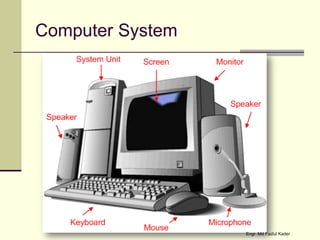
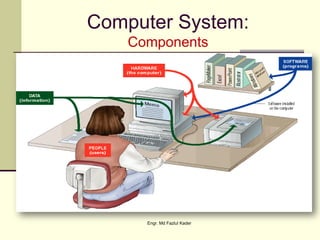
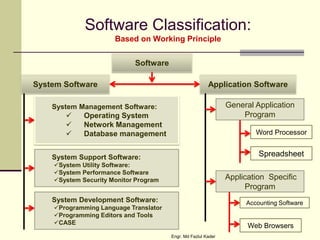
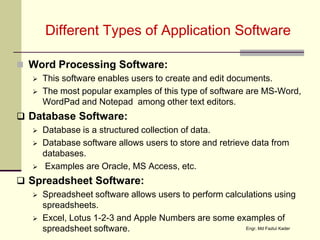
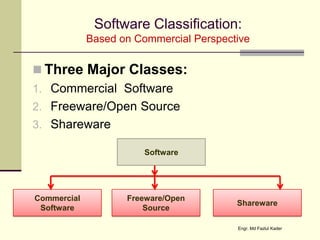
This document discusses the components of a computer system, including hardware, software, humanware, and data/information. It describes the main hardware components such as the CPU, memory, storage, input/output devices. It also covers the different types of software like system software and application software, and discusses commercial, freeware, and shareware models. Humanware refers to the user interface and experience. Data is raw facts while information is structured data that can influence decisions.



























![Computer System:
Data /Information
Examples
1,Rahim,3,
V,name,2,VI,Roll.
Munir,
VII
Karim,Class
Roll Name Class
1 Karim V
2 Rahim VI
3 Munir VII
Data[Unstructured] Information[Data +Structure]
Engr. Md Fazlul Kader](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerhwsw-150214034814-conversion-gate02/85/Computer-hw-sw-35-320.jpg)

