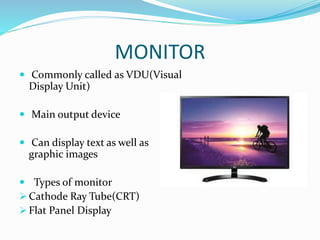
The document discusses various input and output devices used in computing. It describes common input devices like the keyboard, mouse, scanner, microphone and joystick. It also covers output devices such as the printer, monitor, speakers and storage devices including the hard disk, floppy disk, optical media, flash drive and zip disk.