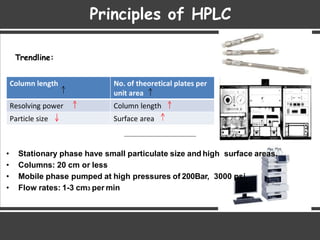
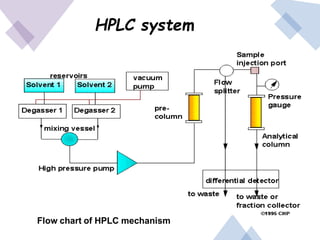
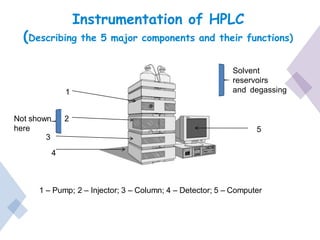
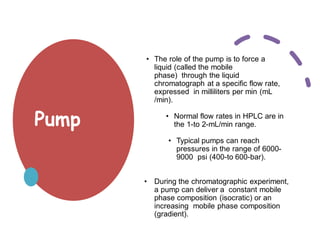
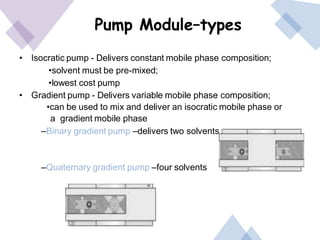
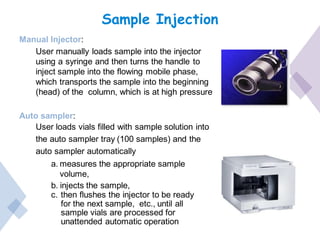
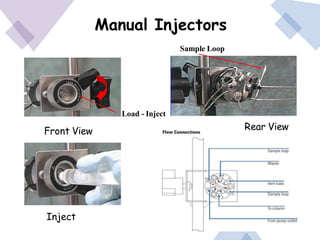
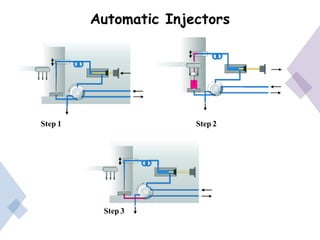
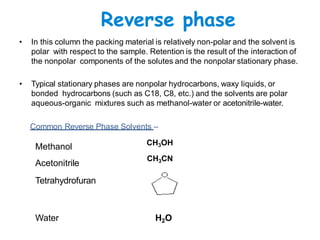
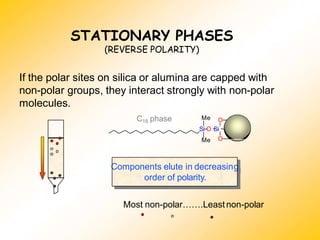
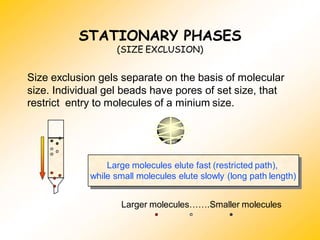
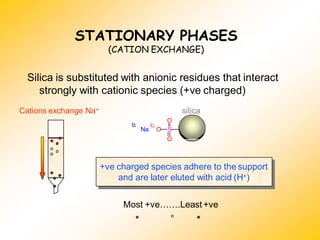
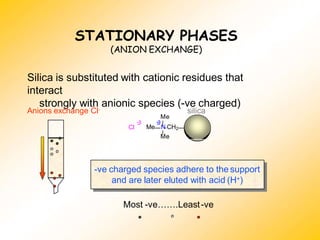
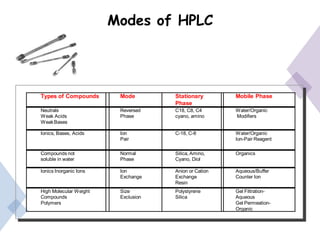
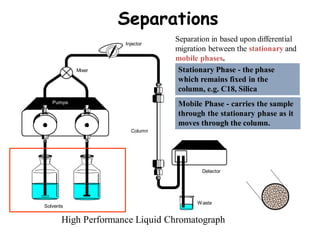
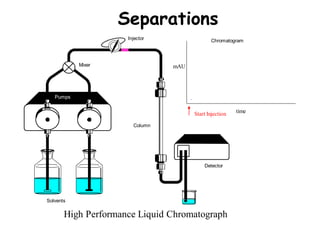
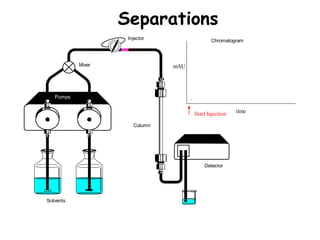
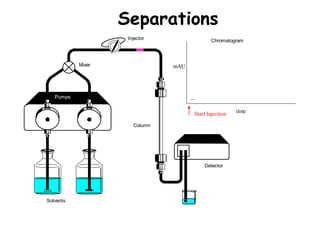
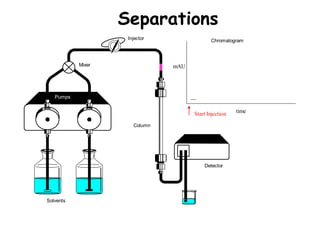
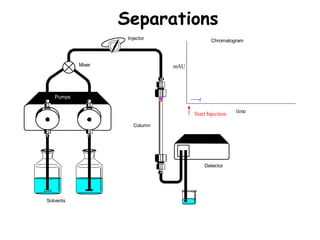
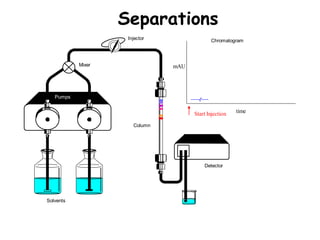
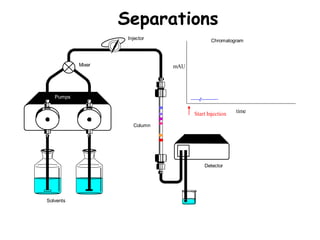
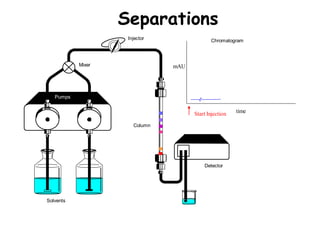
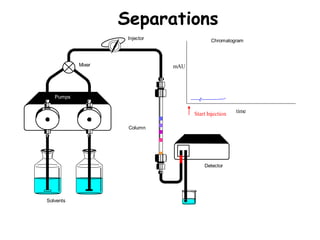
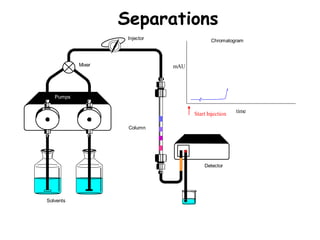
