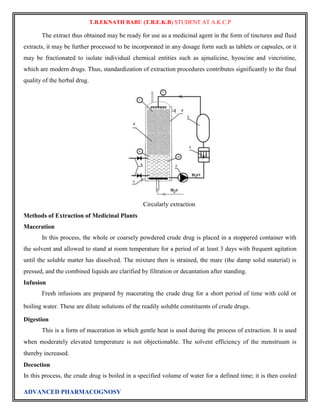
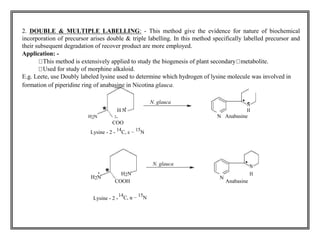
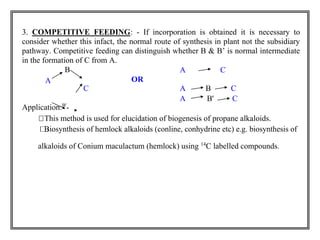
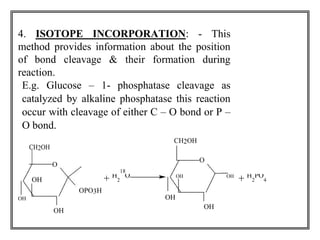
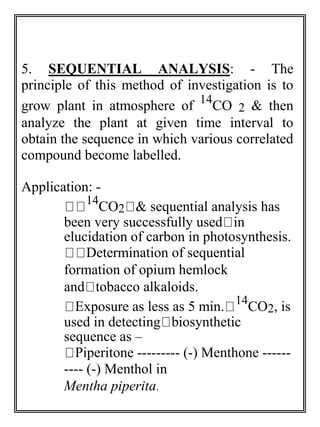
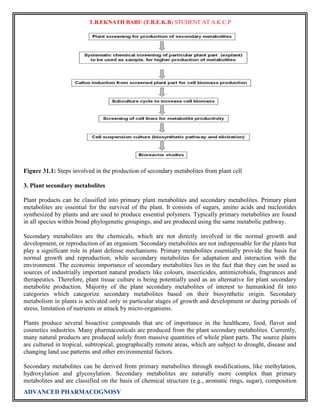
This document discusses tracer techniques used to study biosynthetic pathways in plants. Tracer techniques involve incorporating radioactive isotopes or stable isotopes into presumed precursors of plant metabolites. This allows researchers to trace intermediates and steps in pathways over time. Various techniques are described such as precursor-product sequence, double labeling, competitive feeding, and sequential analysis. Tracer techniques provide high sensitivity and can be applied to all living organisms to study topics like terpenoid biosynthesis, formation of secondary metabolites, and nutrient uptake in plants.



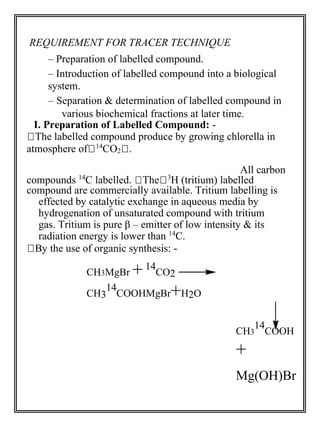
![The labelled compound can be
prepared by use of two types of
isotopes.
» Radioactive isotopes.
» Stable isotopes.
Radioactive isotopes: - [e.g. 1H, 14C,
24Na, 42K, 35S, 35P, 131I decay with emission of radiation]
– For biological investigation – carbon &
hydrogen.
– For metabolic studies – S, P, and alkali
and alkaline earth metals are used.
– For studies on protein, alkaloids, and
amino acid – labelled nitrogen atom
give more specific information.
3
–
H compound is commercially
available.
vii) Stable isotopes: - [e.g. 2H, 13C, 15N, 18O]
– Used for labelling compounds as
possible intermediates in biosynthetic
pathways.
– Usual method of detection are: – MASS
spectroscopy [15N,
18O]
2
13
– NMR spectroscopy [
H,
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-5-320.jpg)




















![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
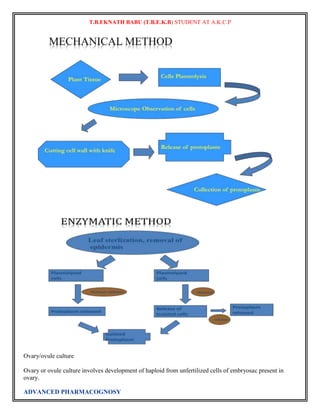
iv. initial establishment of cultures in liquid medium and later transfer to the semi-solid medium.
vi. culture of explants on porous substrate or paper bridges.
vi. addition of activated charcoal (AC) or polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) for adsorbtion of phenolics.
vii. antioxidants like ascorbic acid, citric acid etc. can also be used to prevent browning of tissues in culture.
• Appearance of vitrified tissues (hyperhydricity), a physiological disorder occurring in the in vitro cultures
due to which the tissues look transparent and fluffy resulting from excessive intake of water. Hyperhydricity
can be caused by a high concentration of cytokinin or low concentration of gelling agent or high water
retention capacity of explants if the container is tightly closed.
• Loss of regeneration ability in long-term cultures due to epigenetic variations (temporary variations) and
culture aging, including transition from juvenile to mature stage. Epigenetic variation are phenotypic
temporary variations which disappear as soon as the culture conditions are removed.
• Genotypic variations are also seen in the cultures, therefore, cytological, biochemical and molecular
analyses are required to confirm clonal fidelity of in vitro regenerants. Besides, morphological and
physiological testing is also required to remove undesired genetic variability.
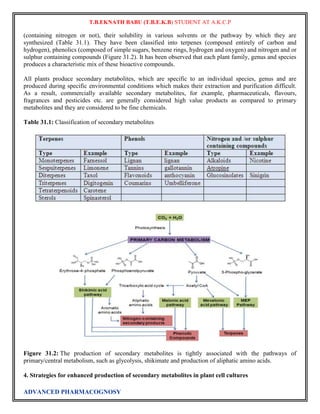
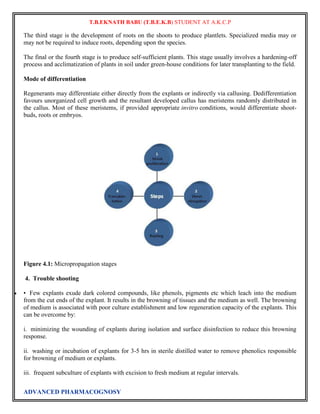
Plant tissue culture
Plant tissue culture is a collection of techniques used to maintain or grow plant cells, tissues or organs
under sterile conditions on a nutrient culture medium of known composition. Plant tissue culture is widely
used to produce clones of a plant in a method known as micropropagation. Different techniques in plant
tissue culture may offer certain advantages over traditional methods of propagation, including:
The production of exact copies of plants that produce particularly good flowers, fruits, or have other
desirable traits.
To quickly produce mature plants.
The production of multiples of plants in the absence of seeds or necessary pollinators to produce seeds.
The regeneration of whole plants from plant cells that have been genetically modified.
The production of plants in sterile containers that allows them to be moved with greatly reduced chances
of transmitting diseases, pests, and pathogens.
The production of plants from seeds that otherwise have very low chances of germinating and growing,
i.e.: orchids and Nepenthes.
To clean particular plants of viral and other infections and to quickly multiply these plants as 'cleaned
stock' for horticulture and agriculture.
Plant tissue culture relies on the fact that many plant cells have the ability to regenerate a whole plant
(totipotency). Single cells, plant cells without cell walls (protoplasts), pieces of leaves, stems or roots can
often be used to generate a new plant on culture media given the required nutrients and plant hormones.
