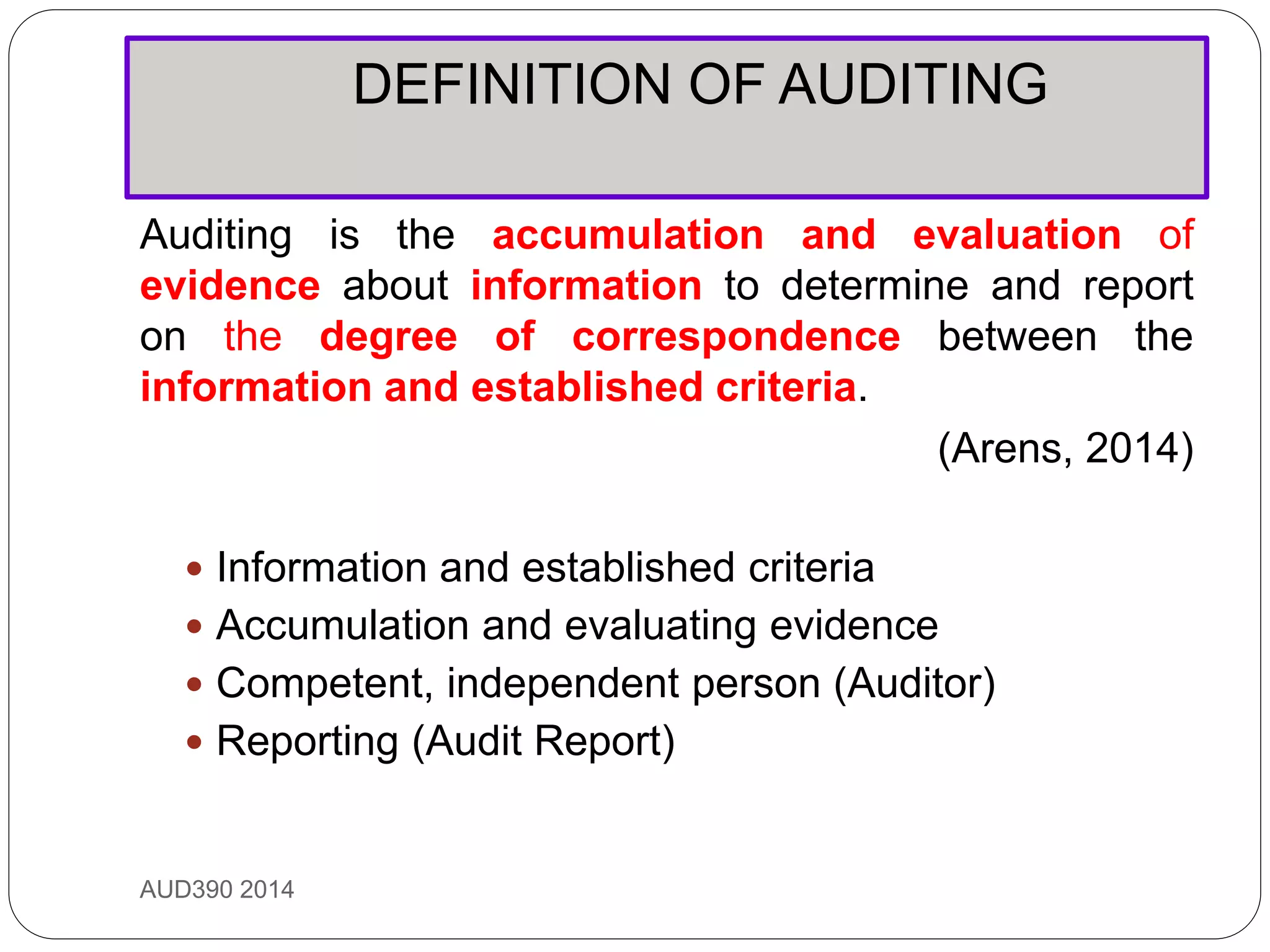
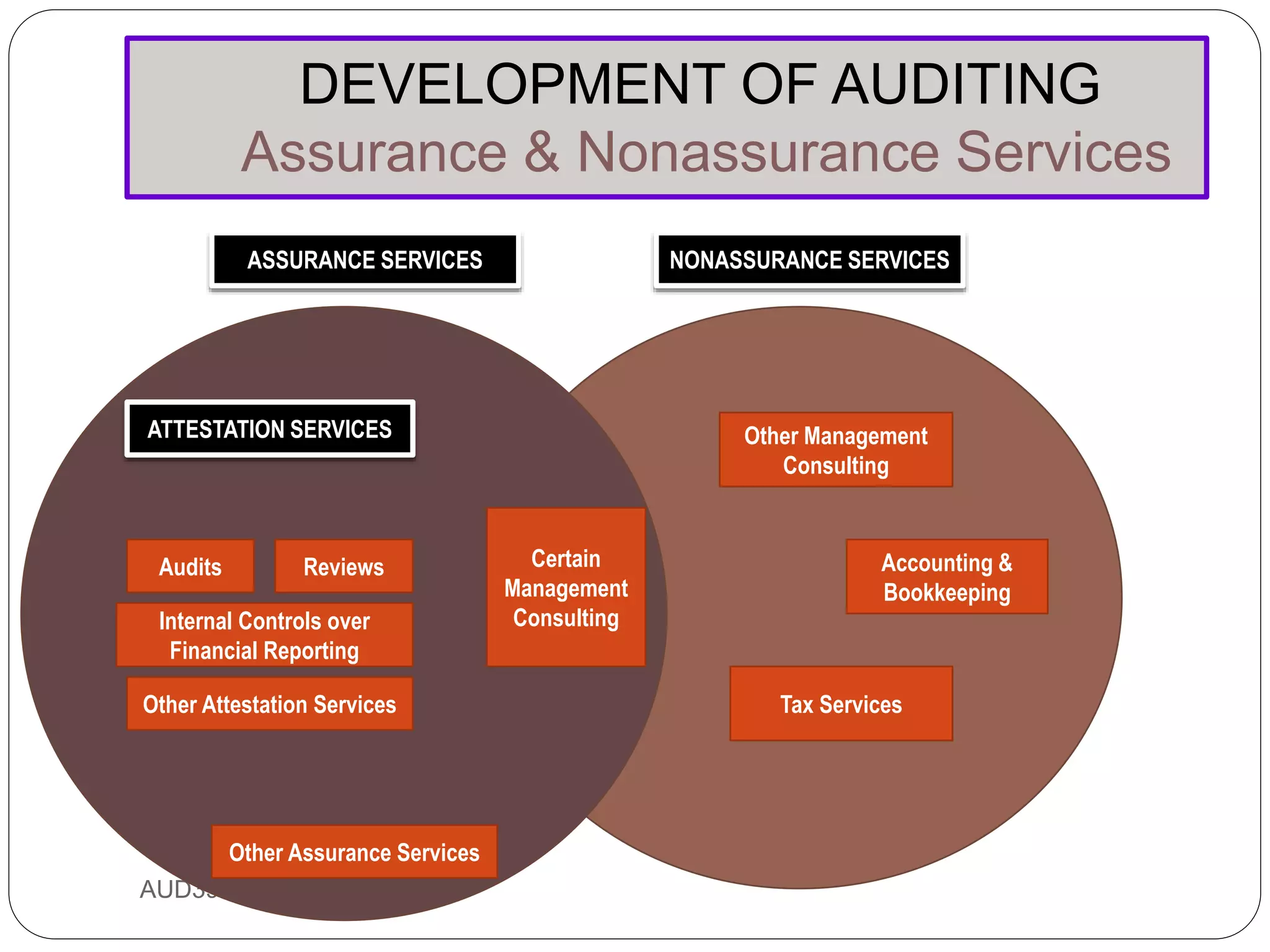
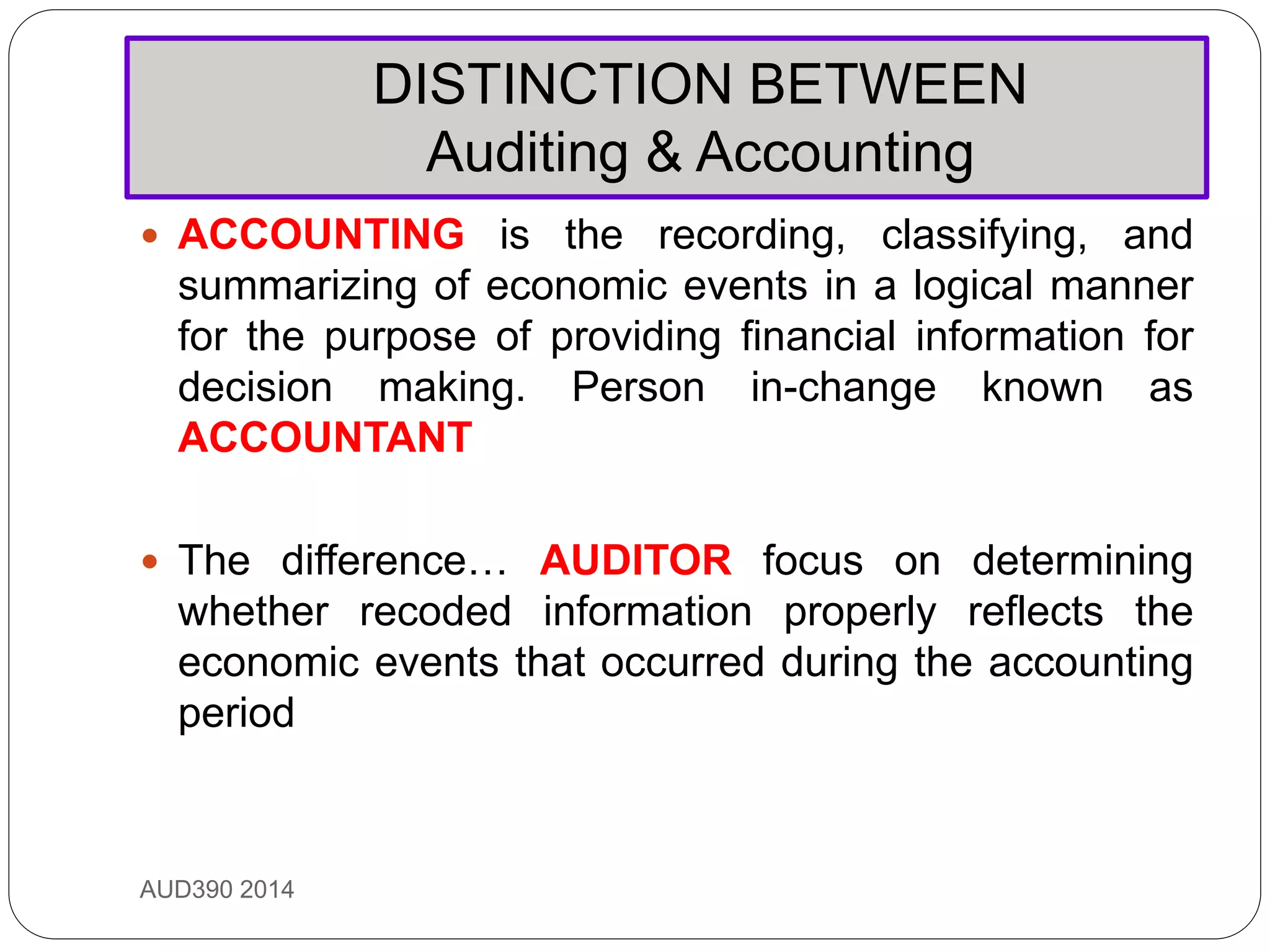
