This document provides an introduction to computers including:
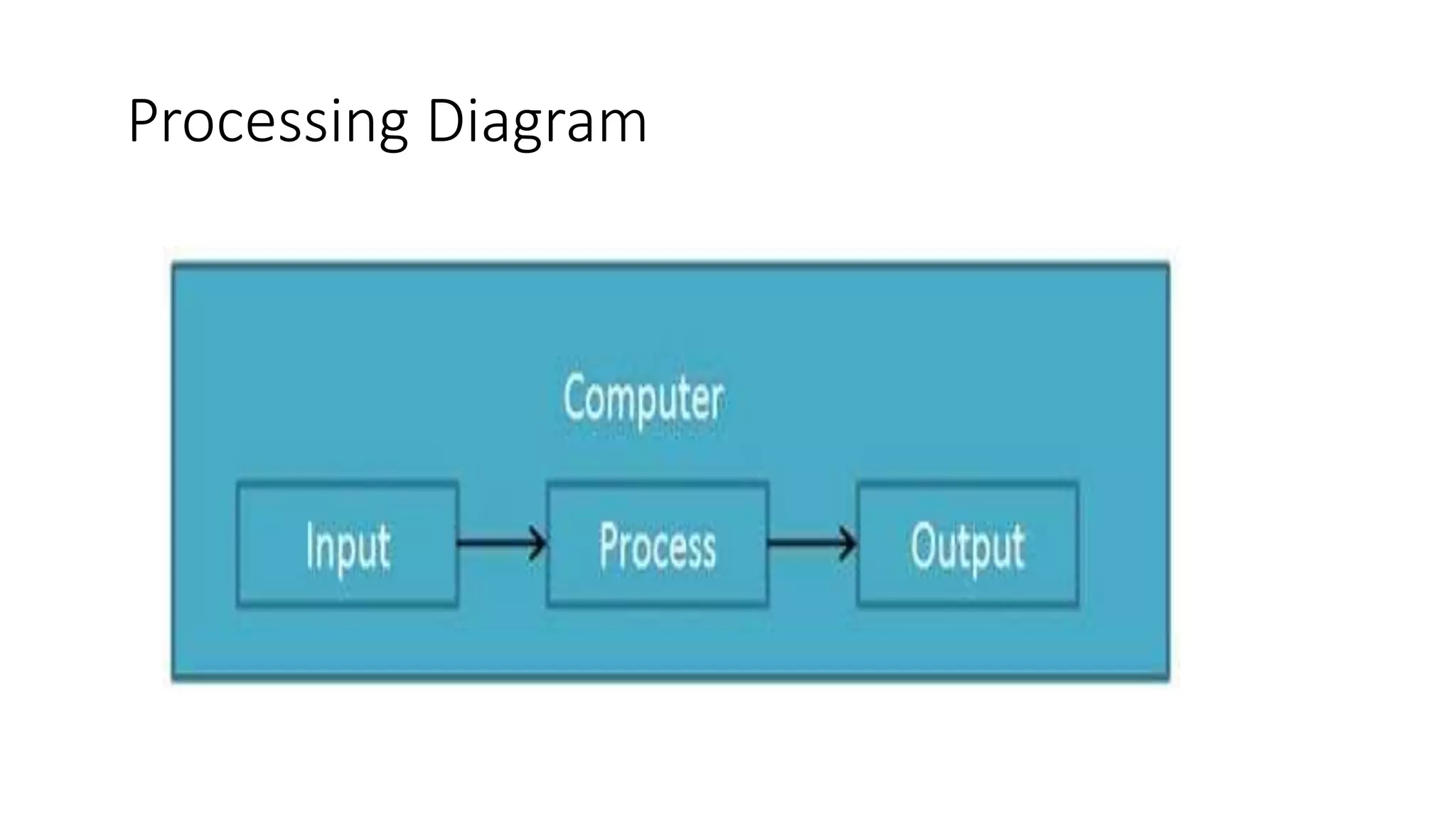
- Computers take in raw data as input, process it under a program's instructions to produce output which is saved for future use.