Techniques
Modern plant tissue culture is performed under aseptic conditions under HEPA filtered air provided by
a laminar flow cabinet. Living plant materials from the environment are naturally contaminated on their
surfaces (and sometimes interiors) with microorganisms, so surface sterilization of starting material
(explants) in chemical solutions (usually alcohol and sodium or calcium hypochlorite or mercuric
chloride[1] is required. Mercuric chloride is seldom used as a plant sterilant today, unless other sterilizing
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-41-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
agents are found to be ineffective, as it is dangerous to use, and is difficult to dispose of. Explants are then
usually placed on the surface of a solid culture medium, but are sometimes placed directly into a liquid
medium, particularly when cell suspension cultures are desired. Solid and liquid media are generally
composed of inorganic salts plus a few organic nutrients, vitamins and plant hormones. Solid media are
prepared from liquid media with the addition of a gelling agent, usually purified agar. The composition of
the medium, particularly the plant hormones and the nitrogen source (nitrate versus ammonium salts or
amino acids) have profound effects on the morphology of the tissues that grow from the initial explant. For
example, an excess of auxin will often result in a proliferation of roots, while an excess of cytokinin may
yield shoots. A balance of both auxin and cytokinin will often produce an unorganised growth of cells,
or callus, but the morphology of the outgrowth will depend on the plant species as well as the medium
composition. As cultures grow, pieces are typically sliced off and transferred to new media (subcultured) to
allow for growth or to alter the morphology of the culture. The skill and experience of the tissue culturist are
important in judging which pieces to culture and which to discard.
As shoots emerge from a culture, they may be sliced off and rooted with auxin to produce plantlets which,
when mature, can be transferred to potting soil for further growth in the greenhouse as normal plants.
Choice of explant
The tissue obtained from a plant to be cultured is called an explant based on work with certain model
systems particularly tobacco it has often been claimed that a totipotent explant can be grown from any part
of the plant and may include portions of shoots, leaves, stems, flowers, roots and single, undifferentiated
cells.,[citation needed] however this has not been true for all plants.[3] In many species explants of various organs
vary in their rates of growth and regeneration, while some do not grow at all. The choice of explant material
also determines if the plantlets developed via tissue culture are haploid or diploid. Also the risk of microbial
contamination is increased with inappropriate explants.
The specific differences in the regeneration potential of different organs and explants have various
explanations. The significant factors include differences in the stage of the cells in the cell cycle, the
availability of or ability to transport endogenous growth regulators, and the metabolic capabilities of the
cells. The most commonly used tissue explants are the meristematic ends of the plants like the stem tip,
auxiliary bud tip and root tip. These tissues have high rates of cell division and either concentrate or produce
required growth regulating substances including auxins and cytokinins.
The pathways through which whole plants are regenerated from cells and tissues or explants such as
meristems broadly fall into three types:
1. The method in which explants that include a meristem (viz. the shoot tips or nodes) are grown on
appropriate media supplemented with plant growth regulators to induce proliferation of multiple
shoots, followed by rooting of the excised shoots to regenerate whole plants,
2. The method in which totipotency of cells is realized in the form of de novo organogenesis, either
directly in the form of induction of shoot meristems on the explants or indirectly via a callus
(unorganised mass of cells resulting from proliferation of cells of the explant) and plants are
regenerated through induction of roots on the resultant shoots,
3. Somatic embryogenesis, in which asexual adventive embryos (comparable to zygotic embryos in
their structure and development) are induced directly on explants or indirectly through a callus
phase.
The first method involving the meristems and induction of multiple shoots is the preferred method for the
micropropagation industry since the risks of somaclonal variation (genetic variation induced in tissue
culture) are minimal when compared to the other two methods. Somatic embryogenesis is a method that has
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-42-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
the potential to be several times higher in multiplication rates and is amenable to handling in liquid culture
systems like bioreactors.
Some explants, like the root tip, are hard to isolate and are contaminated with soil microflora that become
problematic during the tissue culture process. Certain soil microflora can form tight associations with the
root systems, or even grow within the root. Soil particles bound to roots are difficult to remove without
injury to the roots that then allows microbial attack. These associated microflora will generally overgrow the
tissue culture medium before there is significant growth of plant tissue.
Aerial (above soil) explants are also rich in undesirable microflora. However, they are more easily removed
from the explant by gentle rinsing, and the remainder usually can be killed by surface sterilization. Most of
the surface microflora do not form tight associations with the plant tissue. Such associations can usually be
found by visual inspection as a mosaic, de-colorization or localized necrosis on the surface of the explant.
An alternative for obtaining uncontaminated explants is to take explants from seedlings which are
aseptically grown from surface-sterilized seeds. The hard surface of the seed is less permeable to penetration
of harsh surface sterilizing agents, such as hypochlorite, so the acceptable conditions of sterilization used for
seeds can be much more stringent than for vegetative tissues.
Tissue cultured plants are clones. If the original mother plant used to produce the first explants is susceptible
to a pathogen or environmental condition, the entire crop would be susceptible to the same problem.
Conversely, any positive traits would remain within the line also.
Applications
Plant tissue culture is used widely in the plant sciences, forestry, and in horticulture. Applications include:
The commercial production of plants used as potting, landscape, and florist subjects, which uses
meristem and shoot culture to produce large numbers of identical individuals.
To conserve rare or endangered plant species.[4]
A plant breeder may use tissue culture to screen cells rather than plants for advantageous characters,
e.g. herbicide resistance/tolerance.
Large-scale growth of plant cells in liquid culture in bioreactors for production of valuable compounds,
like plant-derived secondary metabolites and recombinant proteins used as biopharmaceuticals.[5]
To cross distantly related species by protoplast fusion and regeneration of the novel hybrid.
To cross-pollinate distantly related species and then tissue culture the resulting embryo which would
otherwise normally die (Embryo Rescue).
For production of doubled monoploid (dihaploid) plants from haploid cultures to achieve homozygous
lines more rapidly in breeding programmes, usually by treatment with colchicine which causes doubling
of the chromosome number.
As a tissue for transformation, followed by either short-term testing of genetic constructs or
regeneration of transgenic plants.
Certain techniques such as meristem tip culture can be used to produce clean plant material
from virused stock, such as potatoes and many species of soft fruit.
Production of identical sterile hybrid species can be obtained.
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-43-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Callus Culture:
When the cells divide into an undifferentiated mass it is called as callus. Any part of a plant can be used to
produce the calli. It may be a stem, leaf, meristem or any other part. It is used to produce variations among
the plantlets. Callus formation is induced from plant tissues after surface sterilization and plating onto in
vitro tissue culture medium. Plant growth regulators, such as auxins, cytokinins, andgibberellins, are
supplemented into the medium to initiate callus formation or somatic embryogenesis. Plant callus is usually
derived from somatic tissues. The tissues used to initiate callus formation depends on plant species and
which tissues are available for explant culture. The cells that give rise to callus and somatic embryos usually
undergo rapid division or are partially undifferentiated such as meristematic tissue. In alfalfa,Medicago
truncatula, however callus and somatic embryos are derived from mesophyll cells that
undergo dedifferentiation.[17] Plant hormones are used to initiate callus growth.
Specific auxin to cytokinin ratios in plant tissue culture medium give rise to an unorganized growing and
dividing mass of callus cells. Callus cultures are often broadly classified as being either compact or friable.
Friable calluses fall apart easily, and can be used to generate cell suspension cultures. Callus can directly
undergo direct organogenesis and/or embryogenesis where the cells will form an entirely new plant.
Callus induction and tissue culture
A callus cell culture is usually sustained on gel medium. Callus induction medium consists of agar and a
mixture of macronutrients and micronutrients for the given cell type. There are several types of basal salt
mixtures used in plant tissue culture, but most notably modified Murashige and Skoog medium,[13] White's
medium,[14] and woody plant medium.[15] Vitamins are also provided to enhance growth such as Gamborg
B5 vitamins.[16] For plant cells, enrichment with nitrogen, phosphorus, andpotassium is especially important.
Callus cells deaths
Callus can brown and die during culture, but the causes for callus browning are not well understood.
In Jatropha curcas callus cells, small organized callus cells became disorganized and varied in size after
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-44-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
browning occurred.[18] Browning has also been associated with oxidation and phenolic compounds in both
explant tissues and explant secretions.
