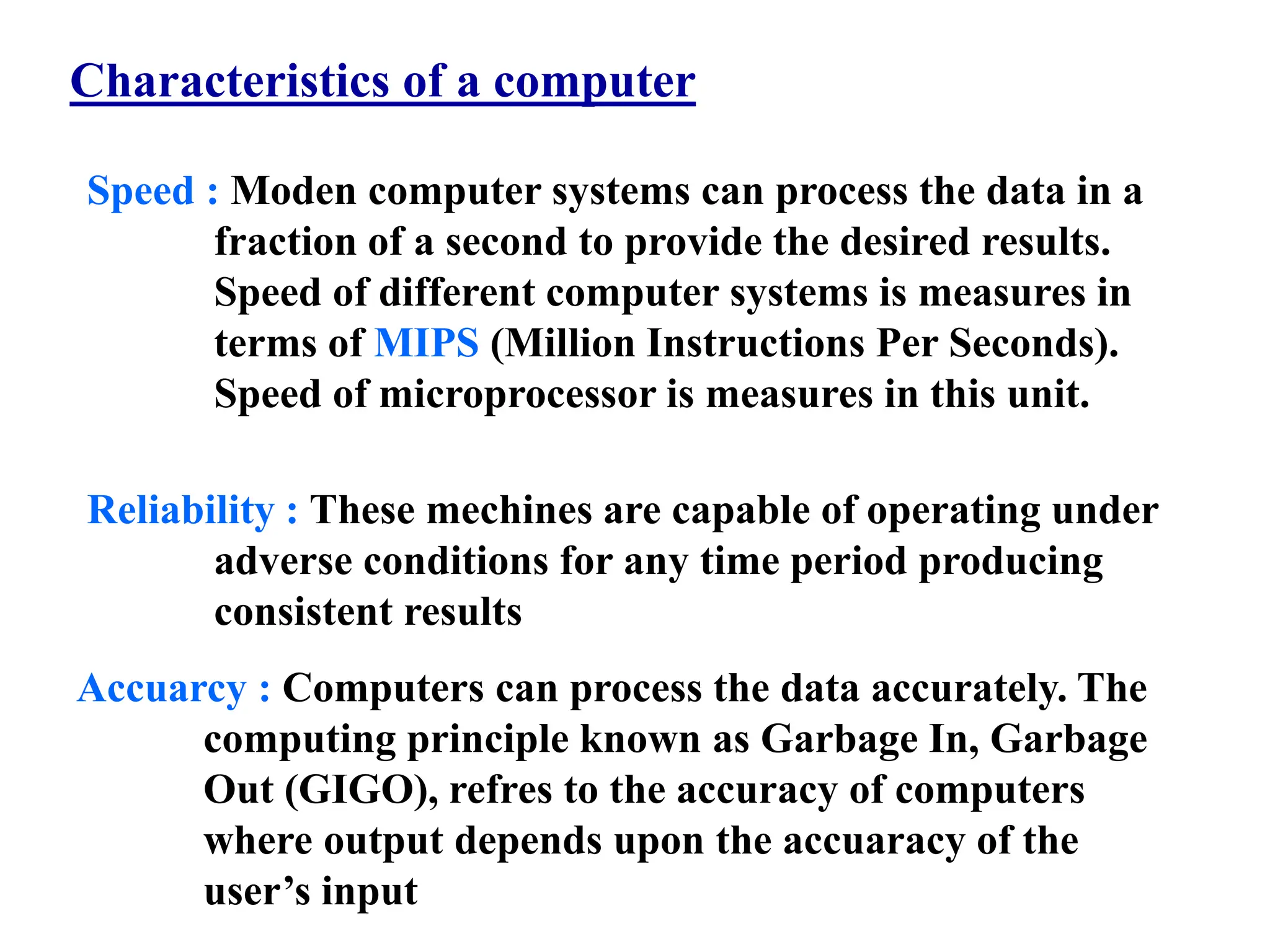
1. Computers are electronic machines that can perform calculations quickly and accurately under the control of stored instructions called programs.