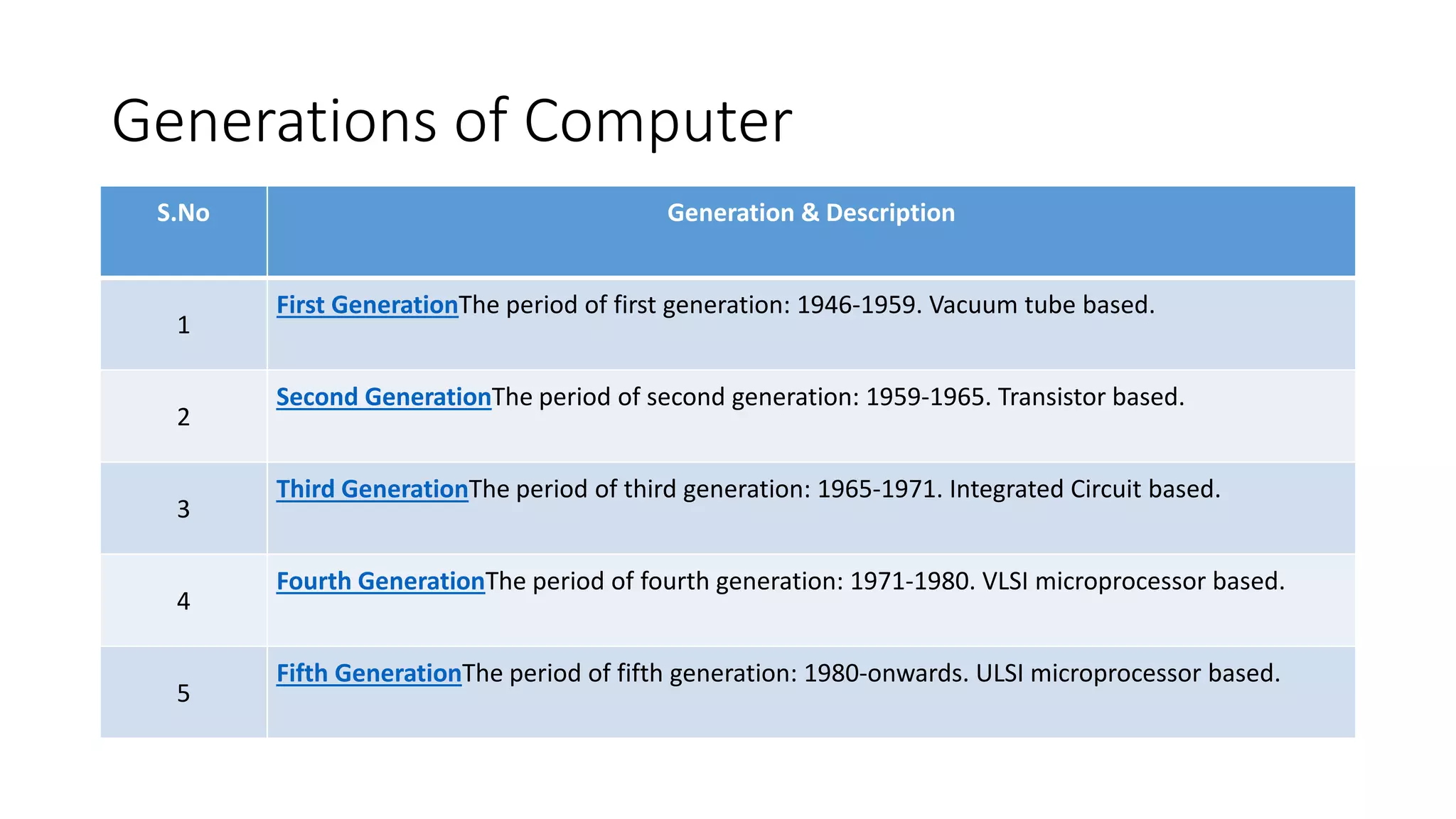
- Generations of computers progressed from vacuum tubes to transistors to integrated circuits to modern microprocessors.
