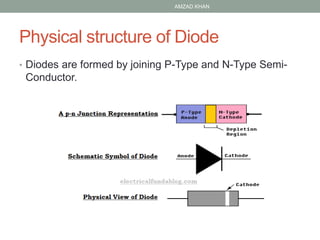
1. A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in only one direction. It has a p-type and n-type semiconductor junction.
2. Under forward bias, current flows easily from the p-type to the n-type side. Under reverse bias, very little current flows.
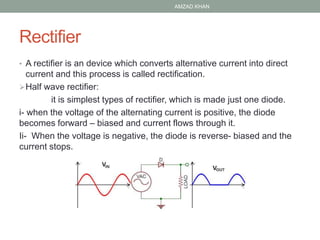
3. Common diode applications include rectification circuits (half-wave, full-wave, and bridge rectifiers), which convert alternating current to direct current. Rectifiers use the one-way conduction of diodes to filter out the negative portions of the AC waveform.