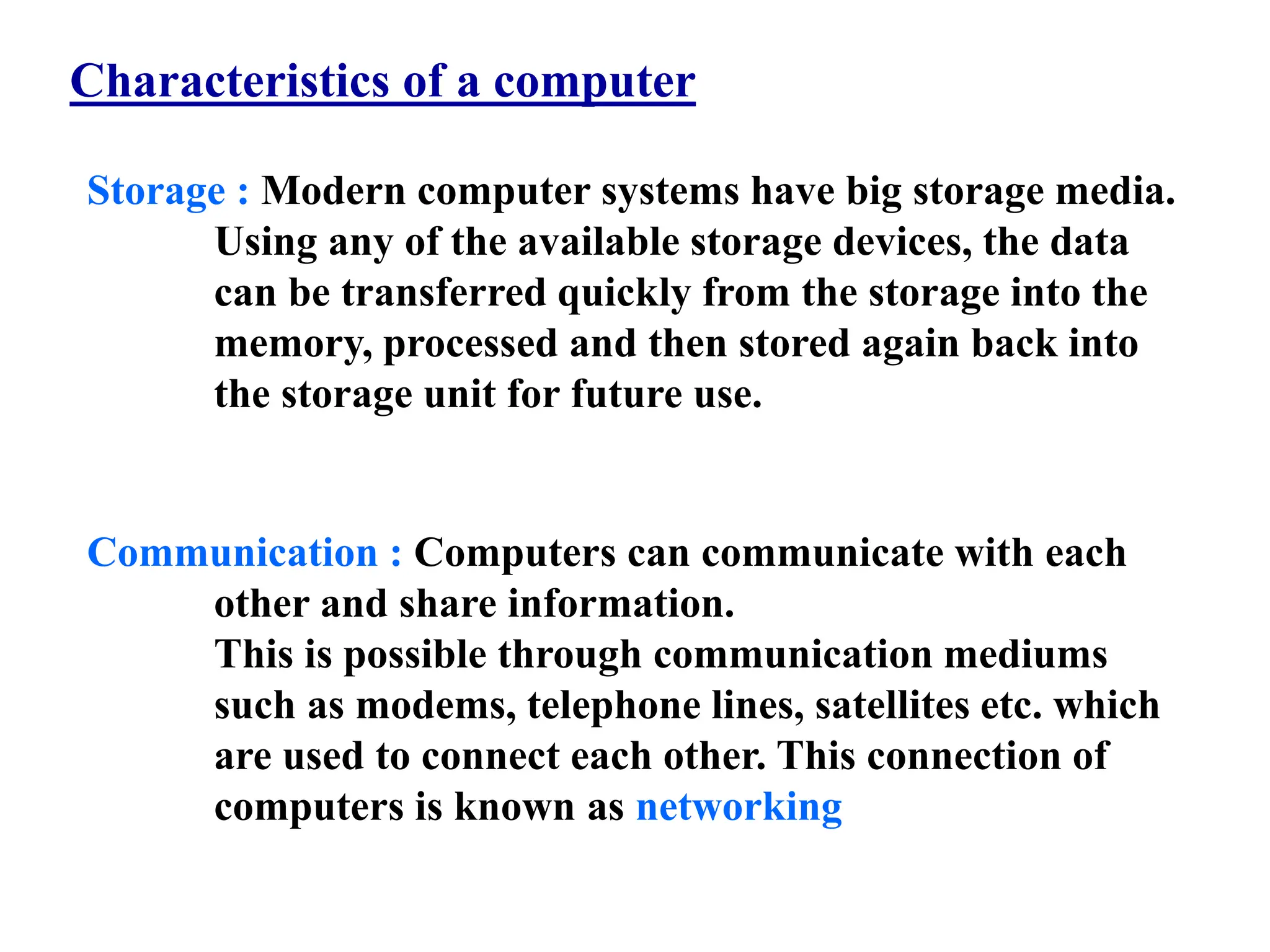
2. Computers accept data as input, process it, and provide the results as output. They have high-speed processing capabilities and can reliably store and retrieve large amounts of data.