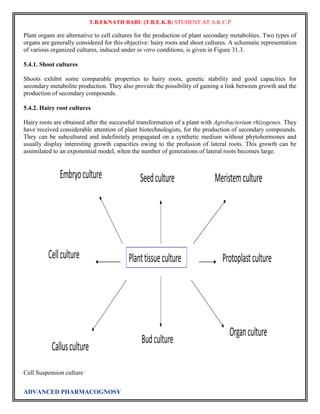
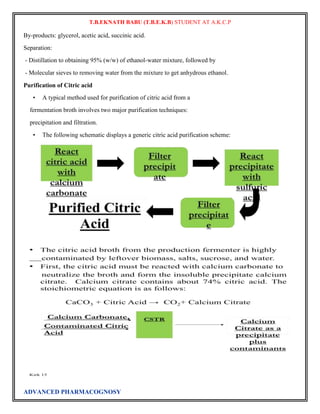
Suspension culture:
The callus produced from the explants are grown on nutrient solutions (that are semi solid) for a period of
time and they are induced to produce plants with new traits. A callus crumbles into smaller clumps and
single cells in liqu~d~medium by gentle agitation (100-120rPM) on a shaker. Shaking the cultures also
helps to aerate the cells. Such suspension cultures however rarely comprise single cells alone because cells
tend to aggregate in clusters of 2-100. Suspension cultures can be maintained indefinitely by inoculations of
known aliquot5 of cells to a fresh medium. This process is termed as "batch cultures". Alternatively, the
medium is replenished at regu lar intervals. This process is termed as "continuous culture". In the
continuous culture process at the time of replenishing the medium, cells are also harvested (open continuous
system) or the biomass is allowed t~*increase (close continuous system). Suspension cultures are useful in
studying problems related to cell biology including cell cycle and production of secondary metabolites like
alkaloids, steroids, glycosides, napthaquinones, flavones etc. which find medicinal and industrial
application. Pharmaceutical industries use large bioreactors for suspension cultures to obtain valuable
bioorganic compounds. A bioreactor is a vessel of glass or steel in which cells are cultured aseptically and
culture conditions are closely monitored. This results in higher yield of metabolites. In a bioreactor there is
provision for adding fresh medium, for harvesting cells, for the aeration of products, for mixing and
sampling, for controlling pH, 02 content and temperature Plant cells are immobilised in alginate, agarose,
polyacrylamide beads. Immobilisation of cells enables i) re-use of biomass by rotation of cells ii) separation
of cells from the medium and iii) leaching of metabolites in it . Immobilised cells are cultured in column
reactors. Column reactors are of different types with different agitation and flow systems. Such reactors may
be i) stirred tank type ii) air lift type iii) bubble column type and iv) rotating drum type.
11.3.2 Single Cell Culture
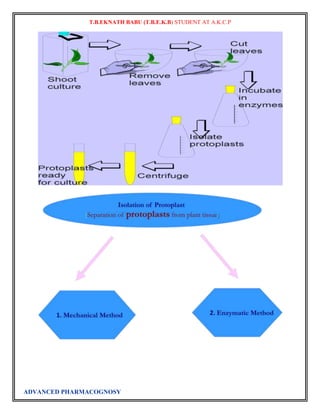
This is an important invitro technique which enables the cloning of selected cells. Single cells can be
obtained directly from plant organs by treatment with enzymes that dissolve middle lamellae. The separate
cells can sieve into liquid medium to start a suspension culture. The most widely used technique for single
cell culture is the Bergmann's method of Cell Plating and. Microchamber technique.
Bergmann's Method of Cell Plating:
In this method free cells are suspended in a liquid medium at a density twice the Plant Tissue And Organ
finally desired plating density. Melted agarcontaining medium of otherwise the Culture same composition as
the liquid medium is maintained at 35Oc in water bath. Equal volumes of the two media are mixed and
rapidly spread out in petri dishes in such a manner that the cells are evenly distributed and fixed in a thin
layer (about 1 mm thick) of the medium after it has cooled and solidified. The dishes are sealed with
parafilm. The cells to be followed are marked on the outside of the plate and before the colonies derived
from individual cells grow large enough to merge with each other. They are transferred to.separate plates.
(Fig. 11.3). Another popular method for single cell culture is the microchamber technique, developed by
Jones et al. (1960). In this method mechanically isolated single cells are cultured in separate droplets of
liquid medium. While Jones et al. used sterile microslides and three coverglasses to make microchamber, it
is now possible to buy pre-sterilised plastic plates with several microwells (Cuprak dishes). Individual cells
are cultured in separate wells each containing 0.25 ml of the liquid medium. The culture requirement of
single cells increases with decrease in the plating cell density, and the cell cultured in complete isolation
require a very complex culture medium. A simple medium conditioned by growing cell suspension for some
time rlso fulfils the requirements of single cell culture at low density
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-45-320.jpg)


![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Plant tissue culture techniques have also helped in large- scale production of plantsthrough micropropagation or
clonal propagation of plant species. Small amounts of tissue canbe used to raise hundreds or thousands of plants
in a continuous process. This is beingutilized by industries in India for commercial production of mainly
ornamental plants likeorchids and fruit trees, e.g., banana. Using this method, millions of genetically identical
plantscan be obtained from a single bud. This method has, therefore, become an alternative tovegetative
propagation. Shoot tip propagation is exploited intensively in horticulture and thenurseries for rapid clonal
propagation of many dicots, monocots and gymnosperms.
c. Genetic Transformation
Tissue culture, in combination with genetic engineering is very useful in gene transfers.For example, the transfer
of a useful bacterial gene say, cry (crystal protein) gene from
Bacillus thuringiensis
, into a plant cell and, ultimately, regeneration of whole plants containing andexpressing this gene (transgenic
plants) can be achieved.
d. Production of Pathogen-free Plants
Eradication of virus has been an outstanding contribution of tissue culture technology.It was found that even in
infected plants the cells of shoot tips are either free of virus or carry anegligible amount of the pathogen. Such
shoot tips are culturedin a suitable culture medium to obtain virus- free plants. This technique is economical
andused very frequently in horticulture, production of virus- free ornamentals etc.
e. Production of Secondary Metabolites
Cultured plant cells are also known to produce biochemicals [secondary metabolites]like, alkaloids, terpenoids,
phenyl propanoids etc. of interest. The technology is now availableto the
industry. The commercial production of ‘shikonin’[a naphthoquinone] from cell cultures
of Lithospermum erythrorhizon, has been particularly encouraging
Applications of immobilized enzymes
The first industrial use of an immobilized enzyme is amino acid acylase by Tanabe Seiyaku Company,
Japan, for the resolution of recemic mixtures of chemically synthesized amino acids. Amino acid acylase
catalyses the deacetylation of the L form of the N-acetyl amino acids leaving unaltered the N-acetyl-d amino
acid, that can be easily separated, racemized and recycled. Some of the immobilized preparations used for
this purpose include enzyme immobilized by ionic binding to DEAE-sephadex and the enzyme entrapped as
microdroplets of its aqueous solution into fibres of cellulose triacetate by means of fibre wet spinning
developed by Snam Progetti. Rohm GmbH have immobilized this enzyme on macroporous beads made of
flexiglass-like material
By far, the most important application of immobilized enzymes in industry is for the conversion of glucose
syrups to high fructose syrups by the enzyme glucose isomerase95. Some of the commercial preparations
have been listed. It is evident that most of the commercial preparations use either the adsorption or the
cross-linking technique. Application of glucose isomerase technology has gained considerable importance,
especially in nontropical countries that have abundant starch raw material. Unlike these countries, in tropical
countries like India, where sugarcane cultivation is abundant, the high fructose syrups can be obtained by a
simpler process of hydrolysis of sucrose using invertase. Compared to sucrose, invert sugar has a higher
humectancy, higher solubility and osmotic pressure. Historically, invertase is perhaps the first reported
enzyme in an immobilized form96. A large number of immobilized invertase systems have been patented97.