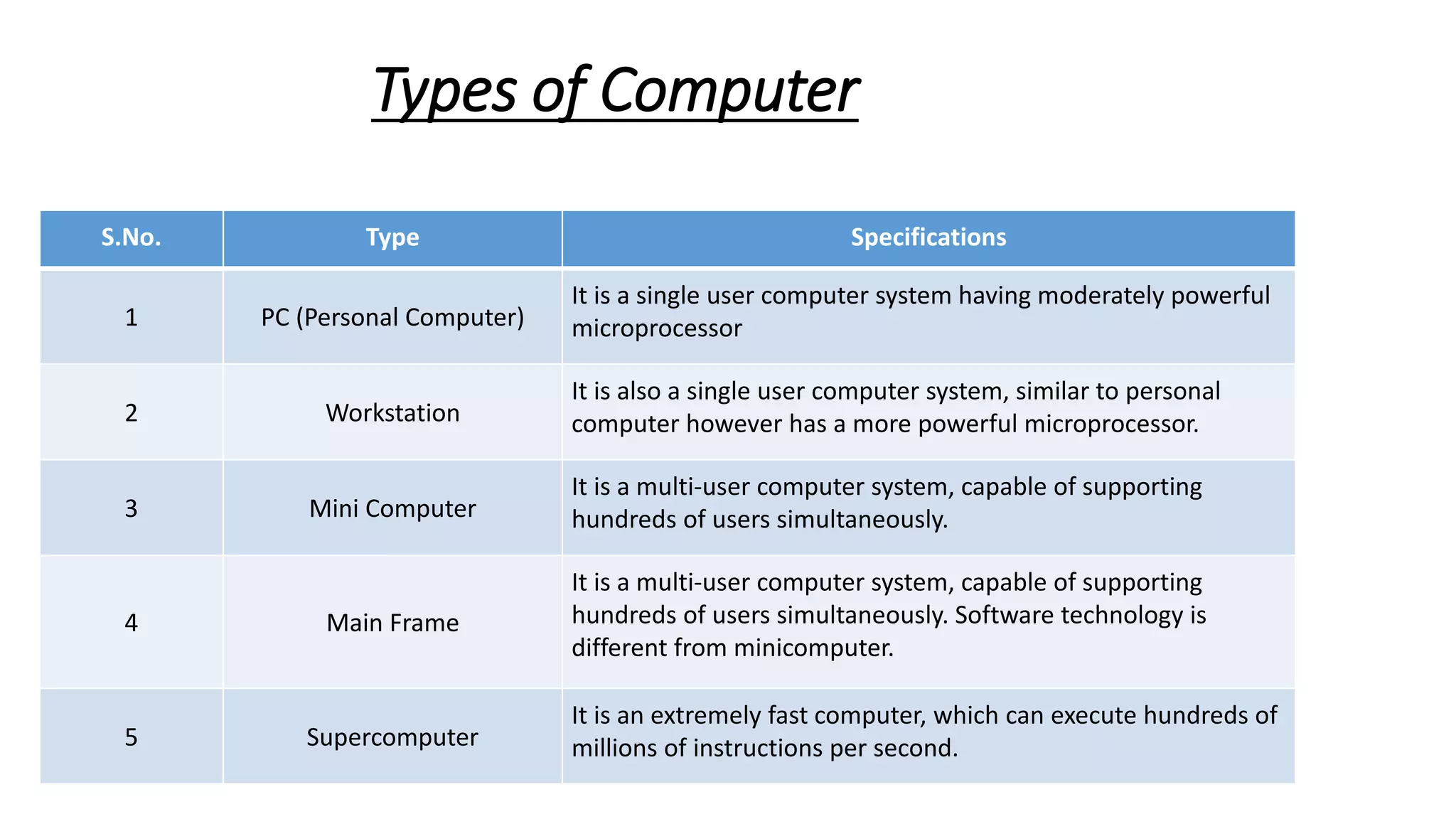
- Common computer types include PCs, workstations, mini computers, mainframes, and supercomputers.
