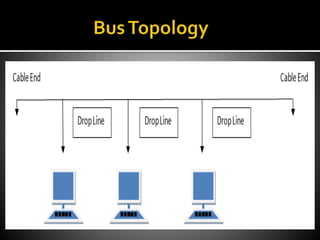
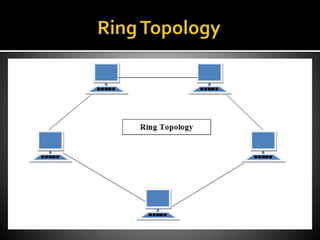
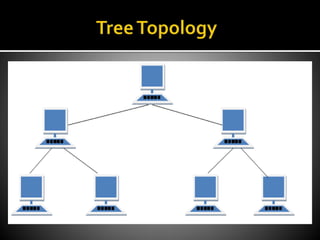
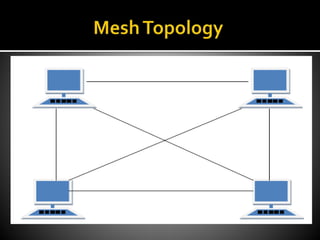
The document outlines various types of network topologies, including bus, ring, star, tree, and mesh topologies, detailing their characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Each topology has unique features, such as cost-effectiveness and ease of expansion for bus topology, the sequential data flow in ring topology, and the centralization of star topology. Additionally, it highlights the complexities and challenges in installation, maintenance, and performance in different network structures.