The possible use of whole cells of yeast as a source of invertase was demonstrated by D’Souza and
Nadkarni as early as 1978. A systematic study has been carried out in our laboratory for the preparation of
invert sugar using immobilized invertase or the whole cells of yeast. These comprehensive studies carried
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-48-320.jpg)








![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
The Skraup synthesis is a chemical reaction used to synthesize quinolines. It is named after the Czech
chemist Zdenko Hans Skraup (1850-1910). In the archetypal Skraup reaction, aniline is heated with sulfuric
acid, glycerol, and an oxidizing agent such as nitrobenzene to yield quinoline.[1][2][3][4]
In this example, nitrobenzene serves as both the solvent and the oxidizing agent. The reaction, which
otherwise has a reputation for being violent ("the Chemical Inquisition"), is typically conducted in the
presence of ferrous sulfate.[5] Arsenic acid may be used instead of nitrobenzene and the former is better
since the reaction is less violent.[6]
8-aminoquinolines• Drugs in this group have amino group at position 8 of quinoline ring• Important
members of this family include 1- Pamaquine 2- Primaquine, etc.
2. • Such drugs have OCH3 group at position 6• This molecule has antimalarial activity but when side chain
is introduced at amino group antimalarial activity is intensified e.g pamaquine• It causes hemolysis of RBCs
Diethyl amino pentyl side chain
3. • It contains tertiary amino group and when it is converted into primary amino group the compound is
called primaquine, which is – Less toxic – Well tolerated – It is the most commonly used agent in this group
in the treatment of malaria
4. • OCH3 is not necessary for antimalarial activity but when replaced by OC2H5 the compound became –
less active – Toxic in nature• OCH3 when replaced by CH3 the compound become inactive• Introduction of
halogens increases toxicity• Presence of quinoline ring is necessary for antimalarial activity. When pyridine
ring is converted to piperidine (saturated) the compound became inactive
5. • Pentyl side chain gives maximum activity, increase or decrease of chain result is reduction of activity.•
The branched side chain when converted into straight chain pentaquine is obtained• It has less antimalarial
activity as compared to both pamaquine and primaquine
6. Chemical synthesis (pamaquine)• Glycerol undergoes dehydration to produce propene aldehyde•
Dehydrating agent is sulphuric acid
7. • Addition reaction of propene aldehyde and 4 methoxy 2-nitro aniline to form 4 methoxy 2- nitro
propene aldehyde
8. • Tautomerization: 4 methoxy 2-nitro propene aldehyde (keto form) converted in enol form
9. • Enol form undergoes cyclization to form 8 nitro 6 methoxy dihydroquinoline which then oxidized to
form 8 nitro 6 methoxy quinoline
10. • 6 methoxy 8 nitro quinoline undergoes reduction to form 8 amino 6 methoxy quinoline
11. • 8 amino 6 methoxy quinoline reacts with 2 chloro diethyl amino pentane to form pamaquine
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-57-320.jpg)



![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
• Citric acid is widely used as a pH adjusting agent in creams and gels of all kinds.
• Citric acid is commonly used as a buffer to increase the solubility of brown heroin.
• Citric acid is used as one of the active ingredients in the production of antiviral tissues.
Dyeing
• Citric acid can be used in food coloring to balance the pH level of a normally basic dye.
• It is used as an odorless alternative to white vinegar for home dyeing with acid dyes.
Photography
• Citric acid can be used as a lower-odor stop bath as part of the process for developing photographic
film.
INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION OF DIOSGENIN:
DIOSGENIN TUBERS COLLECTED---------- WASHED ------- DRIED----------- EXTRACTED WITH
HOT WATER OR 90% ETHANOL FOR 6 HRS……………………… ALCOHOLIC EXTRACT
CONCENTRATED UNDER VACUUM………….. FILTER IT ……….. FILTERATE + SOLVENT
ETHER OR LEAD ACETATE SOLUTION…………HYDROLYSIS BY ACID ……………………..
EXTRACTED WITH PET. ETHER……….EVAPORATE SOLVENT …………………… DIOSGENIN
COLLECTED, DRIED AND PACKED .
INDUSTRIAL PRODUCTION OF SOLSODINE
SOLSODINE BY TWO METHODS METHOD 1 B. METHOD 2
METHOD. 1 Dried berries is powdered-------- Oil is removed------------- Defatted is extracted with ethanol--
------------------- Resultant is filtered , Concentrated & Treat with HCl & Reflux ---------------- Extract is
made alkaline by ammonia…………. Reflux for 1 hr……………. Filter it…………………Dry and wash
Residue ……………. Mix in chloroform …………. Evaporate solvent……….. Solasodine , solid residue is
obtained.
METHOD. 2 Powdered drug + ethanol-------- Soxhlation 6 hrs.------------- Solvent distilled off……………
Concentrated to syrupy mass ---------Add 5 ml HCl , Boil …….. Reflux for 2 hr……………. Cool it &
Filter………… Residue + Boil water………. Adjust pH-9 by NH 3 (10%) …………. Boil under reflux for
2 hrs ……… Cool & Filter…..Dry Ppt ……….. Solasodine , solid residue is obtained.
Atropine
The final problem in the synthesis, the combination of tropine and tropic acid, was overcome by a
Fischer-Speier esterification [13]. The acid and alcohol were heated together in the presence of HCl to
yield atropine
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-62-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
The biosynthesis of atropine starting from L-Phenylalanine first undergoes
a transamination forming phenylpyruvic acid which is then reduced to phenyl-lactic acid.[14] Coenzyme A
then couples phenyl-lactic acid with tropine forming littorine, which then undergoes a radical rearrangement
initiated with aP450 enzyme forming hyoscyamine aldehyde.[14] A dehydrogenase then reduces the aldehyde
to a primary alcohol making (-)-hyoscamine, which upon racemization forms atropine.
Atropine is a naturally occurring tropane alkaloid extracted from deadly nightshade (Atropa belladonna),
Jimson weed (Datura stramonium),mandrake (Mandragora officinarum) and other plants of the
family Solanaceae. It is a secondary metabolite of these plants and serves as a drugwith a wide variety of
effects.
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-63-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
In general, atropine counters the "rest and digest" activity of glands regulated by the parasympathetic
nervous system. This occurs because atropine is a competitive antagonist of the muscarinic acetylcholine
receptors (acetylcholine being the main neurotransmitter used by the parasympathetic nervous system).
Atropine dilates the pupils, increases heart rate, and reduces salivation and other secretions.
