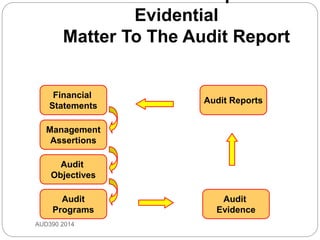
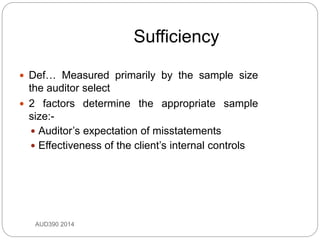
This document discusses audit evidence and auditing procedures. It defines audit evidence as information used by the auditor to arrive at conclusions to support the audit opinion. Audit procedures are actions taken to acquire evidence. The document outlines different types of audit evidence like physical examination, confirmation, documentation, analytical procedures, inquiries, re-performance, and observation. It discusses the characteristics of appropriate evidence including relevance, independence, and timeliness. The document also covers sufficiency of evidence and different types of audit procedures.