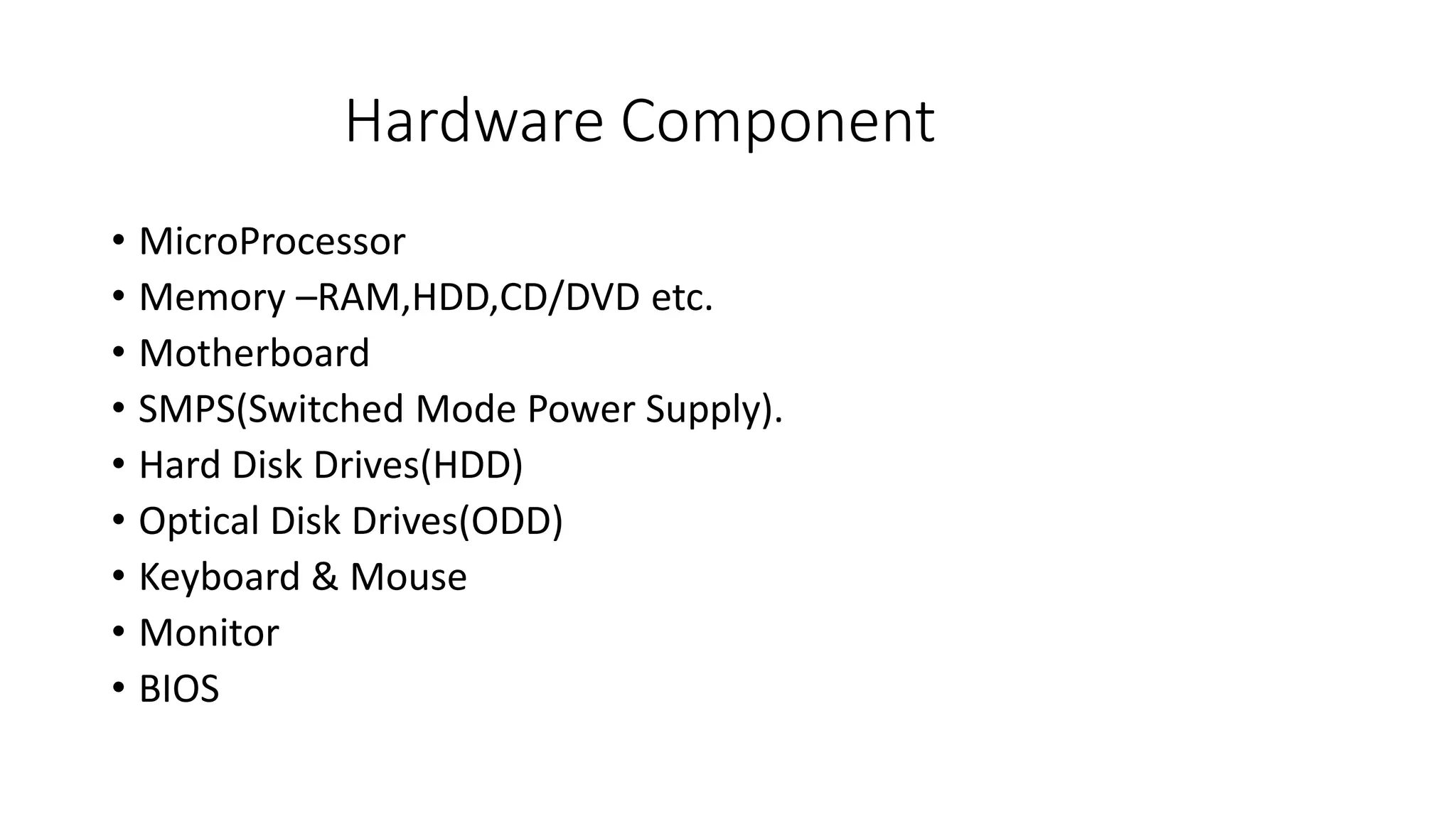
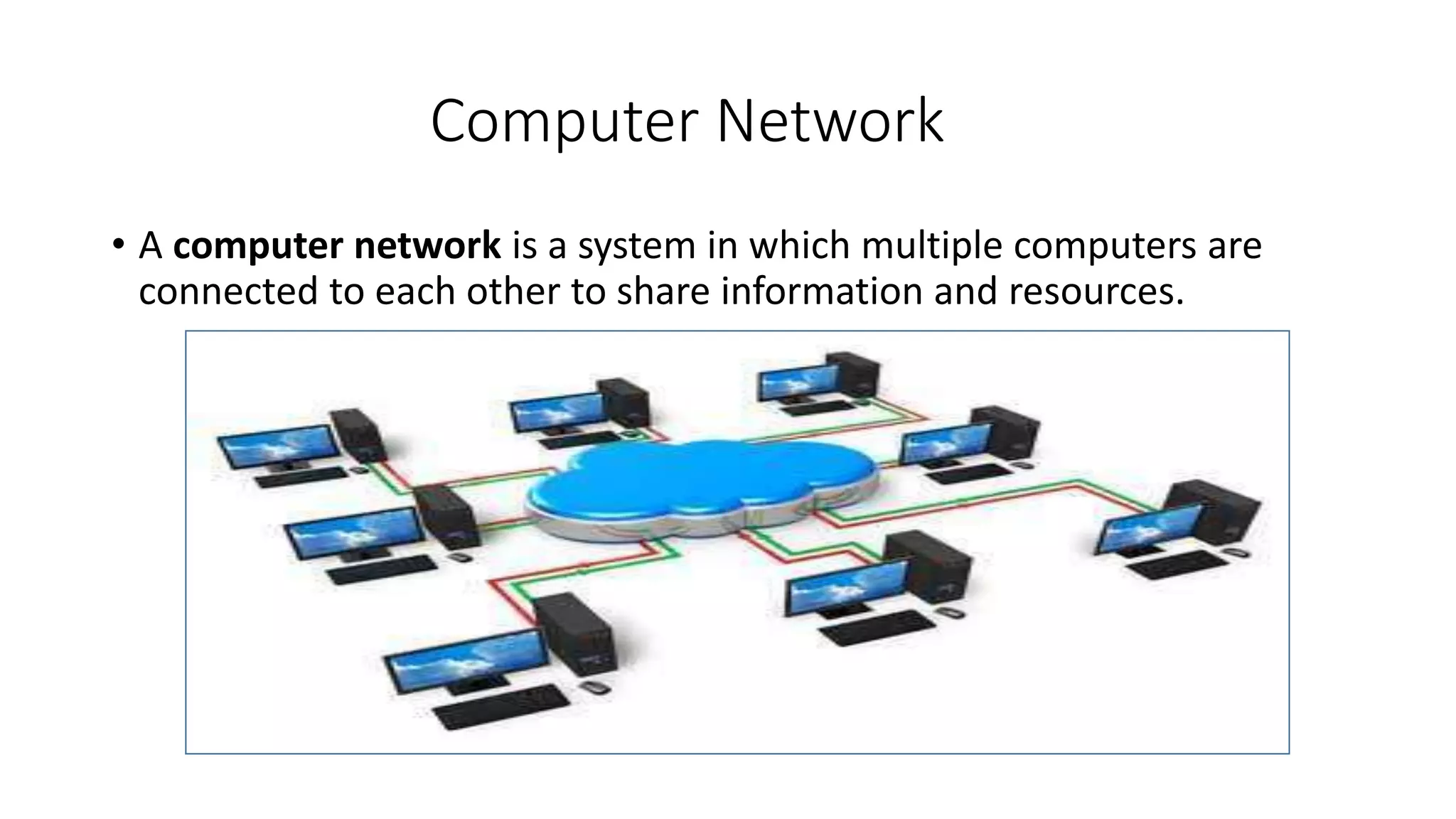
- Basic computer components are hardware, software, and networks. Hardware includes input/output devices and internal components. Software is divided into system software and application software.