Chemistry[edit]
Ergometrine, 1-hydroxymethylethylamide lysergic acid, is synthesized by esterification of D-lysergic
acid using 2-aminopropanol indimethylformamide and direct treatment of the reaction mixture
with phosgene.[5]
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-64-320.jpg)

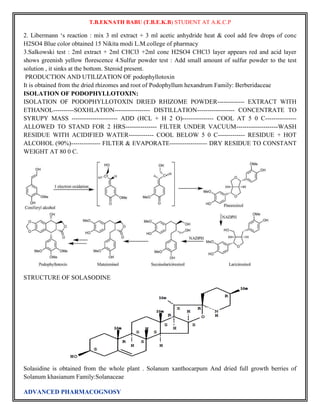

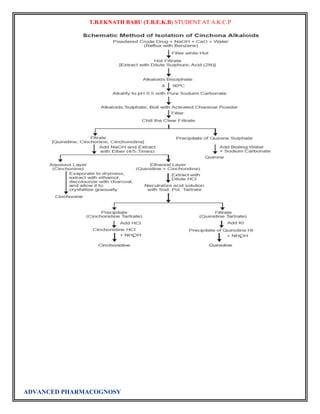
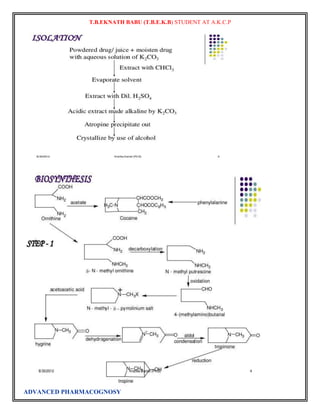
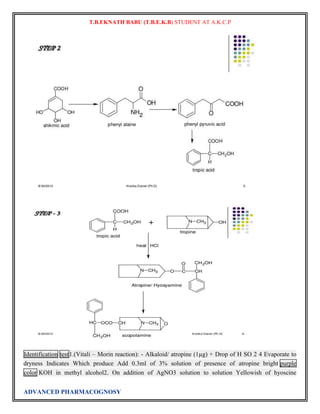

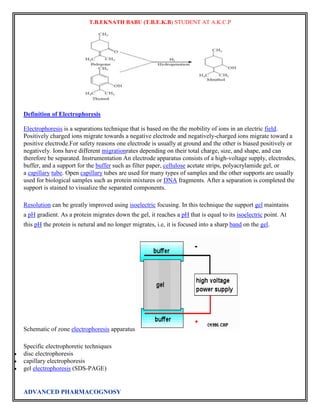
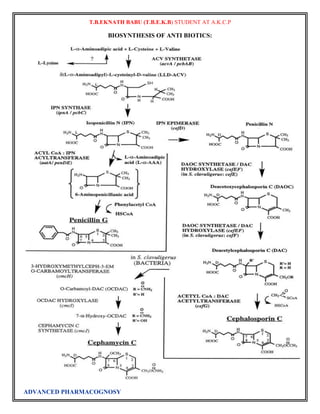
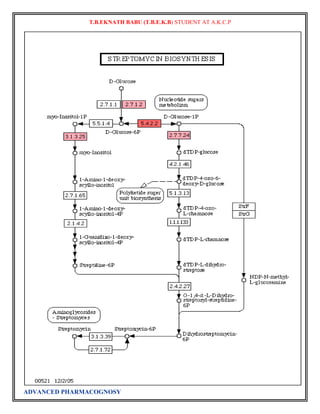
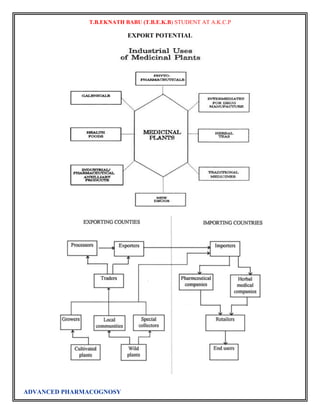
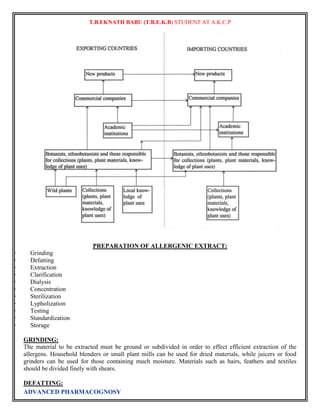
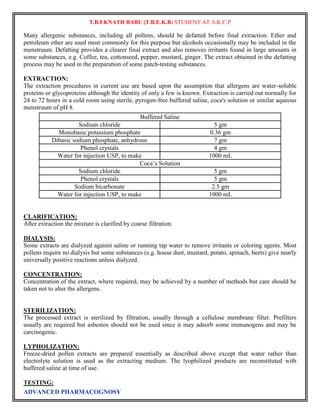
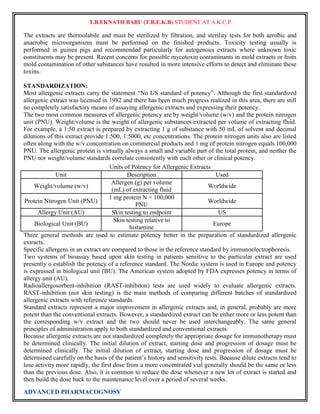
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
STORAGE:
Allergenic extracts tend to show reduced potency within a matter of weeks or months after their preparation,
but there have been few detailed studies on the stability of these products. Both high temperatures and
freezing usually have deleterious effects, and the latter may cause agglomeration of adjuvant extracts. Some
extracts also contain proteolytic enzymes and these may contribute to decomposition of the allergens. Both
glycerinated and lyophilized products are more stable than aqueous extracts. Very dilute extracts tend to
lose potency by adsorption to the surfaces of containers and syringes and thus usually are prepared close to
the time of use. Several studies have shown that the inclusion of Tween 80, Teen 20 or human serum
albumin reduces or adsorption but a more-complete investigation of this problem is required. The adjuvant
extracts should not be diluted with either phosphate buffered saline or Coca’s solution since these may cause
partial release of allergen; normal saline containing 0.4% phenol is a satisfactory diluents. The adjuvant
extracts may be mixed with one another but should not be mixed with other types of extracts.
All allergenic extracts should be refrigerated at 2 to 8 ̊ and freezing should be avoided. The expiration date
for aqueous extracts is usually 18 months, while for glycerinated scratch test and bulk extracts is usually 3
years. Lyophilized products have an expiration date of 4 years or 18 months after reconstitution, so long as
the time falls within the original 4 years. Care must be exercised in changing to new lots or different
dilutions of extracts because of possible variations in potency. It generally is recommended that quantities of
extract sufficient to last the patient for 1 year be prepared to avoid frequent changes in extracts.
Classification of allergens in plants
1.1 Inhalent allergens
Inhalent allergens from grass or tree pollens, house dust mite and animal dander are the major
substances that are capable of provoking type I hyperresponsiveness. Among those allergens, one of the
most common ones is pollen of plants[3]. An individual who has hypersensitivity to pollen often suffers
from seasonal allergic rhinitis or extrinsic asthma. Weeds, grasses and trees are common sources of pollen,
and high concentrations of these pollen allergens in the air surrounding us correspond well to pollen-related
hypersensitivity disease. The major and most widespread allergenic components of pollen is the group I
allergens. Thus, the allergy caused by these allergens is often termed "seasonal". These allergenic proteins
in pollens with molecular weight about 30 kD are quickly and profusely released by grass pollen upon
hydration[4]. In recent years, research in this area has focused on the characterization of relevant grass
pollen allergens because as many as approximately 40% of allergic individuals start their symptoms
immediately after contacting with grass pollens[5].
1.2 Ingestent allergens
Ingestent allergens often refer to substances inducing allergy after the sensitized individuals eating a
certain food. Typical symptoms of this type allergy include mouth or throat itching and lip swelling. In
recent years, an increase in tree nut and peanut allergy has been reported in Europe and in US. For example,
peanut and/or tree nut allergy affect approximately 1.1% of US population, corresponding to 3 million
individuals at risk of adverse reaction to these foods[6]. Of these individuals, 50% considered in the survey
performed by Sicherer et al.[7] were reactive to peanut, 30% to walnut and 10% to almond, while only 4%
were reactive to both peanut and tree nut. In previous reports, the percentage of allergic individuals
symptomatically reactive to two or more nuts has been found to be nearly 10%, which corresponds to at
least half a million individuals in the world reactive to two related nuts. On the other hand, a recent study
reported that approximately 35% patients with pollen allergy were also sensitive to fresh fruits and
vegetables[8].
1.3 Contactent allergens
Latex is the most important contactent allergens in plants. Since the late 1980's, this immediate-type
allergy provoked by natural rubber products has been reported around the world[9]. It is now known as latex
allergy. It also can be induced by wide-ranging latex products. In addition, allergy to exotic fruit is
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-80-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
frequently reported in studies on latex-allergic subjects. Subjects suffering from the latex-fruit syndrome
become primarily sensitized to latex and then develop food allergy as a result of cross-reacting IgE against
protein, such as in banana and avocado[10]. Nowadays, plant defense-related proteins induced by stress
were reported as a main kind of latex allergen.
2 The biological functions of allergens in plants
In last decade, with the implementation of molecular biological techniques in the field of allergen
characterization, the sequence, nature, and three-dimensional structure of several important allergens have
been revealed. Application of molecular cloning techniques also enable us to understand the natural
functions of the IgE-binding proteins in plants. There are at least three major biological functions for the
allergens in plants.
