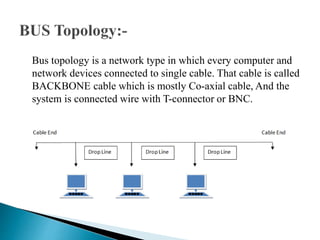
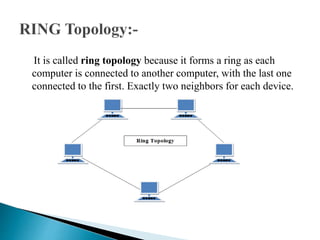
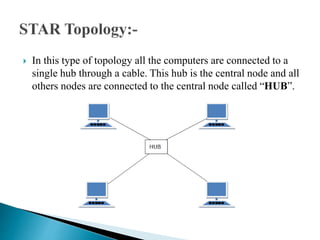
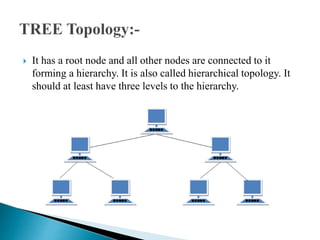
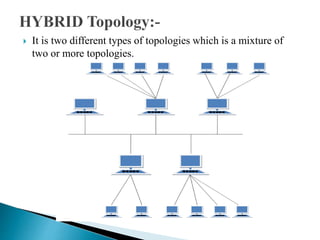
This document discusses network topology, which refers to the arrangement of elements like nodes and links in a communication network. There are several common network topologies including bus, ring, star, mesh, tree, and hybrid. Each has advantages and disadvantages related to aspects like cost, performance, scalability, and fault tolerance. The document provides details on the characteristics of each topology type and their applications in network design.