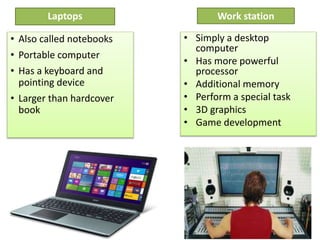
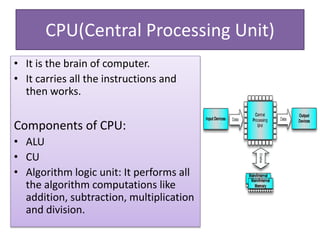
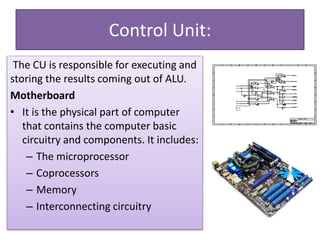
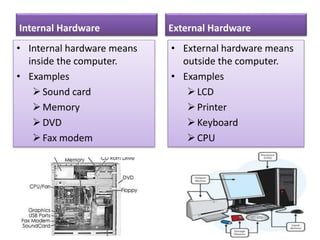
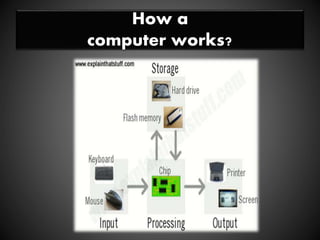
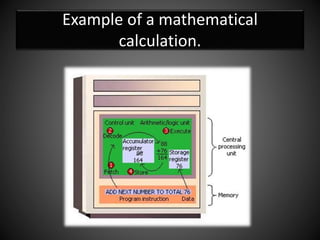
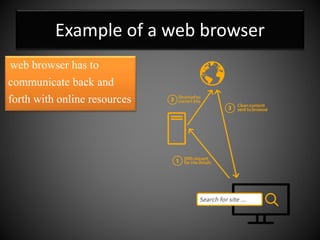
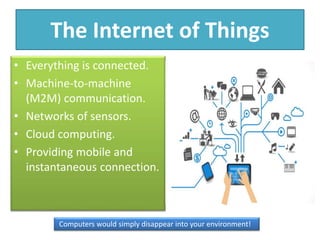
The document explains the concept of a system and its characteristics, types of systems, and provides a detailed overview of computers and computer systems, including their types, components, and software. It also discusses future trends in computing, such as the Internet of Things, virtual and augmented reality, and advancements in wireless technology. The document categorizes hardware into input, output, processing, and storage devices while differentiating between system software and application software.