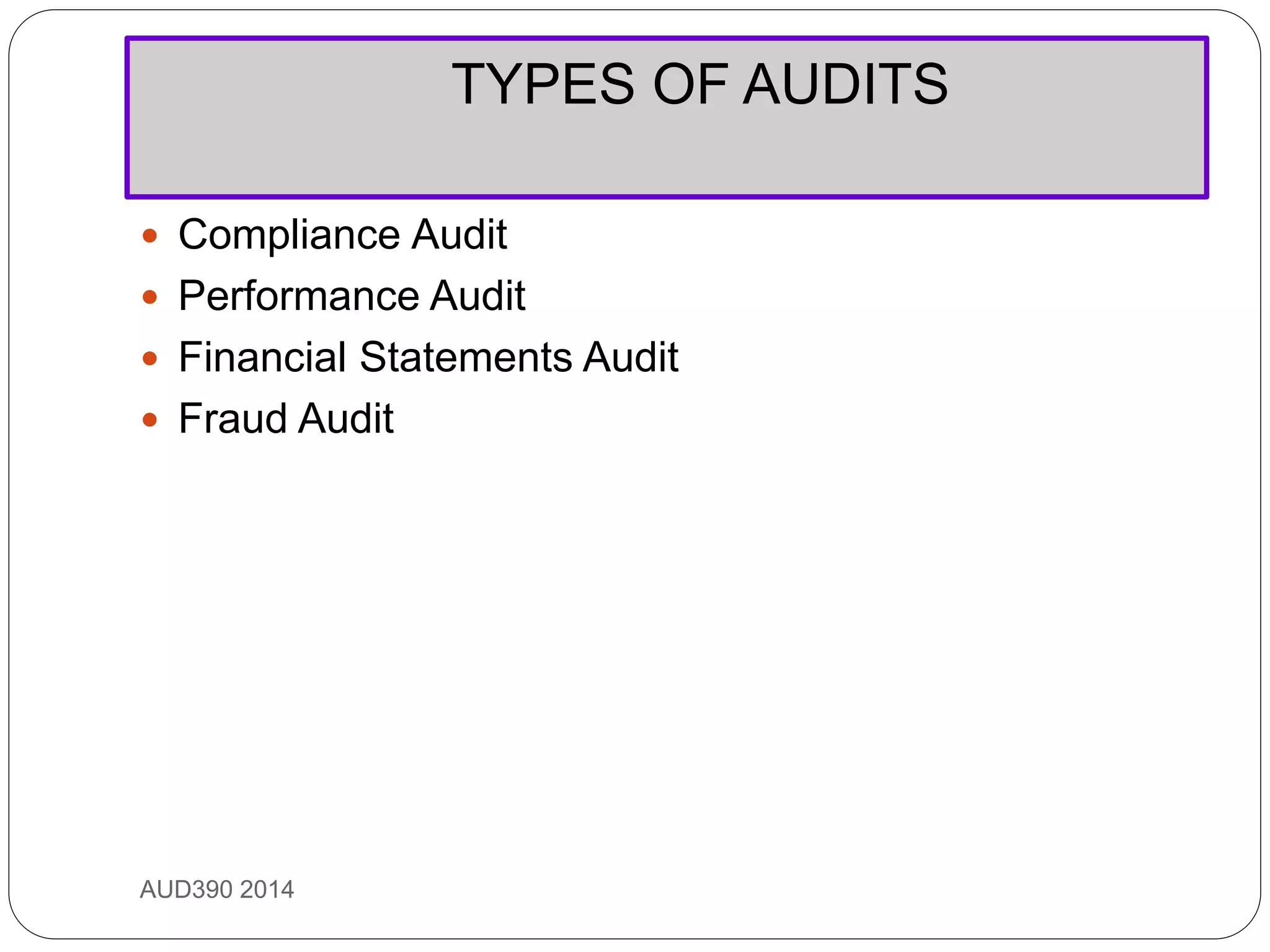
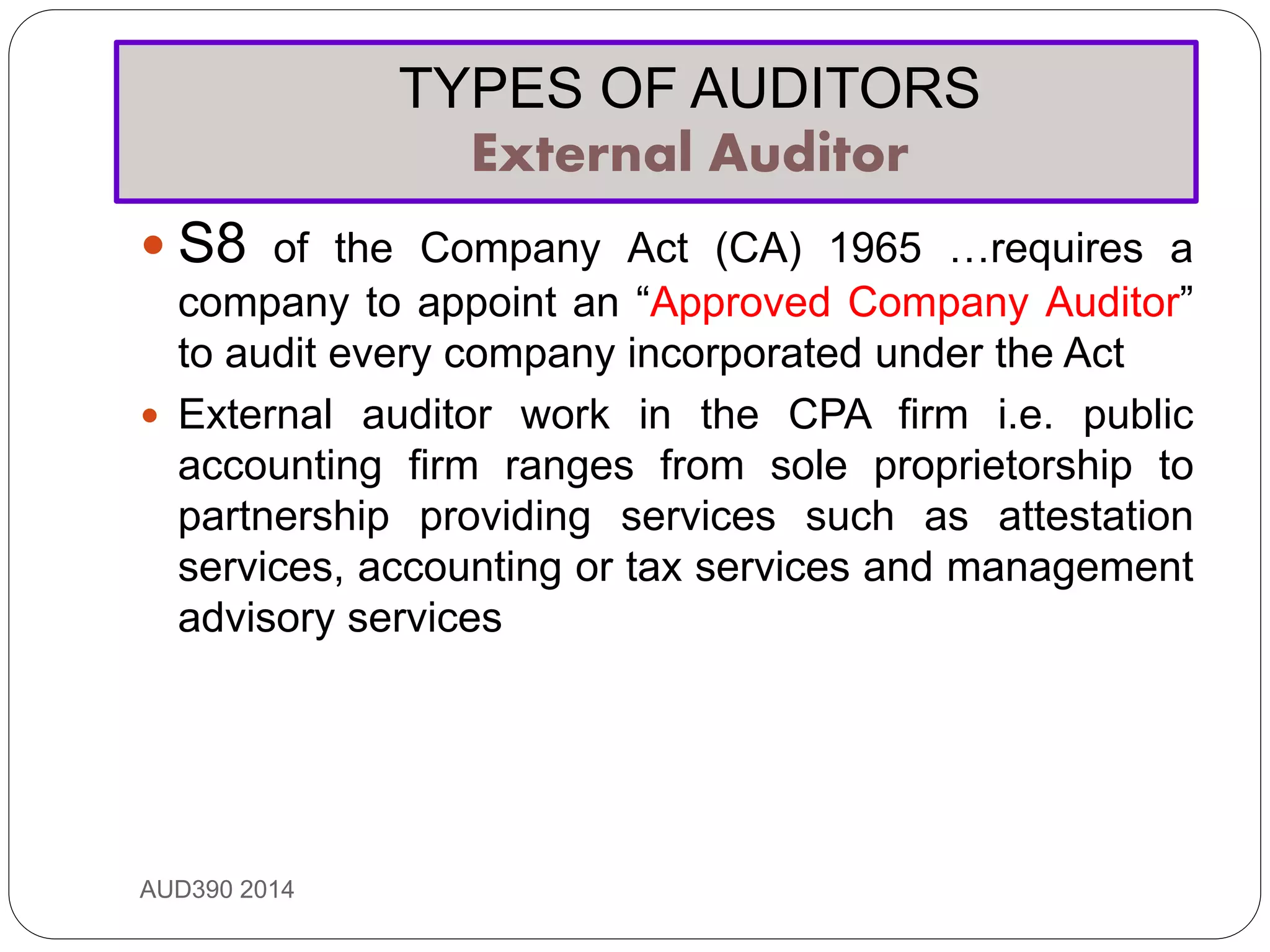
