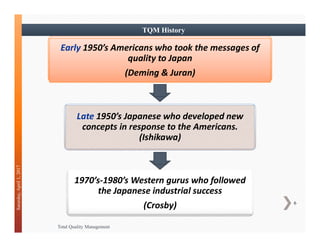
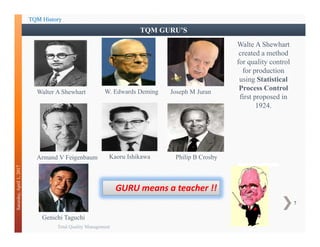
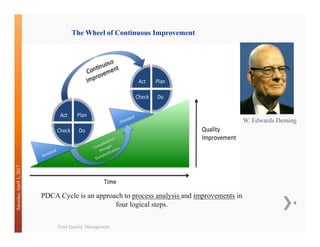
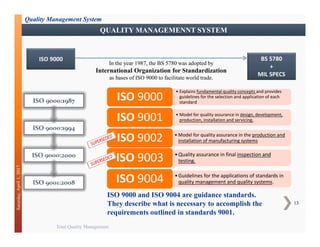
This document discusses Total Quality Management (TQM). It provides an overview of TQM principles and history, including contributions from quality gurus like Deming, Juran, and Crosby. It also describes the evolution of quality standards like ISO 9000 and how a quality management system can be implemented based on a process approach across an organization.












![Total Quality Management
18
Saturday,April1,2017
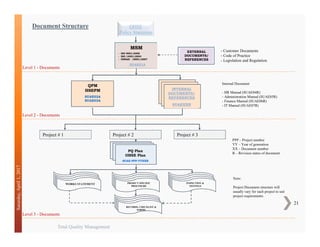
MANAGEMENT RESPONSIBILITY
- Management Commitment
- Policies, Objectives
- Customer Satisfaction
- Management Review
- Quality Planning
- Communication of Responsibility/Authority
RESOURCE MANAGEMENT
- Identification of Resources
- Management Approvals
- Implementation / Provision of Resources
- Competence, Awareness & Training of
Personnel
- Infrastructure & Facilities of Works
PRODUCT REALIZATION
- Project Requirements
- Tender Reviews
- Establishment of Processes/Procedures
- Mobilization of Resources
- Procurement of Materials
- Execution Methods
- Control of Resources and Products (Projects)
- Control of Measuring & Testing Equipment.
MEASUREMENT, ANALYSIS
AND IMPROVEMENT
- Client Feedbacks, Complaints
- Client Satisfaction Surveys
- Information about Competitors
- Process & Product Non conformances
- Internal Audits
- Financial Assessments
- Corrective & Preventive Actions.
Continual Improvement of Quality Management System
Product/Service
[Completed Projects]
Output
Customers
Requirements
Satisfaction
Customers
Input
Model of a Process-Based Quality Management System](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/isoandtqm-170401133113/85/Iso-and-tqm-18-320.jpg)