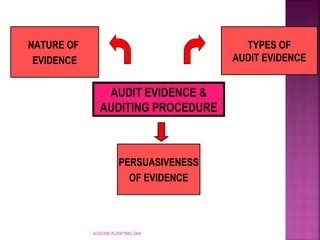
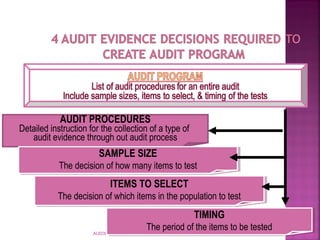
This document discusses audit evidence and auditing procedures. It defines audit evidence as any information used by the auditor to determine if information being audited is stated according to established criteria. It lists six types of audit evidence: physical examination, confirmation, documentation, analytical procedures, inquiries, and re-performance. It also discusses factors that determine the persuasiveness of audit evidence, including appropriateness, sufficiency, and reliability.