyay (MSc. Clinical Biochemist.)
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tracertechniques-200516161418/85/Tracer-techniques-4-320.jpg)