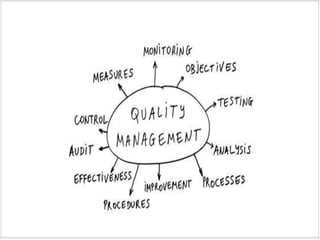
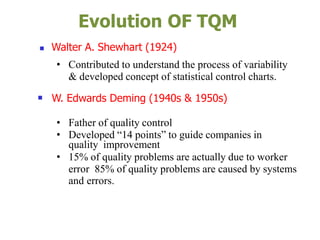
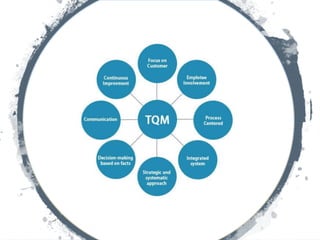
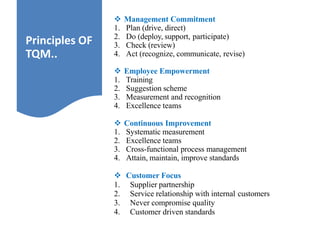
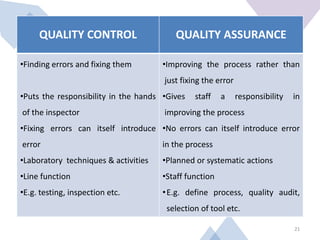
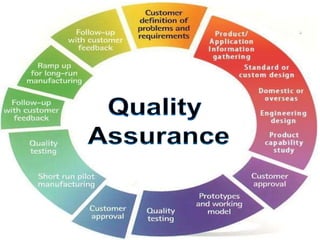
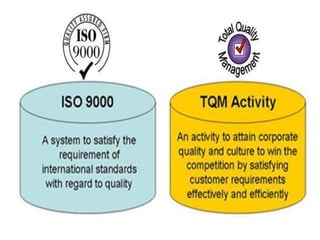
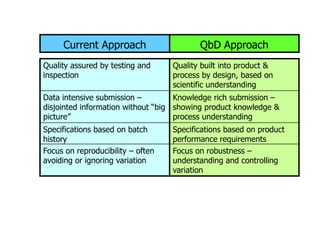
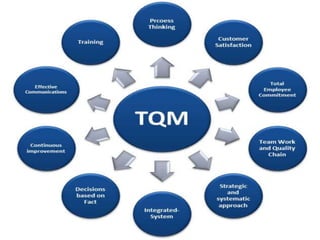
The document outlines the importance of total quality management (TQM) and its impact on organizational success, emphasizing that quality will determine a company's future. It discusses key concepts, principles, and historical figures in quality management, including contributions from Deming and Juran, and contrasts quality control with quality assurance. Additionally, it highlights the benefits of TQM, such as improved profitability, customer satisfaction, and employee morale.