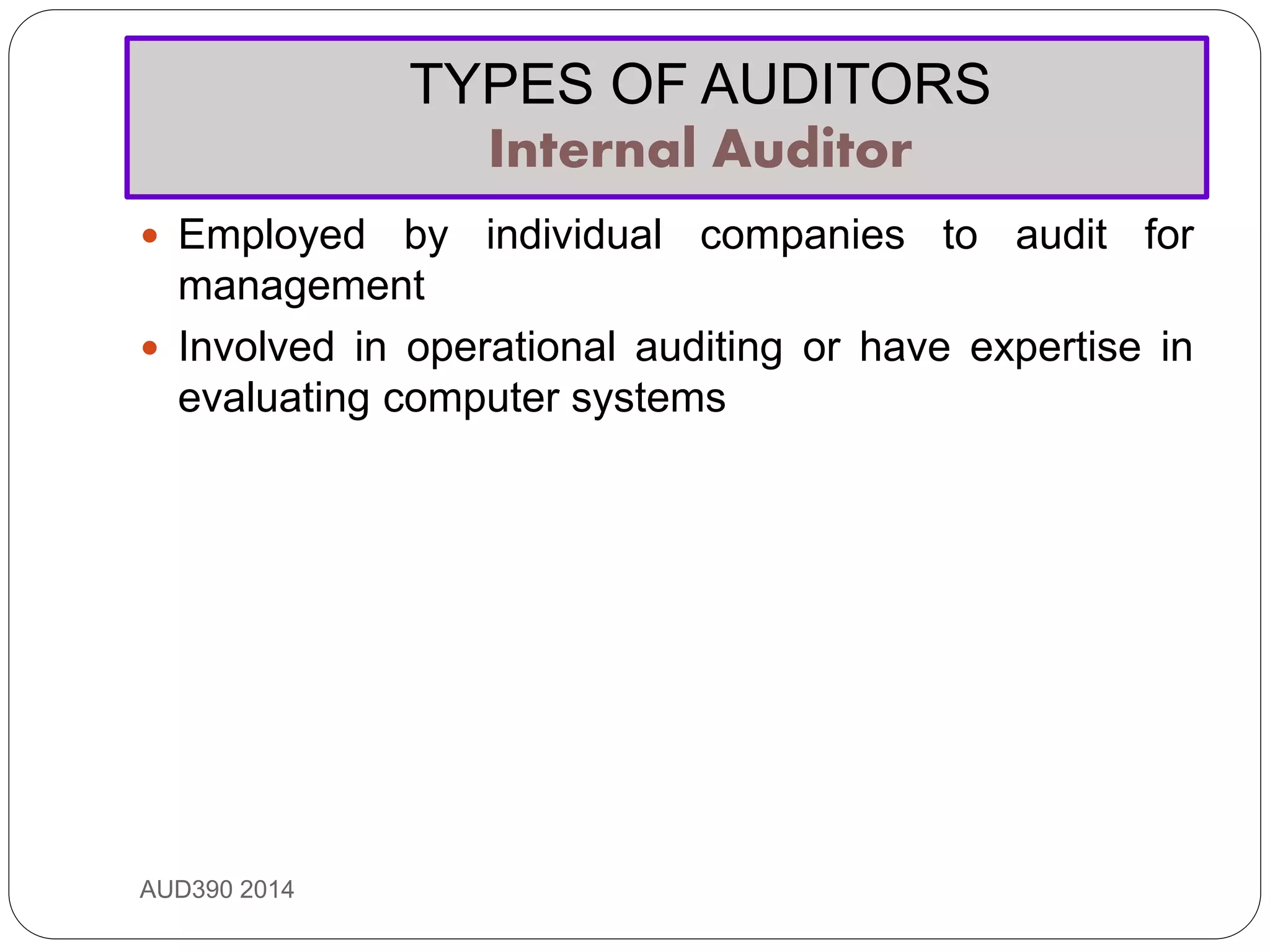
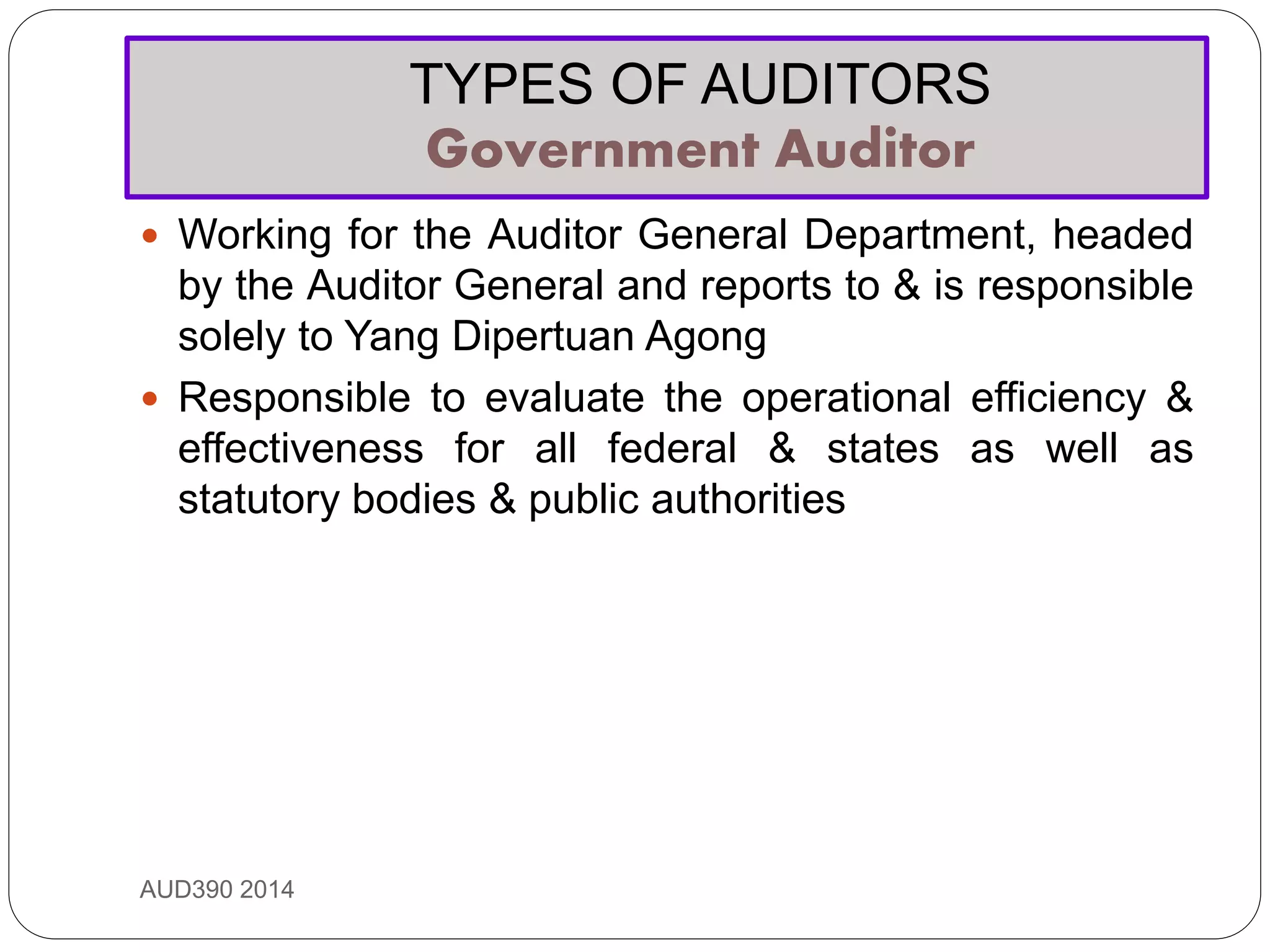
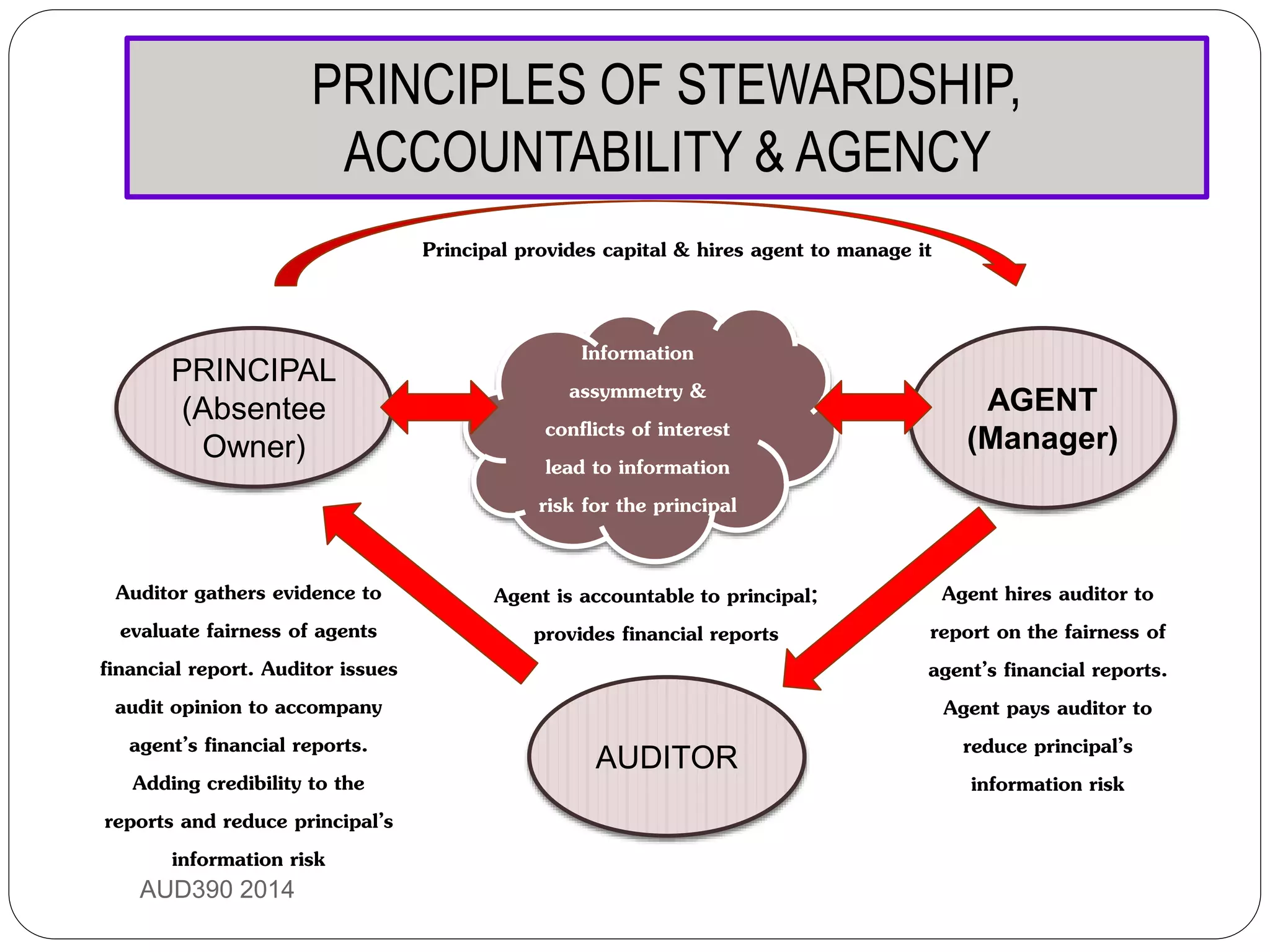
This document provides an overview of auditing and assurance services in Malaysia. It defines auditing and distinguishes it from accounting. It describes the different types of audits including compliance, performance, financial statement, and fraud audits. It also outlines the types of auditors such as external, internal, government, and tax auditors. Finally, it discusses the principles of stewardship, accountability, and agency as they relate to the roles of principals, agents, and auditors, and introduces the Malaysian Approved Standards on Auditing.