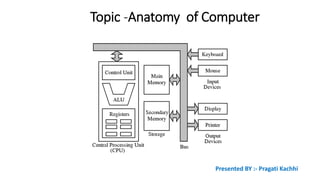
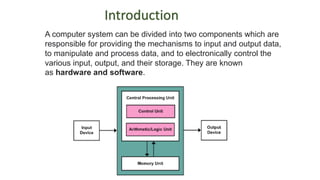
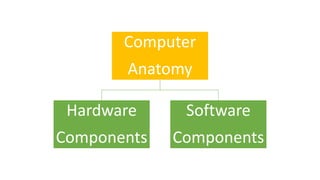
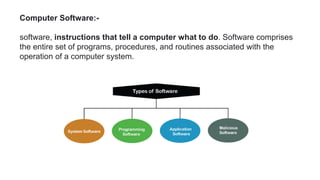
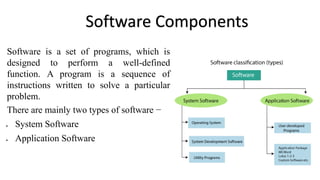
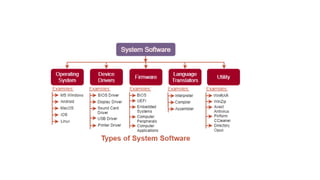
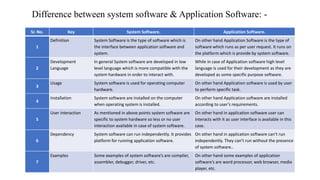
The document presents an overview of computer anatomy, dividing it into two main components: hardware and software. It details various types of computers (micro, mini, mainframe, and supercomputers) and their purposes, alongside classifications based on working principles. Additionally, the document distinguishes between system software and application software, highlighting their characteristics, development languages, usage, and examples.