2.1 Calcium-binding protein
In plant molecular biology, calcium in pollen is recognized as an essential constituent of in vitro pollen-germination
media and a potential chemoattractant guiding pollen growth. In 1999, Rozwadowski et al.[11]
characterized calcium-binding protein from Brassica and Arabidopsis pollen. By sequence comparison, the
protein was revealed as a part of a family of pollen allergens identified recently in several evolutionarily
distant dicot and monocot plants. The protein also has strong immunoreactivity to IgE from a human subject
allergic to Brassica pollen[12]. In addition, the members in the two EF-hand allergen families share an
average sequence identity of 77%, which is of comparable magnitude within and outside the calcium-binding
domain. In fact, several kinds of plant allergens with EF-hand calcium-binding domains have been
identified in birch[13], Bermuda grass[14] and rapeseed[12]. Calcium binding plant proteins have now been
discovered as relevant cross-reactive allergens, and the EF-hand domain is the major epitope for antibody
reorganization in those allergens[15].
2.2 Pathogenesis-related protein (PR protein)
PR proteins which represent an important group of human allergens can be up-regulated in plants in
response to stressors such as freezing, drought, temperature, fungi, viruses or bacteria infection. So far,
several allergenic PR proteins have been biochemically characterized. They belong to different PR protein
groups (there are 10 groups of PR proteins in nature). For example, Jun a 3, the allergen in mountain cedar,
was found to be homologous to the PR-5 protein group. Plant allergens Bet v 1 (in birch), Mal d1 (in apple)
and Dau c 1 (in carrot) are members of PR protein 10 group[16]. Similarly, the major allergen in rubber Hev
b6[17] and its metabolic products, Bar r 2 (in turnip)[18] and Pers a 1 (in avocado)[19] have the properties
of chitinase, and belong to the PR protein 4 group. Investigation of potential common functions and
structures of PR-proteins will uncover some "law" of allergens in plants and will explain the reason for
cross-reaction phenomena in plant allergens.
2.3 Expansins
A cell wall-loosening agent, is extracellular protein that promotes plant cell wall enlargement by
disrupting noncovalent bonding between cellulose microfibrils and matrix polymers[20]. When the first
expansin complementary DNA was sequenced, BLAST searches in GenBank revealed a distant sequence
similarity to a group of grass allergens called group-1 allergen. It was characterized further that group-1
allergens in plants were indeed structurally and functionally related to expansin, and that their vegetative
homologs comprise a second family of expansins, such as LolpI(in ryegrass), Ory s I (in rice) and Zea m
I (in maize)[4]. But different from the original group of expansin, this group of expansin in pollens could
only induce extension in the cell walls of grass and was not effective on the walls from dicotyledons[21].
Recently, the cell wall-loosening agents in pollens have been named as β-expansin family, in order to
distinguish it from the original group of expansins, which are now called α-expansins.
In type I hyperresponsiveness, there are varieties of cross-reaction between allergens in different plants[22].
The common conservative domain and/or isotope among different allergens in plants are the radical cause of
these phenomena. Thus, research on identification and characterization of allergens and their structures and
biological functions will be benefit for the diagnosis and treatment of pollen related allergic diseases.
3 Progress in gene cloning and recombinant protein production of plant allergens
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-81-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Allergen-specific immunotherapy (SIT) represents one of the few curative approaches toward type I
hyperresponsiveness[23]. But, there are three major problems associated with SIT: first, presently SIT is
performed with natural allergen extracts, containing mixtures of allergens, nonallergenic and/or toxic
proteins, and other macromolecules, which are hard to standardize. Second, systemic administration of
allergen can cause severe IgE-mediated side effects during the treatment on patients, and third,
therapeutically effective dose often cannot be achieved because of non-standardized extracts or side effects.
With the clarification of the nature, sequence and three-dimensional structure of several important
allergens, molecular level recognization of allergens and IgE antibodies will become available. To date,
cDNA sequence of 60 pollen allergens from 27 plant species have been deposited in the allergen databank
(www.allergen.com). Since pure and standardized recombinant allergens can be formulated to replace
natural extracts, using genetic engineered allergens for SIT become a possible and promising method for
immunotherapy. In last decade, a variety of recombinant allergens from plants, mites, molds, mammals and
insects have been expressed using various systems, such as E.coli[24], Pichia[25] and plants[26]. Moreover,
the recombinant allergens can be engineered to reduce the risk of the IgE-mediated side effects. The
molecules with reduced allergenicity (hypoallergen) would not lead to anaphylactic reaction upon injection
and would allow higher-dose administration of allergen, which has showed to be more effective in symptom
reduction than low dose. In this way, high dose of allergen can be administered to allergic patients, which
increases the efficacy of the treatment. Based on this consideration, site-directed mutant and comformation
has been applied in the recombination of hypoallergens[27, 28]. The clinical use of these products may lead
to not only improve diagnostic specificity and sensitivity but also safer and more effective immunotherapy.
4 Summary
As the most widespread species on the earth, plant is a part of the human normal life. It is hard to avoid
plant allergens from trees, grasses and weeds. Although specific immunotherapy represents a curative
approach toward allergy, the mechanism operating in SIT still remains not completely understood. In recent
statistics, there has been a significant increase in the prevalence of allergic disease over the past 2 to 3
decades. Currently, more than 130 million people suffer from the asthma and the numbers are
increasing[29]. There is a research considering that air pollutants from industry and automobiles are
cofactors contributing to recent increase in allergic disease and asthma[30]. On the other hand, man cannot
ignorance transgenic plants are widespread in the modern world, it could be the source for new kind of
allergens.
Hallucinogen
Hallucinogens are a general group of pharmacological agents that can be divided into three broad
categories: psychedelics, dissociatives, and deliriants. These classes of psychoactive drugs have in
common that they can cause subjective changes in perception, thought, emotion and consciousness. Unlike
other psychoactive drugs, such as stimulants and opioids, these drugs do not merely amplify familiar states
of mind, but rather induce experiences that are qualitatively different from those of ordinary consciousness.
These experiences are often compared to non-ordinary forms of consciousness such
as trance,meditation, dreams, or insanity.
L. E. Hollister's criteria for establishing that a drug is hallucinogenic is:
in proportion to other effects, changes in thought, perception, and mood should predominate;
intellectual or memory impairment should be minimal;
stupor, narcosis, or excessive stimulation should not be an integral effect;
autonomic nervous system side effects should be minimal; and
addictive craving should be absent.
Not all drugs produce the same effect and even the same drug can produce different effects in the same
individual on different occasions.
