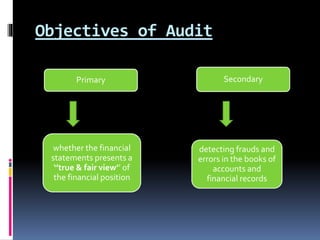
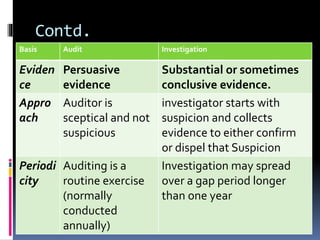
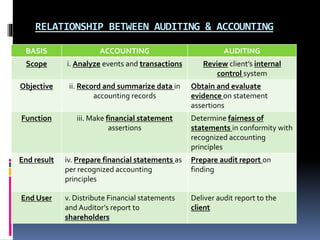
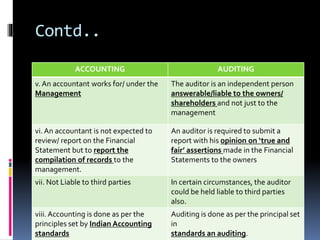
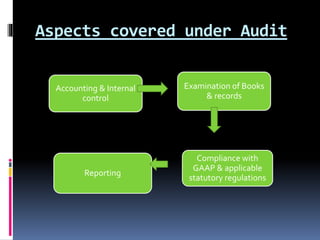
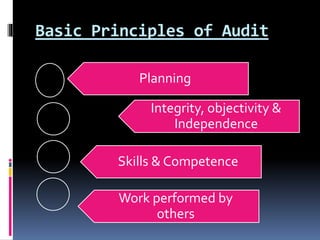
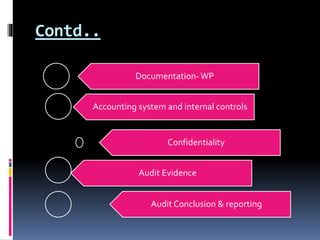
This document defines auditing and outlines the key concepts and principles of auditing. It begins by defining auditing as the accumulation and evaluation of evidence about information to determine the degree of correspondence between the information and established criteria. The document then discusses the objectives of auditing, which include detecting errors and fraud, and determining if financial statements present a true and fair view. It also covers the basic principles that govern audits, such as integrity, objectivity, competence, audit planning, documentation, accounting systems, audit evidence, and reporting. Overall, the document provides a comprehensive overview of the fundamental concepts in the practice of auditing.