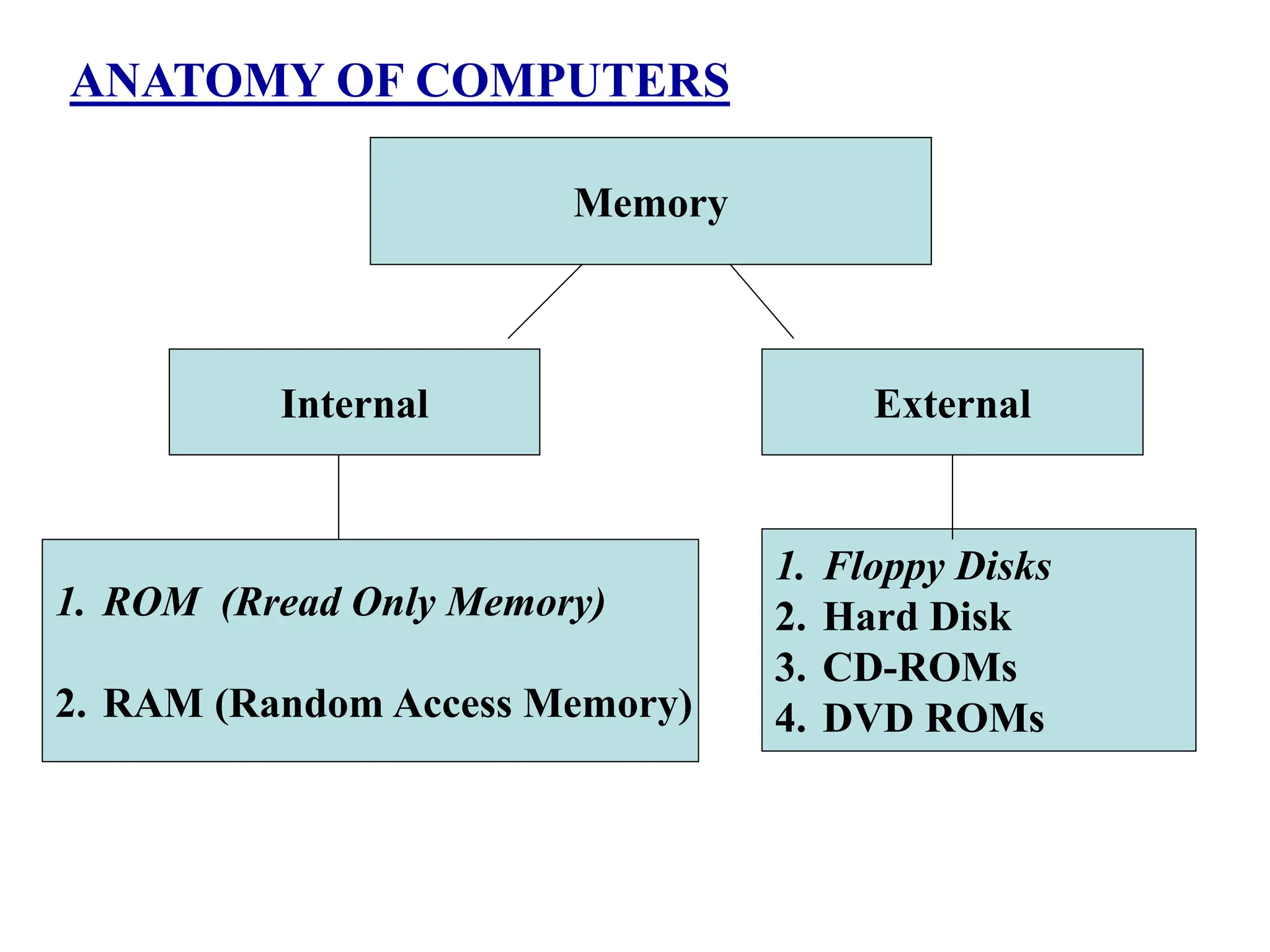
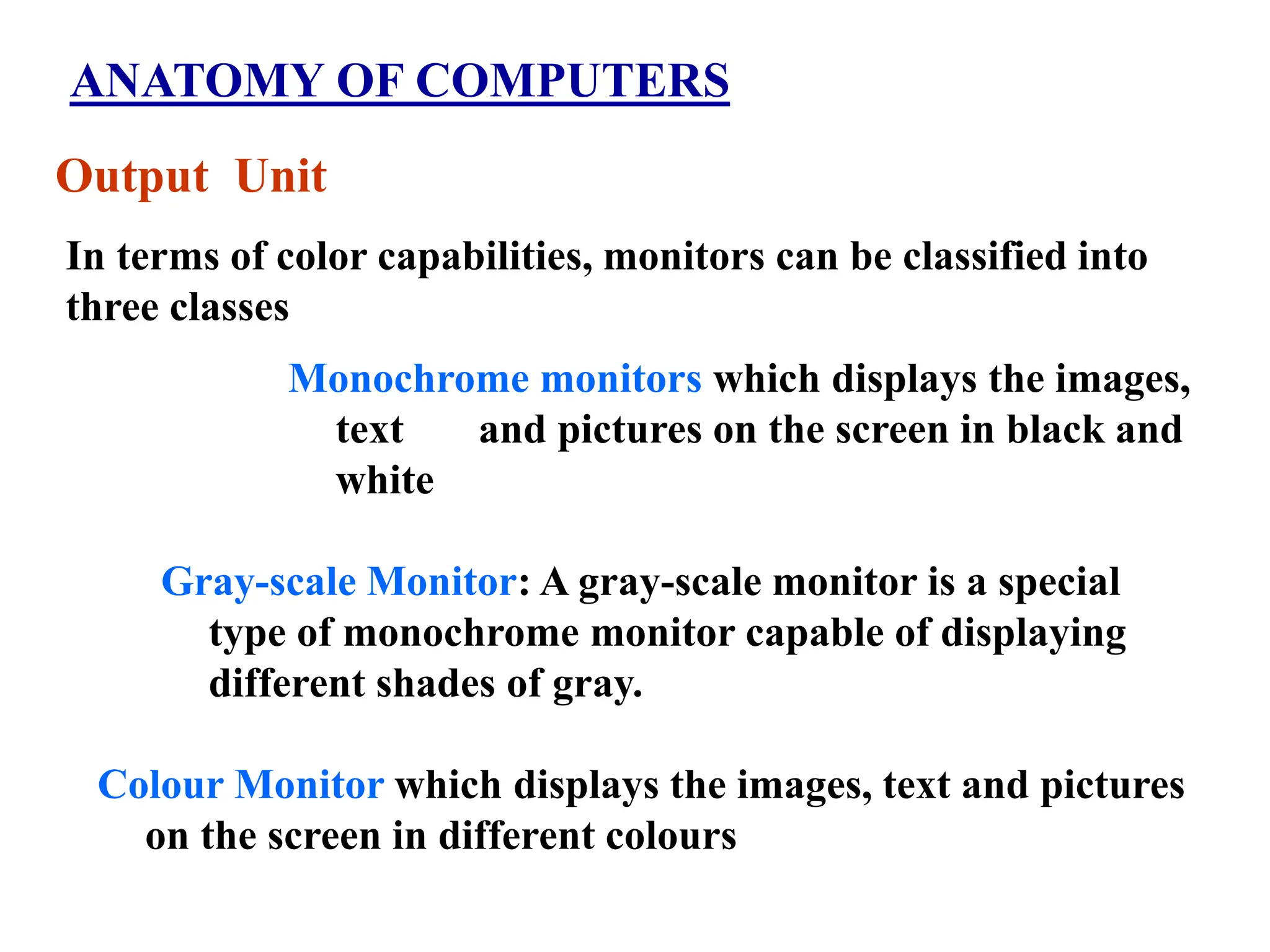
3. Common computer components include the central processing unit, memory, storage devices, input/output mechanisms, and software programs. Computers are widely used in many applications such as business, education, science and entertainment.