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-82-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Dissociatives
Dissociatives produce analgesia, amnesia and catalepsy at anesthetic doses.[10] They also produce a sense of
detachment from the surrounding environment, hence "the state has been designated as dissociative
anesthesia since the patient truly seems disassociated from his environment."[11] Dissociative symptoms
include the disruption or compartmentalization of "...the usually integrated functions of consciousness,
memory, identity or perception."[12]p. 523 Dissociation of sensory input can cause derealization, the
perception of the outside world as being dream-like or unreal. Other dissociative experiences
include depersonalization, which includes feeling detached from one's body; feeling unreal; feeling able to
observe one's actions but not actively take control; being unable to recognize one's self in the mirror while
maintaining rational awareness that the image in the mirror is the same person.[13][14][15] Simeon (2004)
offered "...common descriptions of depersonalisation experiences: watching oneself from a distance (similar
to watching a movie); candid out-of-body experiences; a sense of just going through the motions; one part
of the self acting/participating while the other part is observing;...."[16]
The primary dissociatives achieve their effect through blocking the signals received by the NMDA
receptor set (NMDA receptor antagonism) and
include ketamine, phencyclidine(PCP), dextromethorphan (DXM), and nitrous oxide.[17][18][19] However,
dissociation is also remarkably administered by salvinorin A's (the active constituent in Salvia
divinorumshown to the left) potent κ-opioid receptor agonism[20] and is notably the most potent
psychoactive chemical harnessed directly from the plant kingdom.[citation needed]
Some dissociatives can have CNS depressant effects, thereby carrying similar risks as opioids, which can
slow breathing or heart rate to levels resulting in death (when using very high doses). DXM in higher doses
can increase heart rate and blood pressure and still depress respiration. Inversely, PCP can have more
unpredictable effects and has often been classified as a stimulant and a depressant in some texts along with
being as a dissociative. While many have reported that they "feel no pain" while under the effects of PCP,
DXM and Ketamine, this does not fall under the usual classification of anesthetics in recreational doses
(anesthetic doses of DXM may be dangerous). Rather, true to their name, they process pain as a kind of "far
away" sensation; pain, although present, becomes a disembodied experience and there is much less emotion
associated with it. As for probably the most common dissociative, nitrous oxide, the principal risk seems to
be due to oxygen deprivation. Injury from falling is also a danger, as nitrous oxide may cause sudden loss of
consciousness, an effect of oxygen deprivation. Because of the high level of physical activity and relative
imperviousness to pain induced by PCP, some deaths have been reported due to the release of myoglobin
from ruptured muscle cells. High amounts of myoglobin can induce renal shutdown.[21] Along with most, if
not all of the chemicals in this article, none of the dissociatives have any physically addictive properties,
though psychological addiction has been observed.
Many users of dissociatives have been concerned about the possibility of NMDA antagonist neurotoxicity
(NAN). This concern is partly due to William E. White, the author of the DXM FAQ, who claimed that
dissociatives definitely cause brain damage.[22] The argument was criticized on the basis of lack of
evidence[23] and White retracted his claim.[24] White's claims and the ensuing criticism surrounded original
research by John Olney.
In 1989, John Olney discovered that neuronal vacuolation and other cytotoxic changes ("lesions") occurred
in brains of rats administered NMDA antagonists, including PCP and ketamine.[25] Repeated doses of
NMDA antagonists led to cellular tolerance and hence continuous exposure to NMDA antagonists did not
lead to cumulative neurotoxic effects. Antihistamines such as diphenhydramine, barbiturates and even
diazepam have been found to prevent NAN.[26] LSD and DOB have also been found to prevent NAN.[27]
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-83-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Deliriants
Deliriants, as their name implies, induce a state of delirium in the user, characterized by extreme confusion
and an inability to control one's actions. They are called deliriants because their subjective effects are
similar to the experiences of people with delirious fevers.
Included in this group are such plants as Atropa belladonna (deadly nightshade), Brugmansia species
(Angel's Trumpet), Datura stramonium (Jimson weed), Hyoscyamus niger(henbane), Mandragora
officinarum (mandrake), and Myristica fragrans (nutmeg), as well as a number of pharmaceutical drugs,
when taken in very high doses, such asdiphenhydramine (Benadryl) and its close
relative dimenhydrinate (Dramamine). Uncured tobacco is also a deliriant due to its intoxicatingly high
levels of nicotine.[28]
In addition to the dangers of being far more disconnected from reality than with other drugs and retaining a
truly fragmented dissociation from regular consciousness without being immobilized, the anticholinergics
are toxic, carry the risk of death by overdose, and also include a number of uncomfortable side effects.
These side effects usually includedehydration and mydriasis (dilation of the pupils).
Most modern-day psychonauts who use deliriants report similar or identical hallucinations and challenges.
For example, diphenhydramine, as well as dimenhydrinate, when taken in a high enough dosage, often are
reported to evoke vivid, dark, and entity-like hallucinations, peripheral disturbances, feelings of being alone
but simultaneously of being watched, and hallucinations of real things ceasing to exist. Deliriants also may
cause confusion or even rage, and thus have been used by ancient peoples as a stimulant before going into
battle.
Traditional use
Psychedelics have a long history of traditional use in medicine and religion, where they are prized for their
perceived ability to promote physical and mental healing. In this context, they are often known
asentheogens. Native American practitioners using mescaline-containing cacti (most notably peyote, San
Pedro, and Peruvian torch) have reported success against alcoholism, and Mazatec practitioners routinely
use psilocybin mushrooms for divination and healing. Ayahuasca, which contains the powerful
psychedelic DMT, is used in Peru and other parts of South America for spiritual and physical healing as
well as in religious festivals.
Taxonomy
Hallucinogens can be classified by their subjective effects, mechanisms of action, and chemical structure.
These classifications often correlate to some extent. In this article, they are classified
as psychedelics,dissociatives, and deliriants, preferably entirely to the exclusion of the inaccurate word
hallucinogen, but the reader is well advised to consider that this particular classification is not universally
accepted. The taxonomy used here attempts to blend these three approaches in order to provide as clear and
accessible an overview as possible.
Almost all hallucinogens contain nitrogen and are therefore classified as alkaloids. THC and salvinorin
A are exceptions. Many hallucinogens have chemical structures similar to those of human neurotransmitters,
such as serotonin, and temporarily modify the action of neurotransmitters and/or receptor sites.
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-84-320.jpg)









![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Quwa (Faculties of Power) are nothing but ability to perform. All organs have been assigned a particular
type of action on the basis of their nature and compositions. The main four faculties of power are Quwwat-e-
Haiwaniyah, Quwwat-e-Nafsaaniyah, Quwwat-e-Tab’iyah and Quwwat-e-Tanaasuliyah and the four vitals
organs i.e. Heart, Brain, Liver, Testes/ Ovaries are responsible for these powers respectively.
Afa’al (Functions) are bodily activities essential for fulfilling the objectives of the body. [The organs and
also testimony perform these to the presence of power in them.]
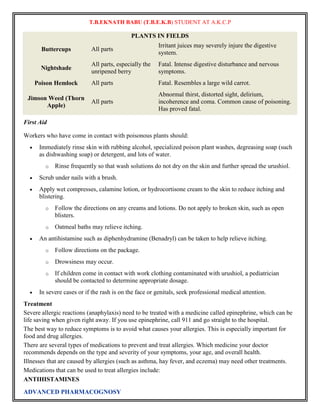
Principles of Homeopathy
Similia Similibus Curanter
This is the law of similars. It states that 'that which can cause can cure'. The onion, which produces tears in
the eye and irritation (similar to a cold), can be used as a homeopathic medicine to cure colds which have
irritating tears. The early Indians recognised this principle and states that Vishasya Vishamevam
Aushadam and Samaha Samena Shantihi, but it was Dr.Samuel Hahnemann, who through his studies and
experiments on the various medicines available in nature, practically proved the law.
Simplex Similimum Minimum
This principle consists of three words.
The first is Simplex i.e : simple medicines not compound should be prescribed. This is the doctrine of single
remedy. Mixture of medicines or polypharmacy is not allowed. Only one medicine must be given at a time.
Similimum - As discussed previously the totality of symptoms of the patient must be taken. This will yield
a picture which corresponds to one medicine, the similimum, which must be given. That medicine which
has been tested on various provers and has produced similar symptoms as that of the patient is the similar
remedy.
Minimum - A low dosage of medicine is recommended. In homeopathy less is more, so medicines of low
potency and given at long intervals have a better impact. Hahnemann, in fact used to give just one dose of
the medicine and wait to see the reaction over a period of time.
Principle of Individualisation
Treat the patient, not the disease. This is the most important doctrine of homeopathy. Not two human beings
are alike and so the medicines used for their treatment need not be alike. Homeopathic medicines are
prescribed based on the totality of symptoms of that individual. So, the name of the disease is not important
to the doctor who tries to get a complete picture of the patient - his symptoms,the modalities of symptoms,
his likes and disliked, his environment, etc to arrive at the individualised remedy - which is the
similimum.
Principle of Potentisation
Homeopathic medicines are diluted in alcohol or milk-sugar(lactose) to make them more palatable and also
to reduce the harmful effects. It has been found that the more the medicine is diluted, the more effective and
powerful it becomes. So, the process of the dilution is called as potentisation and the medicines are referred
to as potencies.The crude homeopathic medicine(eg : Cinchona/Lachesis) is triturated in alcohol to yield the
mother tincture. The mother tincture is denoted by the symbol ø.