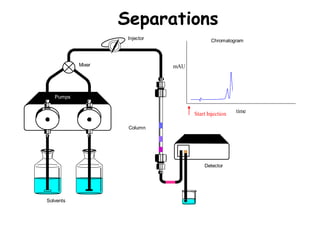
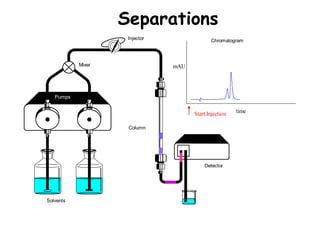
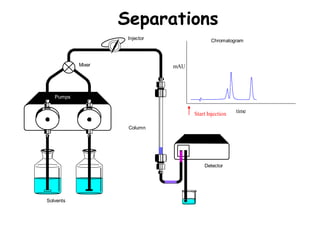
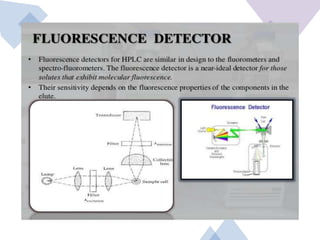
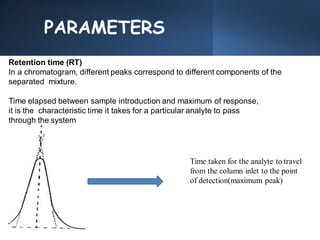
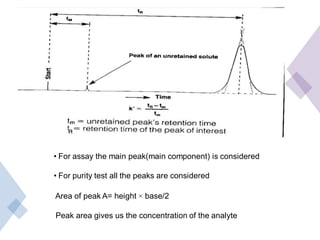
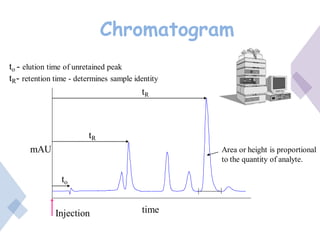
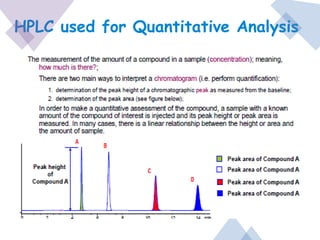
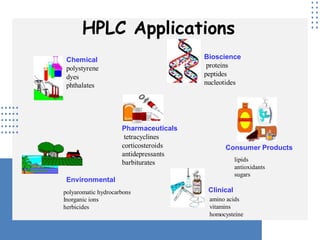
High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) is a separation technique that involves injecting a small volume of liquid sample into a column packed with tiny particles. Individual components of the sample are then transported through the column by a mobile phase and separated based on interactions with the stationary phase. These separated components exit the column and are detected, providing a chromatogram. HPLC uses small particle sizes, high column pressures up to 6000-9000 psi, and flow rates of 1-3 mL/min to achieve fast, efficient, and high resolution separations of both volatile and non-volatile compounds.