Potency :
1x potency of the medicine signifies 1 part of mother tincture diluted with 9 parts of alcohol / milk sugar.
2x potency is 1x of medicine diluted with 9 parts of sugar milk / alcohol.
1C potency is mother tincture diluted with 99 parts.
1M potency is mother tincture diluted with 999 parts.
Low potency : 1x, 3x , 6x (3c), 12x (6c)
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-96-320.jpg)



![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
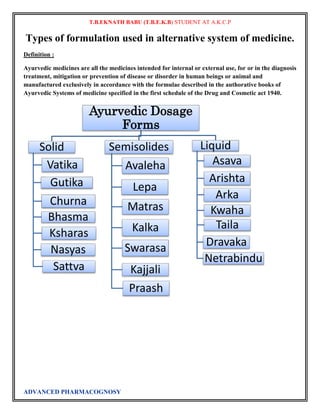
HERBALS AND THEIR FORMULATIONS
Tinctures are concentrated herbal extracts that are made using alcohol and chopped herbs. The tincture is
especially effective in drawing out the essential compounds of plants, especially those that are fibrous or
woody, and from roots and resins.[1] Since this method ensures that the herbs and their nutrients can be
preserved for a long time, it is often mentioned in herbal books and remedies as a preferred way of using
herbs.
In addition, many herbalists love tinctures for other beneficial reasons, such as their being easy to carry,
their utility for long-term treatments, and their ability to be absorbed rapidly, as well as allowing for
immediate dosage changes.[2] As well, should the tincture prove bitter, it's easily added to juice to disguise
the flavor. Another benefit of tinctures is that they keep nutrients from the plants in a stable, soluble form
and they retain the volatile and semi-volatile ingredients that are otherwise lost in heat-treatment and
processing of dry herbal extracts.
Fresh Herb
• Finely chop or grind clean herb to release juice and expose surface area.
• Fill jar 2/3 to 3/4 with herb. ~ OR ~ Fill jar 1/4 to ½ with roots.
• Pour alcohol over the herbs. Cover completely!
• Jar should appear full of herb, but herb should move freely when shaken.
Dried Herb
• Use finely cut herbal material.
• Fill jar 1/2 to 3/4 with herb ~ OR ~ Fill jar 1/4 to 1/3 with roots.
• Pour alcohol over the herbs. Cover completely!
• Roots will expand by ½ their size when reconstituted!
Purchase quality alcohol. The preferred type of alcohol for producing a tincture isvodka.[3] This is owing
to its being colorless, odorless, and fairly flavorless. If you cannot obtain vodka, brandy, rum, or whiskey
can be substituted. Whatever alcohol is chosen, it must be 80 proof (namely, 40% alcohol) to prevent
mildewing of the plant material in the bottle.It is also possible to make a tincture from quality apple cider
vinegar or glycerin.[4] The alternatives may work better where the patient refuses alcohol.
Use a suitable container. The container for the tincture should be glass or ceramic. Avoid using metallic or
plastic containers because these can react with the tincture or leach dangerous chemicals over time. Items
such as a Mason jar, a glass bottle with an attached stopper, etc., are ideal for steeping a tincture. In
addition, you will need to get some small dark glass tincture bottles for storing the tincture in once it has
been made; these bottles should have a tight screw-on or tight clip-on lid to prevent air intrusion during
storage but to allow for ease of use. Ensure that all containers are both washed clean and sterilized prior to
use.
Prepare the tincture. You can prepare a tincture by measurement or by sight; it really depends on your
level of comfort with simply adding herbs and judging by eye, or whether you feel more comfortable adding
them by measured weight. Also, you should know whether you want to add fresh, powdered, or dried
herbs to the tincture. Some suggestions for adding the herbs in the order of fresh, powdered, or dried are as
follows:
Add enough fresh chopped herbs to fill the glass container. Cover with alcohol.[5]
Add 4 ounces (113g) of powdered herb with 1 pint (473ml) of alcohol (orvinegar/glycerin).[6]
Add 7 ounces (198g) of dried herb material to 35 fluid ounces (1 liter) of alcohol (or vinegar/glycerin).
Using a butter knife, stir around the edge of the glass container to ensure that air bubbles are broken.
Seal the container. Place it into a cool, dark area; a cupboard shelf works best. The container should be
stored there for 8 days to a month.[7]
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-102-320.jpg)
![T.B.EKNATH BABU (T.B.E.K.B) STUDENT AT A.K.C.P
Shake the container regularly. Humbart Santillo recommends shaking it twice a day for 14 days,[8] while
James Wong recommends shaking it occasionally.[9]
Be sure to label the steeping tincture so that you know what it is and the date on which it was made. Keep it
out of the reach of children and pets.
Strain the tincture. Once the steeping time is finished (either the tincture instructions you're following will
inform you of this or you'll know already from experience but if not, about two weeks is a good steeping
time), strain the tincture as follows:
Place a muslin cloth across a sieve. Place a large bowl underneath to catch the strained liquid.
Gently pour the steeped liquid through the muslin-lined sieve. The muslin will capture the plant material
and the liquid will pass through into the bowl underneath.
Press the herb material with a wooden or bamboo spoon to squeeze out some more liquid, and lastly, twist
the muslin to extract any leftover liquid from the herbs.
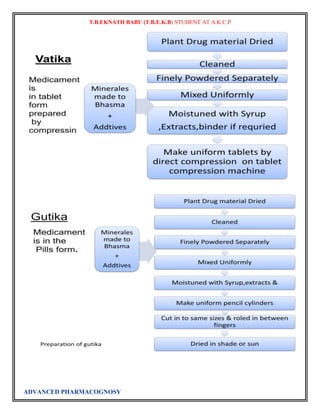
Burdock Root Extract
Natural healers use this
herb as an effective
blood purifier, believing
that it rids the body of
toxins. Excellent for
arthritis and applied
externally for skin
problems. Burdock is
still used today as a
diuretic, and to support
the healing of chronic
acne and psoriasis.
Butchers Broom
Extract
For centuries European
herbalists have used this
herb to relieve water
retention and to treat the
discomfort and pain
caused by poor
circulation in the legs.
This plant contains
steroid-like compounds
that may constrict veins
and reduce inflammation
caused by arthritis and
rheumatism.
ADVANCED PHARMACOGNOSY
Capsicum Tincture
Capsicum tincture
produces a local
stimulant and analgesic
effect. Use in cases of
pain along the spinal
nerves and other nerve
endings, nerve root
syndrome, inflammation
of the voluntary muscles,
lower back pain, and
pain in the hips. Do not
use in case of
hypersensitivity.
How to Make Herbal Syrups
Herbal syrups are not hard to make and are a good alternative way to prepare some mixtures especially
some of the herbs that are really bitter. Some of the herbs are bitter which serves a natural purpose – it keeps
us from overusing and also stimulates digestive juices. The bitterness can also make us not want to take the
medicine, especially children. Syrups help in this area and also it can extend the storage life of the herb.
Syrups are good to use for colds and flu and to soothe a sore throat.
Make sure you never use honey for children younger than one to two years old.
First decide which herb you want to use
For a basic syrup you can use a infusion or decoction that you have made.
Put 1 part infusion or decoction to 1 part honey or sugar in a saucepan
Gently heat this until the sugar or honey is completely dissolved.
Cool slightly and pour into clean glass or ceramic jars or bottles
Keep in the refrigerator for three to six months
You can use 1 to 2 teaspoons of the syrup up to three times a day.
A really popular herbal syrup is elderberry syrup, you can make it with fresh or dried berries. There are
red and blue elderberries, the red ones have seeds that are toxic so use the blue ones. Or just buy some dried
elderberries. It is good for cold and flu among other things.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fullcopy-141005025502-conversion-gate01/85/Advanced-Pharmacognosy-Notes-103-320.jpg)